Curriculum

Foundation Term 3 2023 Curriculum Overview
Literacy | |
Reading
Exploring how the combination of print and images can create meaning
Making links between events in a text and student’s own experience Simple, retelling of narrative texts in sequence of events
Relating one or two key facts in a text
Little Learners Love Literacy Stage 1-6 Heart Words
Little Learners Love Literacy Phonics
| Writing
Learn to construct letters in correct formation and combine these into words
Retell familiar texts through performance, drawings and images
Use beginning concepts about print, sound/letter knowledge, word knowledge and punctuation to create short texts
|
Numeracy |
Represent practical situations to model addition and subtraction
Sort, describe and name familiar two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in the environment
Use direct and indirect comparisons to decide which is longer, heavier or holds more, and explain reasoning in everyday language
Represent practical situations to model sharing
Understand language and processes of counting by naming numbers in sequences, initially to and from 20, moving from any starting point
Use direct and indirect comparisons to decide which is longer, heavier or holds more, and explain reasoning in everyday language
Interpret simple data displays about yes / no questions |
Science & Geography |
Chemical Science Materials and Objects are Used for Different Reasons Geography Places Important to Me |
Year 1/2 Term 3 2023 Curriculum Overview
Literacy | |
Reading Different sounds created from letter combinations including graphs, digraphs and trigraphs using Little Learners Love Literacy or SMART Spelling
Making and adjusting predictions before, during and after reading, using explicit and implied meaning
Asking questions during the reading process to increase comprehension
Concepts of print and screen such as headings, navigation bars, images and scrolling to access digital print
Analyse visual elements or books and digital print and how they contribute to meaning | Writing Selecting interesting and relevant ideas for writing Using descriptive words and phrases to add detail to writing Creating complex sentences using conjunctions Using punctuation to enhance meaning
Presentation - headings, handwriting, spacing, diagrams and illustrations
Narrative and procedural writing elements
|
Numeracy |
Recognise and describe one-half as one of two equal parts of a whole
Recognise and interpret common use of halves, quarters and eighths of shapes and collections
Compare and order several shapes based on length, area, volume, and capacity using appropriate informal units
Recognise and represent multiplication as repeated addition, groups, and arrays
Count and order small collections of Australian coins and notes according to their value
Investigate the effect of one-step slides and flips
Represent data with objects and drawings where one object or drawing represents one data value. Describe the displays.
Recognise and represent division as grouping into equal sets and solve simple problems using these representations
Investigate number sequences, initially those increasing and decreasing by twos, threes, five and ten from any starting point, then moving to other sequences |
Science & Geography |
Chemical Science Materials and Objects are used for Different Reasons Geography Places Important to Me |
Dear F-2 Parents,
Decodable books will build a strong foundation for your child’s future reading success. They are phonically controlled, so children are always able to read unknown words by sounding out and blending those sounds together to say the word. Children experience success and build confidence whilst developing habits of strong readers.
Top tips:
*Before reading, ask your child to warm up by saying sounds used in the book and by decoding some single words used in the book.
*Whilst reading, encourage your child to sound out to read unknown words when they get stuck, and then re-read the sentence for fluency. Remind your child to pause when they come across full stops and other punctuation.
*Make sure your child tracks their finger underneath the words as they read them.
*When your child finishes reading the book, discuss the content and any new words you came across.
Repeated reading and fluency
Fluency is the ability to read accurately, at a conversational rate and with expression – it is an important aspect of reading comprehension. Listening to a child read a decodable book for the first time can be slow, as children work hard to sound out the words accurately. But when your child reads the same decodable book multiple times, they become more automatic and can concentrate on the meaning. Encourage your child to read the same decodable book multiple times and celebrate their progress as they become more confident and fluent readers.
Please note:
We have replaced our old take-home readers with new phonics readers that complement the Little Learners Love Literacy classroom program. These books are levelled differently from the previous reading sets so your child will have a new reading level that corresponds with the LLLL Stages we use in the classroom.
