From the 1/2 Classrooms
Multiplication and Division Strategies

From the 1/2 Classrooms
Multiplication and Division Strategies
Throughout Term 2 our Grade 1/2 students have been exploring more exciting operations in mathematics... multiplication and division! Students have read some fantastic big books and experimented with a range of strategies they can use when solving multiplication and division problems!


















What are equal groups? Equal Groups is defined as the act of putting an assortment of items or numbers into the same amounts in small piles or groups. Equal groups, grouping or sharing is a simple way of solving multiplication and division word problems, because it allows for a visual illustration of the numbers used in the problem where no remainders are found. Students also explored what would happen if there was a remainder and how this can be represented.
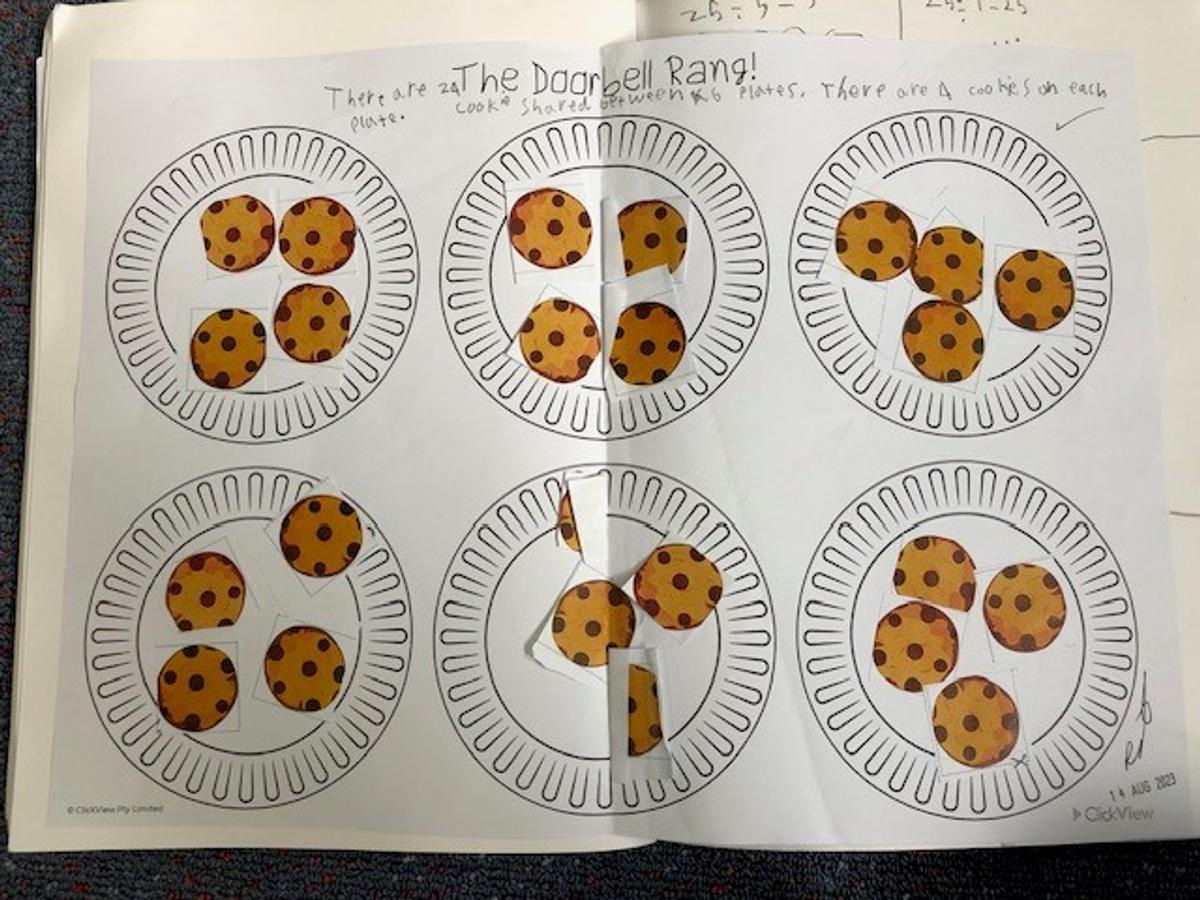
