Mathematics Learning Area Snapshot

Numeracy is a fundamental life skill. The development and application of mathematical knowledge and skills builds students’ conceptual and imaginative worlds, supports problem solving attributes and skills and provides capabilities that contribute to full, participatory citizenship and career pathways.
At Applecross Senior High School,we implement an evidence-based teaching and learning model to deliver strong mathematics outcomes for all students. This includes prioritising explicit, sequential, and systematic approaches to teaching mathematics.
However, coupled with this, is the critical importance of ensuring that students have time to develop mastery.
Evidence from cognitive science research suggests that mastering key mathematic facts so they can be recalled automatically and accurately frees up working memory. Students can then focus on more complex problem solving, rather than reaching cognitive overload trying to calculate simple operations.
Students should practise and apply their learning in varied contexts to maximise the consolidation of knowledge and fluency. This should include revisiting and reviewing learning and spacing practice.
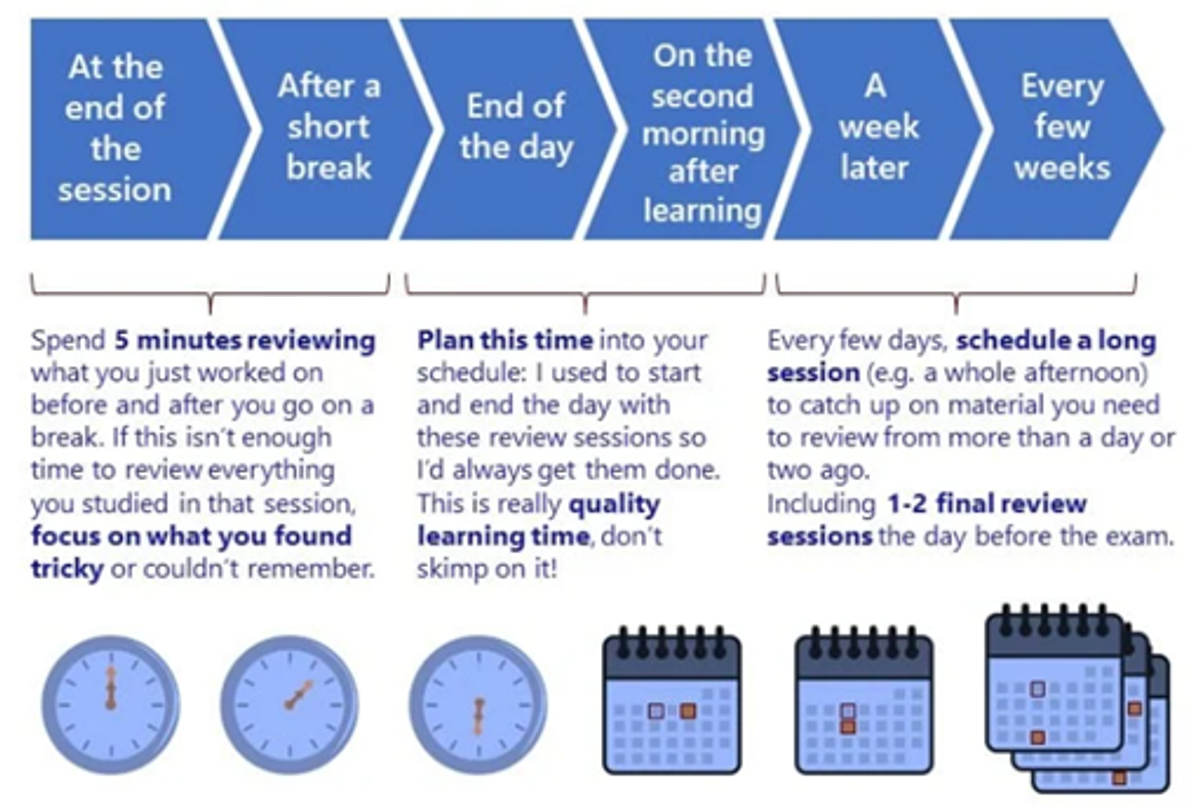
This requires a working study plan at home, in and around students’ extra-curricular, social, work and family activities throughout the week. An example of how to plan for and structure spaced practice is as follows:
During planned study time at home, students might:
Review key skills and concepts learned in the day’s lesson by completing 15–20 minutes of practice questions on CambridgeGO.
Check the accuracy of their responses and ‘flag’ any questions to clarify with their teacher in the next lesson.
Complete a ‘Scorcher’ — a short, timed competition — on CambridgeGO.
Watch a walkthrough video from CambridgeGO, the teacher’s resource platform, or Khan Academy.
Summarise daily lesson notes in their Interactive Notebook.
Review formative assessments from previous lessons (e.g. quizzes, exit tickets) and use teacher feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Reflect on summative assessments and marking key behaviours to identify focus areas and set practice goals.
Together, these strategies help students build mastery over time, by allowing for continuous review, targeted support, and meaningful reflection throughout a topic or Semester.
Donna Collins, HoLA - Mathematics