Thank you
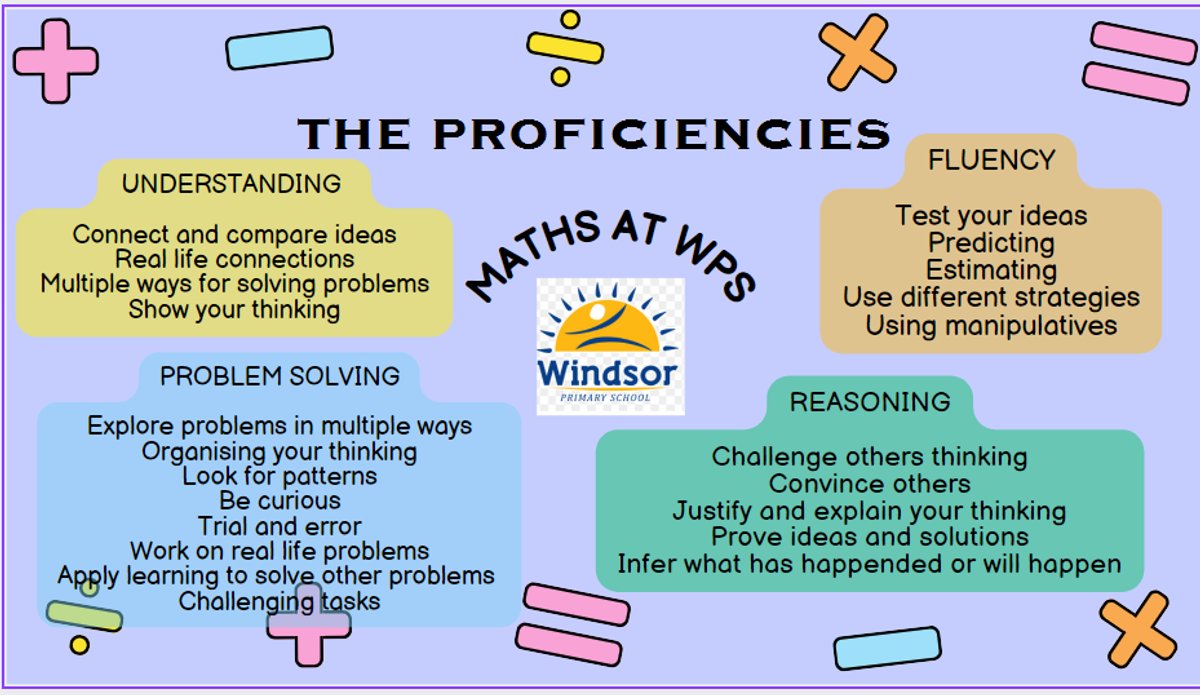
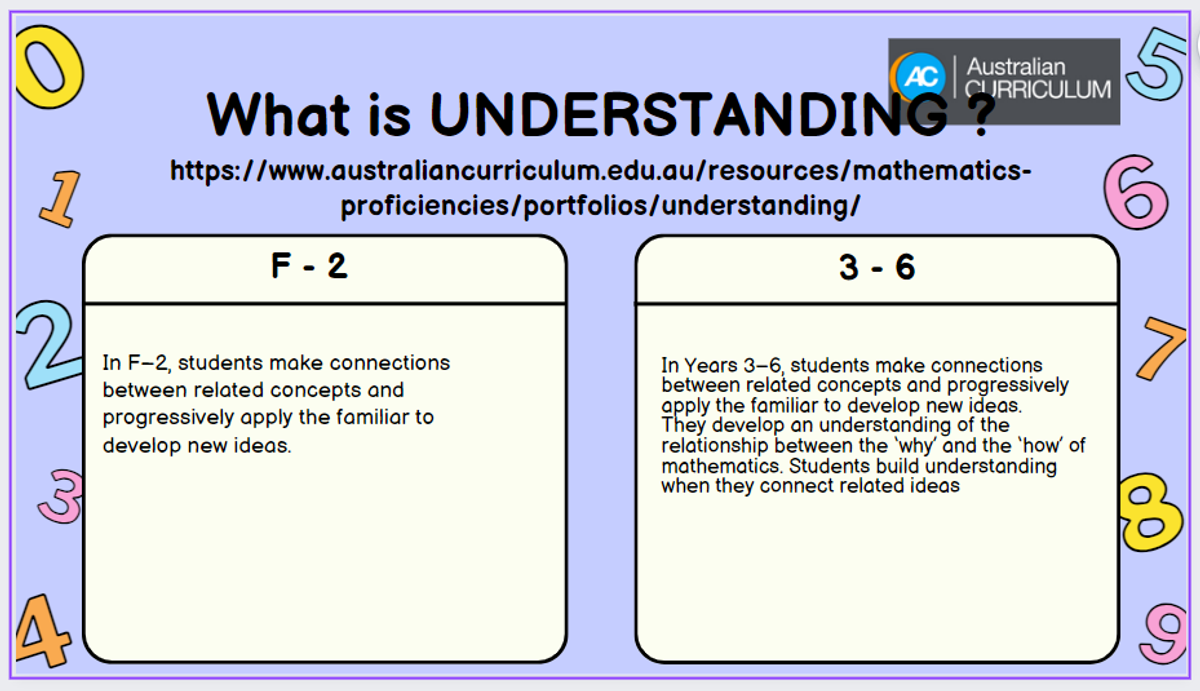
The Australian Curriculum: Mathematics aims to be relevant and applicable to the 21st century. The inclusion of the proficiencies of understanding, fluency, problem-solving and reasoning in the curriculum is to ensure that student learning and student independence are at the centre of the