VCE Vocational Major
Senior School Certificate

VCE Vocational Major
Senior School Certificate
The VCE Vocational Major is an applied learning program within the VCE. You will develop academic and work-related skills, knowledge and confidence. When you graduate from secondary school, you'll graduate with the Victorian Certificate of Education, with the additional words 'Vocational Major'.
Unlike other VCE studies, there are no external assessments of VCE Vocational Major unit 3–4 sequences (although students do sit the GAT), and VCE Vocational Major studies do not receive a study score. If a student wishes to receive study scores, they can choose from the wide range of VCE studies and scored VCE VET programs that contain both internal and external assessment components.
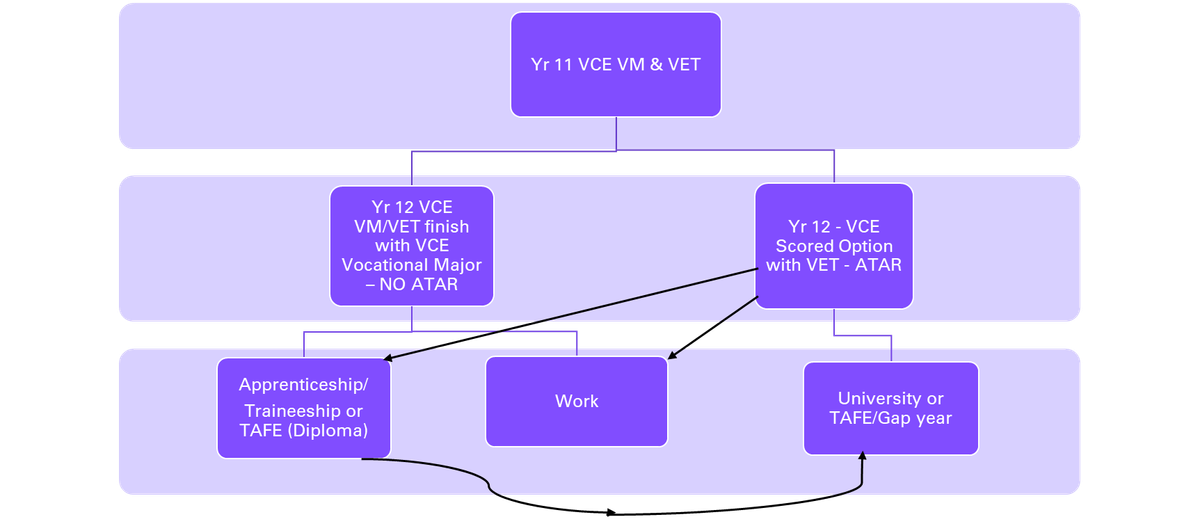
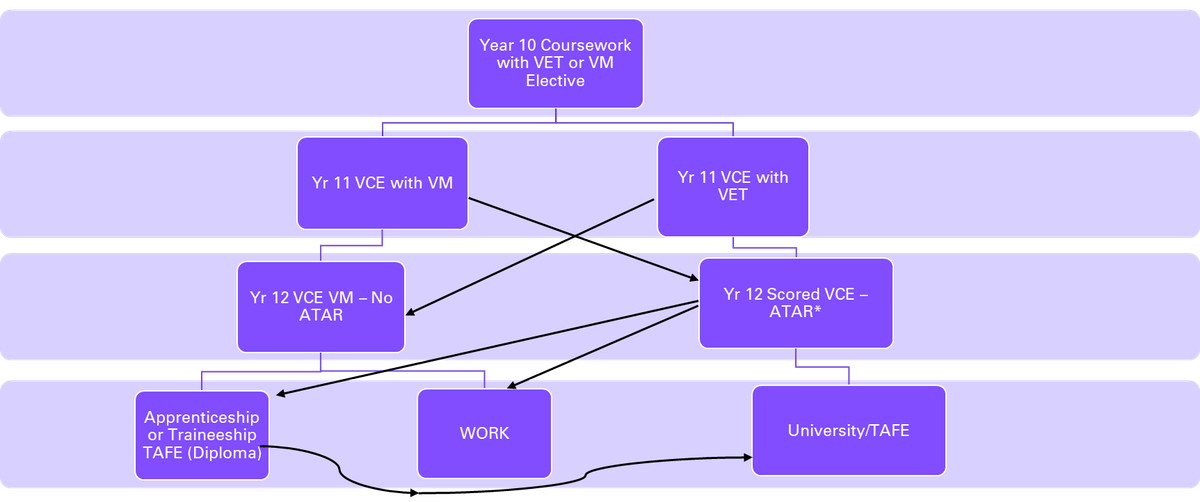
The VCE Vocational Major offers a pathway into:
To get your VCE Vocational Major, you must successfully finish at least 16 units, including:
You must also complete at least 3 other unit 3–4 sequences. This means 3 other full year studies at a year 12 level. You can do other VCE studies or VET.
