Maths
I persist to be the best mathematician I can be.

Maths
I persist to be the best mathematician I can be.
Students will engage with hands-on activities where they will compare objects to decide which is heavier or lighter, larger or smaller or holds more or less.
Much of the second semester will have a mass and capacity focus where students will experiment with measuring using varied objects such as counters, beans, water, rice and blocks. Children will be able to choose the best unit for measuring, using only one object at a time. Using familiar everyday objects, students will experiment with measuring the length of different shapes and surfaces and will investigate the impacts of gaps and overlaps in measuring and their impact on the total length.
Reception students will have the opportunity to investigate how much an object can hold and will begin to make comparisons between objects, understanding that the size and width of the container affects its capacity.
Together students will be involved in constructing word walls with key measurement vocabulary such as heavy, heavier, heaviest, light, lighter, lightest, empty, half empty, full, half full, nearly full, nearly empty, least and most.
We will be focusing on further developing the children’s understanding of number and algebra from the Australian Curriculum.
In Semester One, our focus was on numbers 1-20. This will be further consolidated in Semester 2. The aim to build a solid, consistent transferable understanding, also known as mastery.
Once mastery to 20 is built, we will begin to explore larger numbers 20-50, then beyond to 100.
Key learning for these stages (1-20) (20-50) (50-100) include:
To achieve mastery, students will be explicitly taught these efficient number sense and counting strategies.
Subitising – immediately recognising how many items in a small group without counting.
Children will be explicitly taught the efficient counting strategies such as:
Doubles- identifying objects/numbers that occur in pairs automatically, e.g. (5 and 5, 4 and 4, 2 and 2).
Skip Counting- by 2's, 5's and 10's.
Counting On – understanding that the counting sequence can be continued from any starting point. Children need to remember to always count on from the largest number. For example, if there were 4 apples and 2 more apples, they need to subitise the 4 and count on 2 more.
Part- part -whole (Knowing the value of numbers and how they are made up)
Children will develop their understanding of these strategies with the support of playing-card games and dominoes to develop their automaticity. This is also a great activity to do at home. The students will be able to teach you to consolidate their learning!
Our number system is a base ten number system. All numbers revolve around the number 10. Being confident with and being able to work flexibly with the number 10 will help children in so many areas of math as they go forward. Children need to develop a deep understanding of numbers, in particular the importance of 10 rather than just memorising their names and order.
10 frames
A ten frame is a rectangular frame divided into ten individual boxes. The boxes are arranged in 2 rows of 5. They provide an excellent visual representation of a number and demonstrate its value.
Numbers to 10 can be shown in a ten frame by putting one dot or counter in each box. For example, this ten frame shows the number 5:
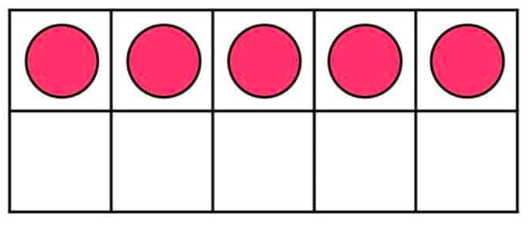

Ten Frames support children's understanding of pairs to 10. (numbers that add up to 10 eg 9 &1, 7&3, 5&5 etc) as they give a visual representation. In the previous example of the 10 frame children will be able to see that there are 5 dots and 5 spaces left. Therefore 5 and 5 more make 10.
Children will be involved in a variety of maths learning activities around data representation and interpretation. They will explore answering yes/no questions to collect information about their world. They will be introduced to tallies and investigate how to represent and analyse pictorial graphs.
Students will use the everyday language of location and direction, such as between, near, next to, forwards, towards to describe where an object is.
Children will have opportunities to give simple directions through games and activities.
Through Discovery Time they will create buildings, roads, cities and jungles and guide each other or objects through.
Through physical activity and activities like obstacle courses and mazes, students will give clear directions to guide others through successfully!




Students will inquire into the days of the week and engage with activities where they will place them in order and link specific days to familiar routines (e.g. School days, weekend). Daily observations of the days of the week and months of the year through our daily calendar will reinforce these concepts. Children will name the days, months and seasons in both English and Kaurna languages.