curriculum. The curriculum focuses on developing increasingly sophisticated and refined mathematical understanding, fluency, reasoning, and problem-solving skills. These proficiencies enable students to respond to familiar and unfamiliar situations by employing mathematical strategies to make informed decisions and solve problems efficiently.
Each of the proficiencies are explained briefly here:
The teaching staff have been engaged in several Professional Learning sessions looking at Fluency and Reasoning tasks, and now have a focus on tasks that promote Understanding.
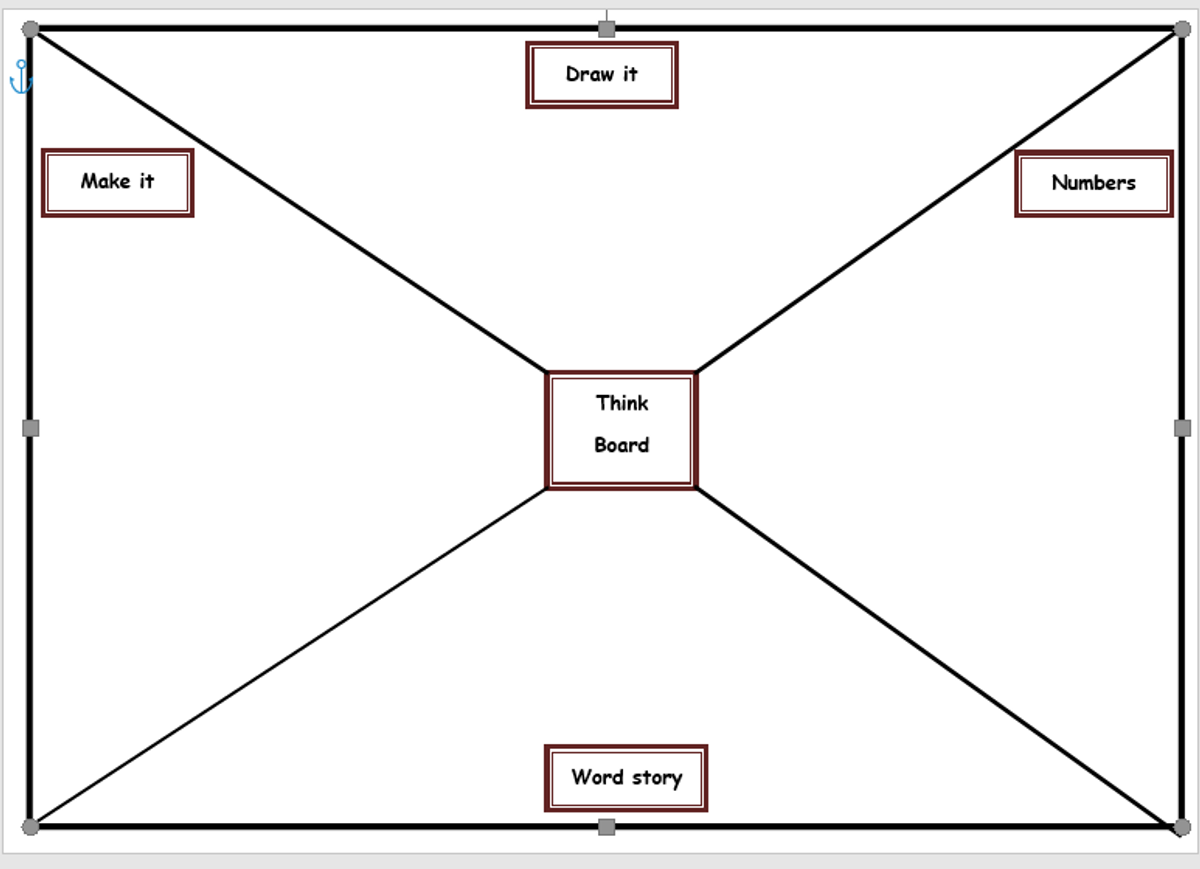
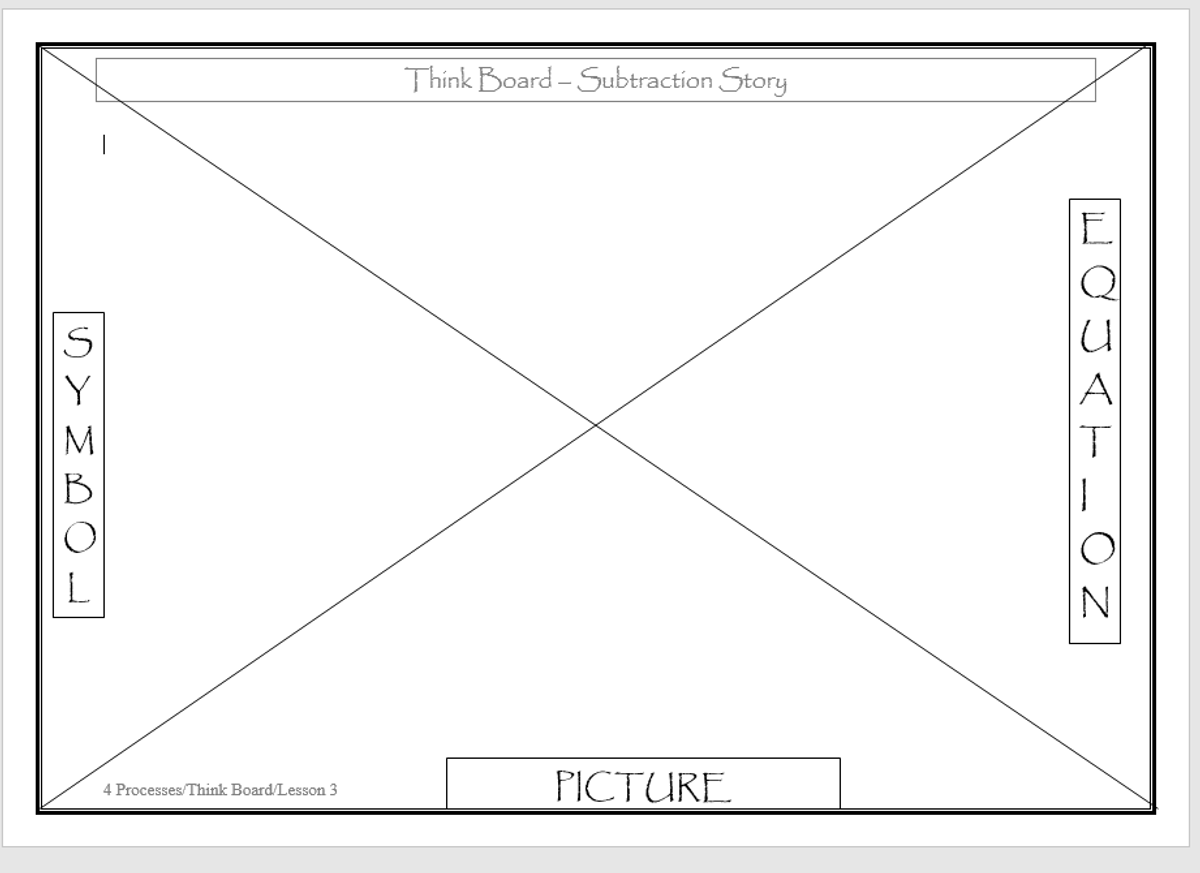
One of the strategies the staff looked at to promote the development of student understanding is the use of a think board.