At Viewbank College – we will be offering students the pathway but with maximum flexibility to allow students to investigate their interests and passions that suit their ongoing learning needs.
All students are advised to select a VET study to start their pathway towards a possible VCE Vocational Major.
Further information for students - Pages - How VCE works – The facts (vcaa.vic.edu.au)
VM Literacy
Unit 1
This unit focuses on the structures and features of a range of texts – print, visual and film – and the personal reasons readers may have for engaging with these texts. Students will read or watch a variety of texts for a personal purpose, such as finding information. Texts should be chosen from a range of local and global perspectives, including First Nations peoples’ and multicultural perspectives, and should include film, TV, online videos, song, poetry, biographies and digital content, and other texts of interest to the cohort. Through discussions and class activities students will develop their understanding of the structures and features of these text types, and examine how they are influenced by purpose, context, audience and culture.
Unit 2
Students will engage in issues that are characterised by disagreement or discussion, developing and expanding upon students’ learning from Unit 1. Students will consider the values and beliefs that underpin different perspectives and how these values create different biases and opinions, including thinking about how these issues might arise in particular vocational or workplace settings. Students will read, view and listen to a range of texts and content that demonstrate diverse opinions on a range of local and global issues, and which may impact on their community or be of particular concern to a vocational or workplace group. Students should consider the language and purpose of different text types and consider how this language is used to influence an audience.
Unit 3
In this area of study students will become familiar with and develop confidence in understanding and accessing texts of an informational, organisational or procedural nature. These texts should reflect real-life situations encountered by students and be representative of the sorts of texts students will encounter in a vocational setting or workplace, or for their health and participation in the community.
Students will learn to recognise, analyse and evaluate the structures and semantic elements of informational, organisational and procedural texts as well as discuss and analyse their purpose and audience. Students will develop their confidence to deal with a range of technical content that they will encounter throughout adulthood, such as safety reports, public health initiatives, tax forms and advice, contracts, promotional videos and vocational and workplace texts.
Unit 4
In this area of study students will investigate, analyse and create content for the advocacy of self, a product or a community group of the student’s choice, in a vocational or recreational setting. Students will research the differences between texts used for more formal or traditional types of advocacy, influence or promotion, as well as some of the forms that are increasingly being used in the digital domain for publicity and exposure.
Students will consider which elements are important for creating a ‘brand’ (including personal branding) and how different texts, images, products and multimedia platforms work together to produce one, central message to influence an audience. Students will compare and contrast the ways in which same message can be presented through different platforms and participate in discussions that consider the effectiveness of these messages, considering their purpose and the social and workplace values associated with them.
VCE Vocational Major Personal Development Skills (PDS) takes an active approach to personal development, self-realisation and citizenship by exploring interrelationships between individuals and communities. PDS focuses on health, wellbeing, community engagement and social sciences, and provides a framework through which students seek to understand and optimise their potential as individuals and as members of their community.
