Mellor 1/2 English
Mellor 1/2 English
The English curriculum for Years 1 and 2 places a strong emphasis on the development of literacy. Children listen to and enjoy texts that entertain, inform and persuade, such as picture books, non-fiction and film. Children grow into more independent readers, learn to create a range of different texts and become more confident when they communicate.
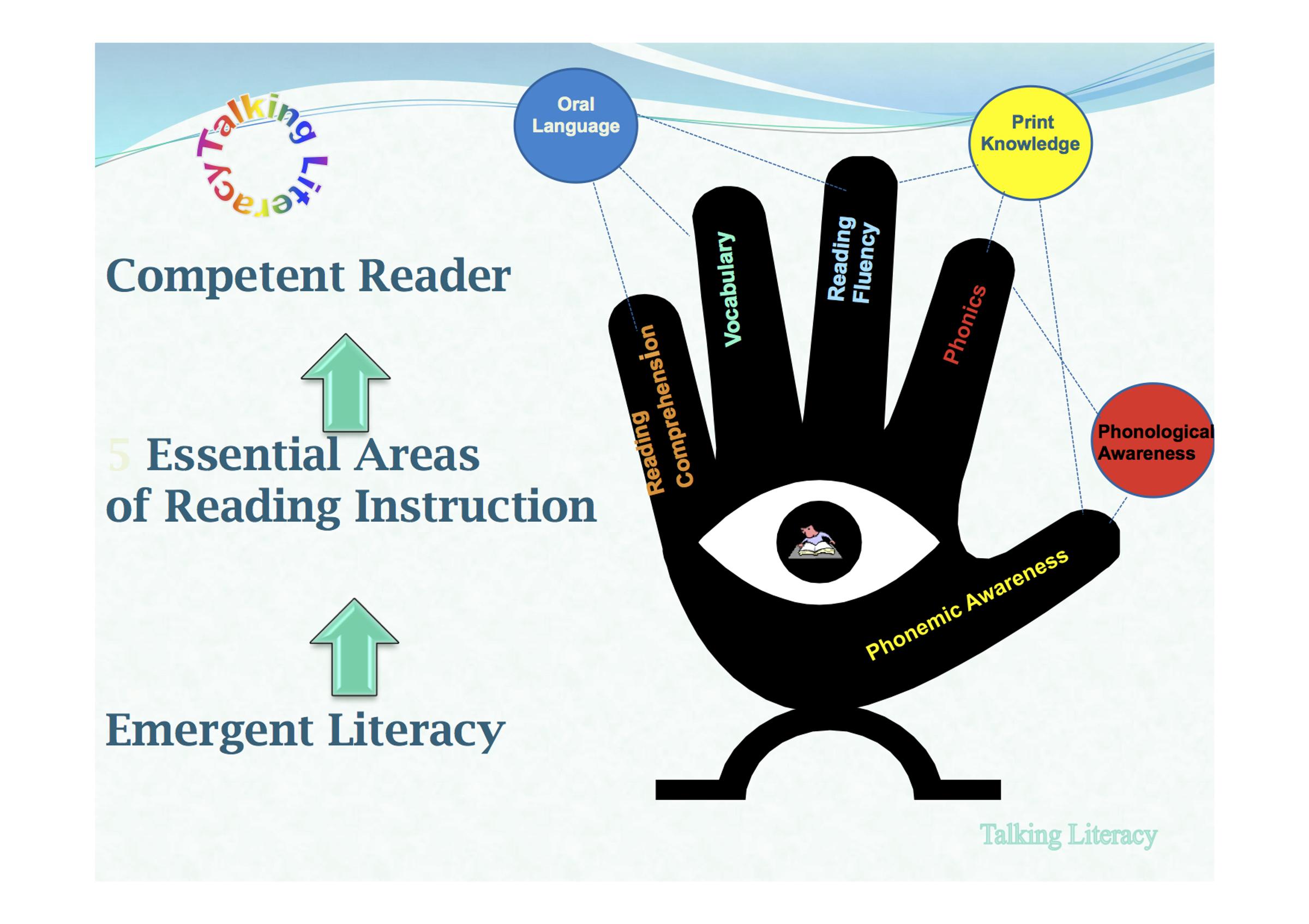
Competent reading rests on the foundations of emergent literacy as illustrated above. Oral language is important for reading comprehension, vocabulary and fluency.