Think boards can be used to make connections between different mathematical concepts or for students to visually represent their understandings and strategies in a range of ways.
When you are talking with your child at home about their mathematics learning for the day, consider the use of a think board to help them with the organisation of ideas and understanding.
Years 3 - 6 Term 3 Overview
Literacy | |
Reading Focus: How Author’s Hold Readers Attention Week 1: Purpose and Audience Week 2: Text Features Level 3:Understand how different types of texts vary in use of language choices, depending on their purpose, audience and context, including tense and types of sentences Level 4: Identify features used in imaginative, informative and persuasive texts to meet the purpose of the text, and understand how texts vary in complexity and technicality depending on the approach to the topic, the purpose and the intended audience Level 5:Understand how texts vary in purpose, structure and topic as well as the degree of formality
Focus: Vocabulary Week 3: Cloze Reading Week 4: Cloze Passage Level 3:Discuss how language is used to describe the settings in texts, and explore how the settings shape the events and influence the mood of the narrative Level 4:Identify and explain language features of texts from earlier times and compare with the vocabulary, images, layout and content of contemporary texts Level 5:Show how ideas and points of view in texts are conveyed through the use of vocabulary, including idiomatic expressions, objective and subjective language, and that these can change according to context
Focus: Literal and Inferential Meaning Week 5: What is the literal meaning? Week 6: What is the inferential meaning? Focus: Factual Comprehension Week 7: Text structures Week 8: Language Features Level 3:Use comprehension strategies to build literal and inferred meaning and begin to evaluate texts by drawing on a growing knowledge of context, text structures and language features Level 4:Use comprehension strategies to build literal and inferred meaning to expand content knowledge, integrating and linking ideas and analysing and evaluating texts Level 5:Use comprehension strategies to analyse information, integrating and linking ideas from a variety of print and digital sources Level 6:Use comprehension strategies to interpret and analyse information and ideas, comparing content from a variety of textual sources including media and digital texts
Focus: Fact and Opinion Week 9: Text structures Week 10: Language Features Level 4:Understand differences between the language of opinion and feeling and the language of factual reporting or recording Level 5:Understand how to move beyond making bare assertions and take account of differing perspectives and points of view Level 6: Understand the uses of objective and subjective language and bias | Writing
Writers Notebook: Create literary texts that explore students’ own experiences and imagining (VCELT298) Students to use picture prompts for writer’s notebook. Mini Lesson with Vocabulary and language Focus before notebook writing. Week 1: Adjectives Week 2: Nouns and Proper Nouns Week 3: Verbs and Groups Week 4: Paragraphing Week 5: Adverbs Week 6: Apostrophes Week 7: Question Marks Week 8: Noun Groups Week 9: Speech Marks
Writing Focus: Poetry Week 1: Building the Field Week 2: Poetic Devices Week 3: Language features focusing on different types of poems e.g. limerick Week 4: Onomatopoeia Week 5: Constructing a Poem Level 3:Discuss the nature and effects of some language devices used to enhance meaning and shape the reader’s reaction, including rhythm and onomatopoeia in poetry and prose Level 4:Understand, interpret and experiment with a range of devices and deliberate word play in poetry and other literary texts Level 5: Understand, interpret and experiment with sound devices and imagery, including simile, metaphor and personification, in narratives, shape poetry, songs, anthems and odes Level 6: Identify the relationship between words, sounds, imagery and language patterns in narratives and poetry such as ballads, limericks and free verse
Focus: Procedural Week 6: Building the Field Week 7: Text Structures Week 8: Language Features Week 9: Shared Writing Week 10: Applying and Editing
Understand that paragraphs are a key organisational feature of written texts Understand that verbs represent different processes (doing, thinking, saying, and relating) and that these processes are anchored in time through tense Plan, draft and publish imaginative, informative and persuasive texts demonstrating increasing control over text structures and language features and selecting print and multimodal elements appropriate to the audience and purpose
|
Numeracy | |
Number and Algebra:
Weeks 1 - 4: Operations Year 3: -Explain the connection between addition and subtraction -Recall multiplication facts of two, three, five and ten and related division facts -Represent and solve problems involving multiplication using efficient mental and written strategies and appropriate digital technologies Year 4: Apply written and mental strategies to add and subtract -Investigate number sequences involving multiples of 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, and 9 Recall multiplication facts up to 10 × 10 and related division facts Year 5: -Use mental and written strategies as well as digital technologies to add. Solve problems involving multiplication of large numbers by one- or two-digit numbers using mental and written strategies. Solve problems involving division by a one digit number, including those that result in a remainder Year 6: - Use addition, subtraction, multiplication and division to solve problems with whole numbers and estimates. -Select and apply efficient mental and written strategies and appropriate digital technologies to solve problems involving all four operations with whole numbers.