Further information about the study and suggested activities could be found HERE
Unit 1
In Unit 1 students will develop their numeracy practices to make sense of their personal, public and vocational lives. They will develop mathematical skills with consideration of their local, community, national and global environments and contexts, and an awareness and use of appropriate technologies.
Unit 2
In Unit 2 students will develop and extend their numeracy practices to make sense of their personal, public and vocational lives. They will develop mathematical skills with consideration of their local, community, national and global environments and contexts, and identification and appropriate selection and use of relevant technologies.
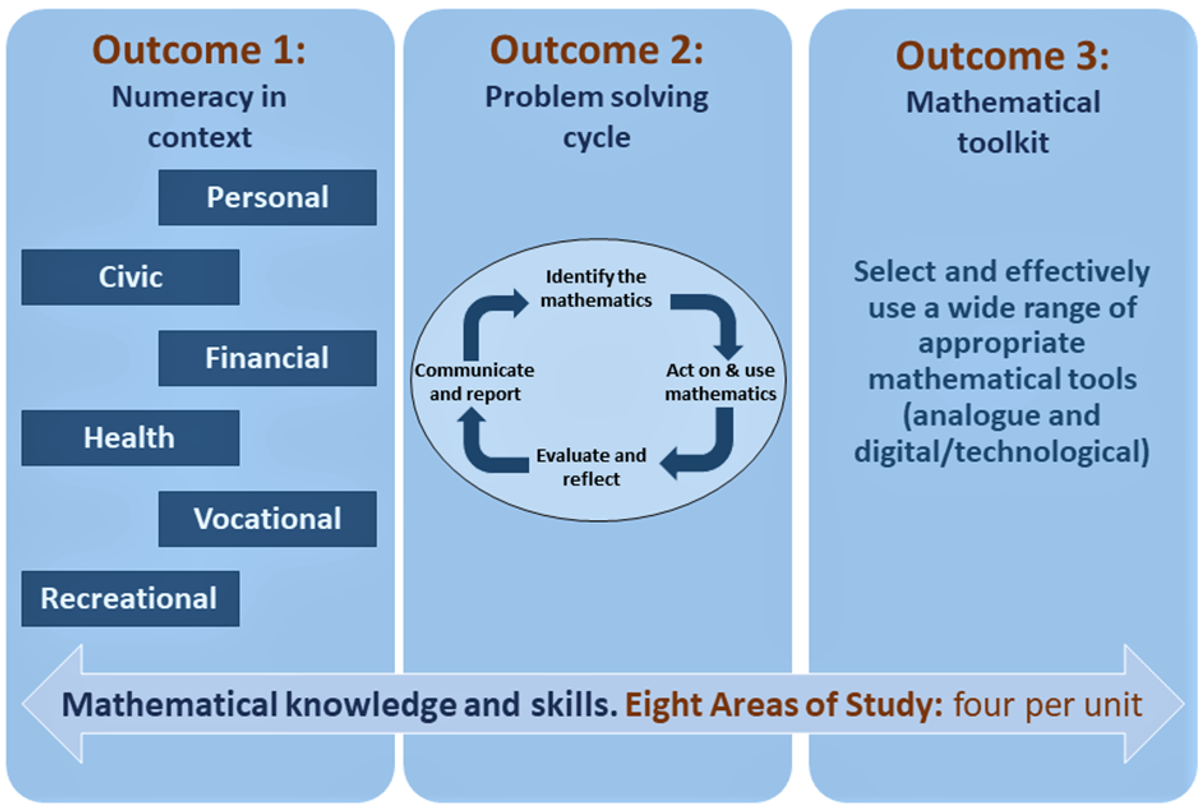
These units provide students with the fundamental mathematical knowledge, skills, understandings and dispositions to solve problems in real contexts for a range of workplace, personal, further learning and community settings relevant to contemporary society.