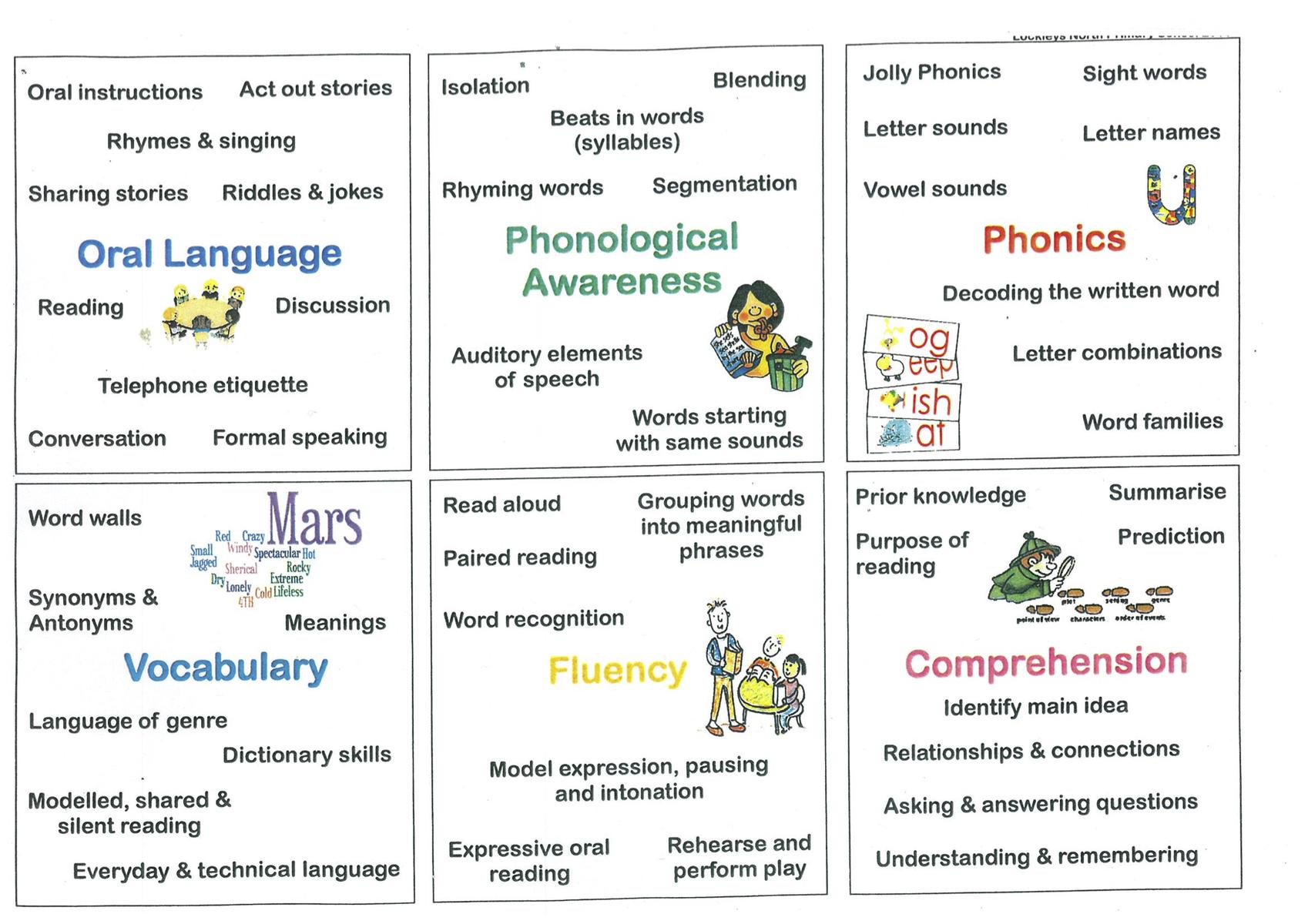
To understand the language at the printed level oral language competency is essential. Children need strong vocabularies to understand the broad range of words in texts; they require strong grammatical skills to understand complex sentences present in many texts; they require the ability to reason and inference so that the necessary links between information in texts is made. Fluency is increased by oral language competency because if language is easily understood, comprehension occurs more rapidly. Print knowledge is important for phonemic awareness, phonics and fluency as these are the keys for decoding. Phonological awareness relates directly to phonemic awareness and phonics because the ability to hear the sounds in words is critical in both areas.

Reading:
Students read short texts with some unfamiliar vocabulary, simple and compound sentences and supportive images. They understand how characters in texts are developed and give reasons for personal preferences.
Students read aloud, with developing fluency. They use knowledge of the relationship between sounds and letters, high-frequency words, sentence boundary punctuation and directionality to make meaning when reading.
Students recall key ideas and recognise literal and implied meaning in texts.
They understand the different purposes of texts.
Students make connections to personal experience when explaining characters and main events in short texts. They identify that texts serve different purposes and that this affects how they are organised describe characters, settings and events in different types of literature.
Writing:
Students create short texts for a small range of purposes. They provide details about ideas or events, and details about the participants in those events.
Students accurately spell high-frequency words and words with regular spelling patterns. They use capital letters and full stops and form all upper- and lower-case letters correctly.
Students create texts that show understanding of the connection between writing, speech and images.
Listening and speaking:
They listen to others when taking part in conversations, using appropriate language features and interaction skills.
Students interact in pair, group and class discussions, taking turns when responding.
They make short presentations on familiar topics.
Reading:
Students read a variety of texts for enjoyment. They listen to, read, view and interpret spoken, written and multimodal texts in which the primary purpose is to entertain, as well as texts designed to inform and persuade.
They read traditional oral texts, picture books, various types of print and digital stories, simple chapter books, rhyming verse, poetry, non-fiction, film, multimodal texts, dramatic performances and texts used by students as models for constructing their own work.
Students read texts independently that involve sequences of events that span several pages and present unusual happenings within a framework and
examine informative texts to present new content about topics of interest and topics being studied in other areas of the curriculum.
They produce varied sentence structures using some unfamiliar vocabulary, use a significant number of high-frequency sight words and words that need to be decoded phonically, and a range of punctuation conventions, as well as illustrations and diagrams that support and extend the printed text.
Writing:
Students create a range of imaginative, informative and persuasive texts including imaginative retellings, reports, performances, poetry and expositions.
create texts, drawing on own experiences, imagination and information learnt.
They read traditional oral texts, picture books, various types of print and digital stories, simple chapter books, rhyming verse, poetry, non-fiction, film, multimodal texts, dramatic performances and texts used by students as models to construct their own work.
They accurately spell words with regular spelling patterns and spell words with less common long vowel patterns.
Students use punctuation accurately,
write words and sentences legibly using unjoined upper- and lower-case letters.
Listening and speaking:
Students listen for particular purposes.
They listen for and manipulate sound combinations and rhythmic sound patterns.
Students listen to, read, view and interpret spoken, written and multimodal texts in which the primary purpose is to entertain, as well as texts designed to inform and persuade.
They use a variety of strategies to engage in group and class discussions and make presentations. They discuss ideas and experiences use everyday language features and topic-specific vocabulary.