Weeks 7 - 8 Money and Financial Mathematics Year 3: Represent money values in multiple ways and count the change required for simple transactions to the nearest five cents Year 4: Solve problems involving purchases and the calculation of change to the nearest five cents with and without digital technologies Year 5: Create simple financial plans Year 6: Investigate and calculate percentage discounts of 10%, 25% and 50% on sale items, with and without digital technologies
| Measurement and Geometry
Weeks 5 - 6 - through Middle Years Maths Challenge ‘The Big Australian Adventure’ Year 3: -Measure, order and compare objects using familiar metric units of length, area, mass and capacity -Tell time to the minute and investigate the relationship between units of time -Create and interpret simple grid maps to show position and pathways Year 4: -Use scaled instruments to measure and compare lengths, masses, capacities and temperatures -Convert between units of time -Use am and pm notation and solve simple time problems -Use simple scales, legends and directions to interpret information contained in basic maps Year 5: -Choose appropriate units of measurement for length, area, volume, capacity and mass -Compare 12- and 24-hour time systems and convert between them -Use a grid reference system to describe locations. Describe routes using landmarks and directional language Year 6: -Convert between common metric units of length, mass and capacity -Solve problems involving the comparison of lengths and areas using appropriate units -Interpret and use timetables Introduce the Cartesian coordinate system using all -four quadrants
Statistics and Probability Weeks 9 - 10 Chance Year 3: -Conduct chance experiments, identify and describe possible outcomes and recognise variation in results Year 4: -Describe possible everyday events and order their chances of occurring -Identify everyday events where one cannot happen if the other happens -Identify events where the chance of one will not be affected by the occurrence of the other Year 5: - List outcomes of chance experiments involving equally likely outcomes and represent probabilities of those outcomes using fractions -Recognise that probabilities range from 0 to 1 Year 6: - Describe probabilities using fractions, decimals and percentages -Conduct chance experiments with both small and large numbers of trials using appropriate digital technologies |
Inquiry Learning Geography and Science |
Geography 3-4 - Australia; mapping Students can identify the different states and territories Students can identify and explain different landmarks both natural and man made Identify and describe the characteristics of places in different locations at a range of scales Identify and describe locations and spatial distributions and patterns Identify and explain the interconnections within places and between places
5-6 - Australia and neighbouring countries; Mapping Students can identify and locate our neighbouring countries on a map Students can describe and identify where other continents are on a map Location of the major countries of the Asian region in relation to Australia and the geographical diversity within the region Differences in the demographic, economic, social and cultural characteristics of countries across the world Influence of people, including the influence of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples, on the environmental characteristics of Australian places
Science Mini-Boss Incursion
3-4 A change of state between solid and liquid can be caused by adding or removing heat Natural and processed materials have a range of physical properties; these properties can influence their use
5-6 Solids, liquids and gases behave in different ways and have observable properties that help to classify them Changes to materials can be reversible, including melting, freezing, evaporating, or irreversible, including burning and rusting |