Unit 3
In this unit students will use estimation, calculations and computational thinking to solve practical problems in community, business and industry contexts. Students will also undertake the study of ‘Data analysis’ including collection and modelling of data, the construction of tables or spreadsheets and graphs to represent data. Students will use data and statistics to make predictions, inferences and draw conclusions.
Unit 4
In this unit students will study financial and consumer math including money management, investments and loans, credit and debit, comparing mortgages versus rental costs, debt consolidation, taxation, financial risk, interest rates and insurance. Students will conduct research into their potential salaries and model their financial future.
Additional Information:
Students are expected to have a calculator as prescribed on the booklist.
Unit 1
students engage in a combination of tasks to develop their skills related to exploring sources of information on future careers and industries, focusing on the labour market, including skills shortages, industry growth areas, emerging industries, and current and future trends.
To do so, they will engage in the following activities:
To consolidate their knowledge, students then complete a careers research presentation, summarising their research. This can be completed in a variety of formats, including (but not limited to) a written report, graph/chart, visual or digital presentation or video recording. Students also submit a planning document, along with their presentation
Unit 2
Students explore the infographics in the Foundation for Young Australian New Work Order research series and the employability skills to gain an understanding of skills, knowledge and aspirations for particular industries. Students further develop their understanding of interest, skills and capabilities within industry through the use of PowerPoint presentations/ short clips, in which they identify industry specific skills, as well as transferable skills across a range of industries. Students also complete an industry skills audit to help identify which skills are transferable across industries, and reflect on their findings. Students apply this knowledge through the completion of a career quiz and research task which help identify their own personal strengths and weaknesses/blockers in relation to their employability skills and personal capabilities and attributes. Students complete the research task by specifically looking at their own skills, and discussing strategies for improvement for future prospects and outcomes.
Students use case studies and a set of structured questions to demonstrate their level of comprehension and examine the link between transferable skills, ongoing training and development, industry exposure, formal and informal education and employability. Students then draw on their knowledge of communication to identify ‘good vs bad’ communication skills. In order to develop their understanding of recruitment and selection processes, students need to apply for a job and complete mock interviews. For this task, they need to develop a set of interview questions that may be asked during the interview for their specific job application, as well as possible interview responses to each question. They will then be able to apply this knowledge to complete the mock interview with their peers/teacher/industry specific individual and evaluate their interview skills based on feedback. Students then list improvement strategies based on the feedback and apply this to conduct a second mock interview
Unit 3
The purpose of this unit is to further establish and consolidate students’ core understanding of the complex nature and the importance of a healthy, collaborative and inclusive workplace. It focuses on developing a range of knowledge, skills and attributes required to achieve these core workplace elements. Each week, students will learn how to maintain positive working relationships with colleagues and employers, understanding the characteristics of a positive workplace culture and its relationship to business success. Students will investigate key areas relating to workplace relations, including a harmonious workplace, communication, safe work practices, employee rights, responsibilities of key stakeholders, workplace roles, working conditions and opportunities, OH&S activities, and using collaborative technologies. An incursion, excursion and applied learning relevant to ‘real life’ learning experiences are used to ensure that what is learnt in the classroom is connected to scenarios and experiences outside the classroom, making that connection as immediate and transparent as possible.
Unit 4
This unit provides a focus for the development and presentation of portfolios. Students will learn to communicate relevant skills, experiences and capabilities to education providers and future employers. Students will use a range of verbal, written and practical strategies to communicate their skills, knowledge and attributes, including visual appeal, varied and appropriate content. The unit aims to develop and apply student knowledge and skills relating to portfolios, including the features and characteristics of a high-quality physical and/or digital portfolio. The unit includes the formal presentation of a completed portfolio in a panel style interview and an evaluation of the end product. Incursions, excursions and applied learning relevant to ‘real life’ learning experiences are used to ensure that what is learnt in the classroom is connected to scenarios and experiences outside the classroom, making that connection as immediate and transparent as possible.