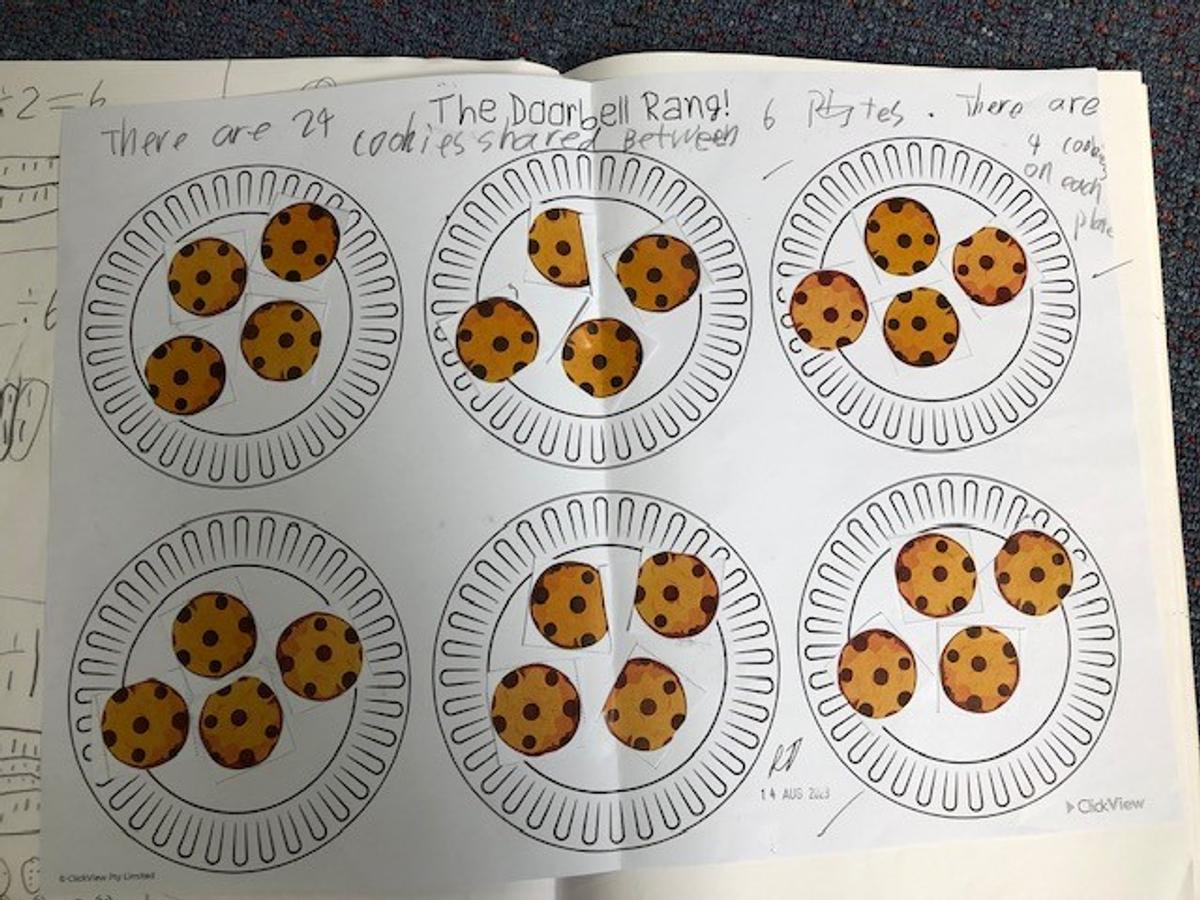
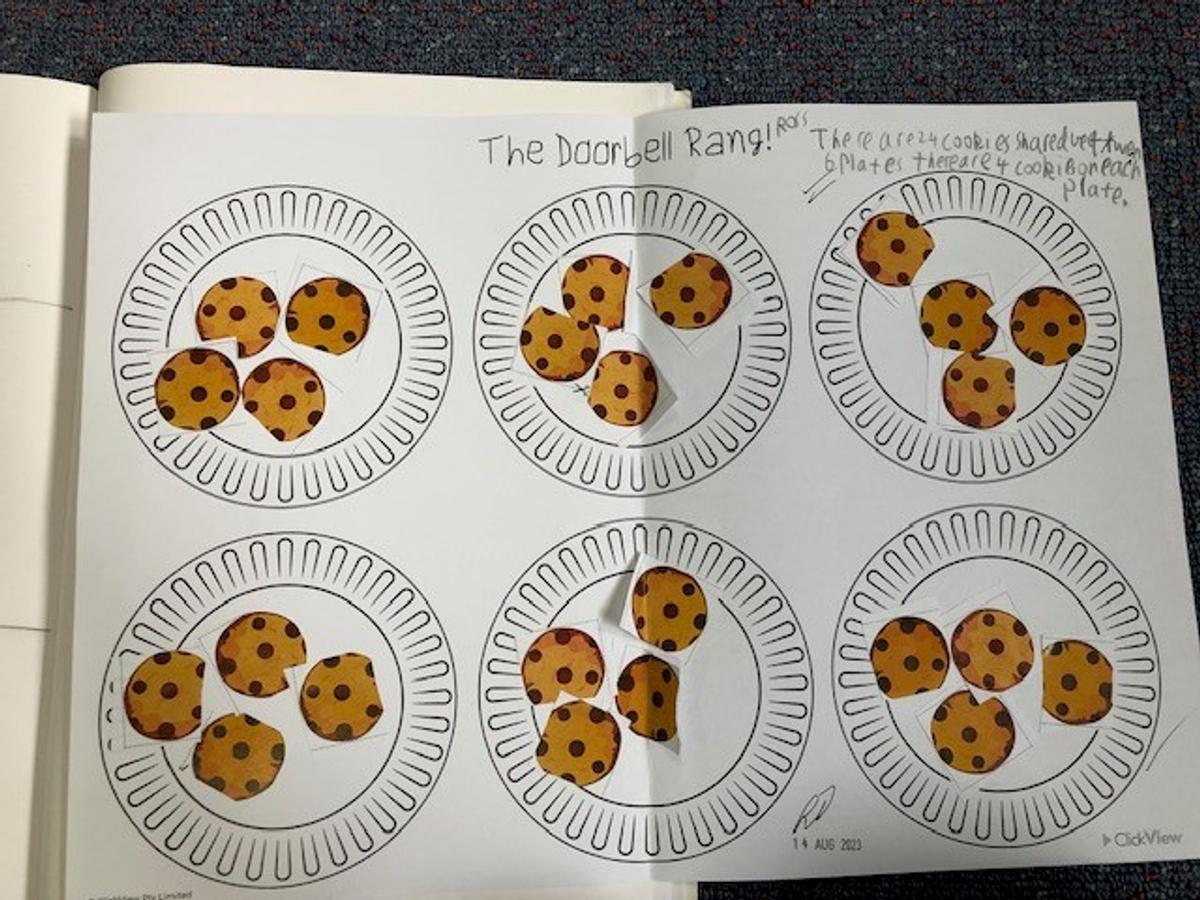


























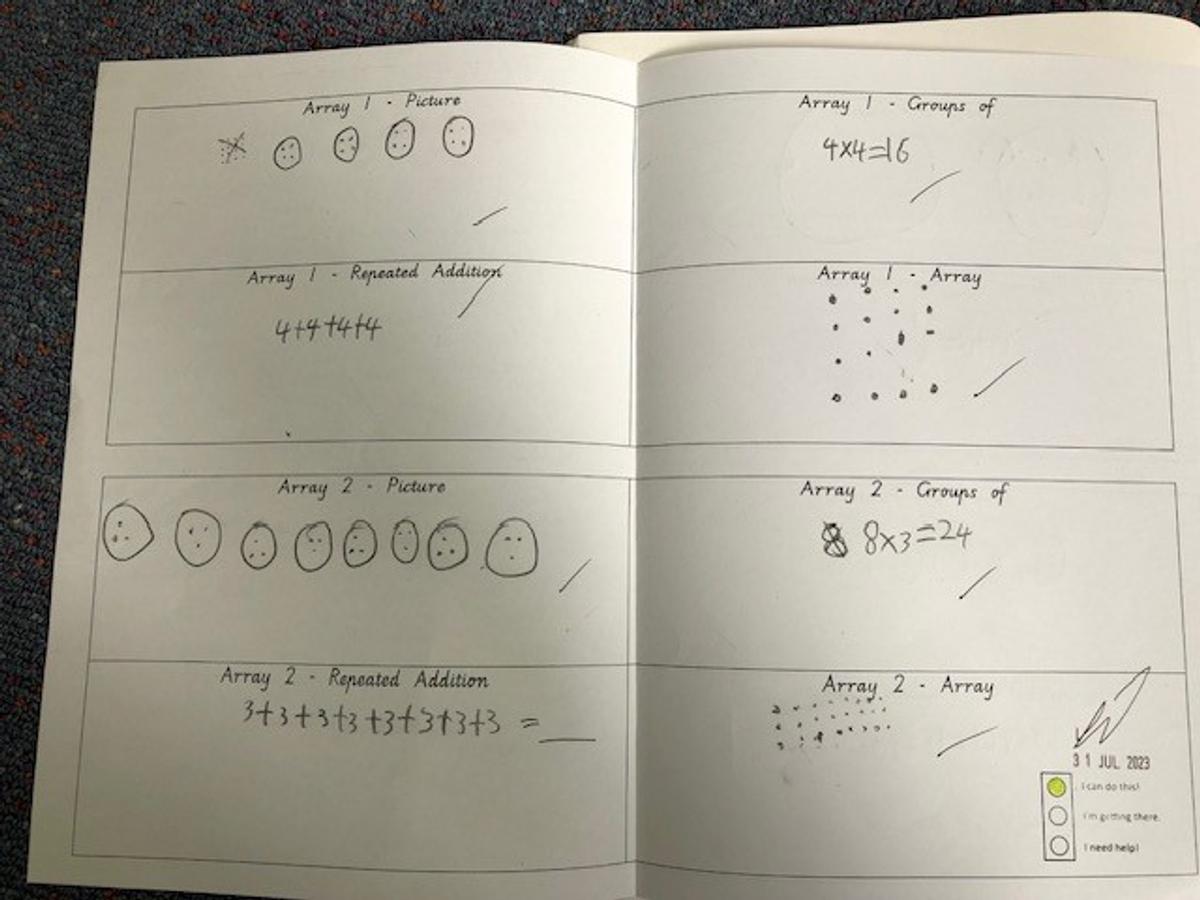
Repeated addition is adding groups of numbers together multiple times. For example 4 multiplied by 5 equals 20 can be written 5+5+5+5=20. Repeated subtraction is a way of teaching about division. It is the repeated subtraction of the same number from a large number down to zero. For example, 20 divided by 5 can be written 20-5-5-5-5=0
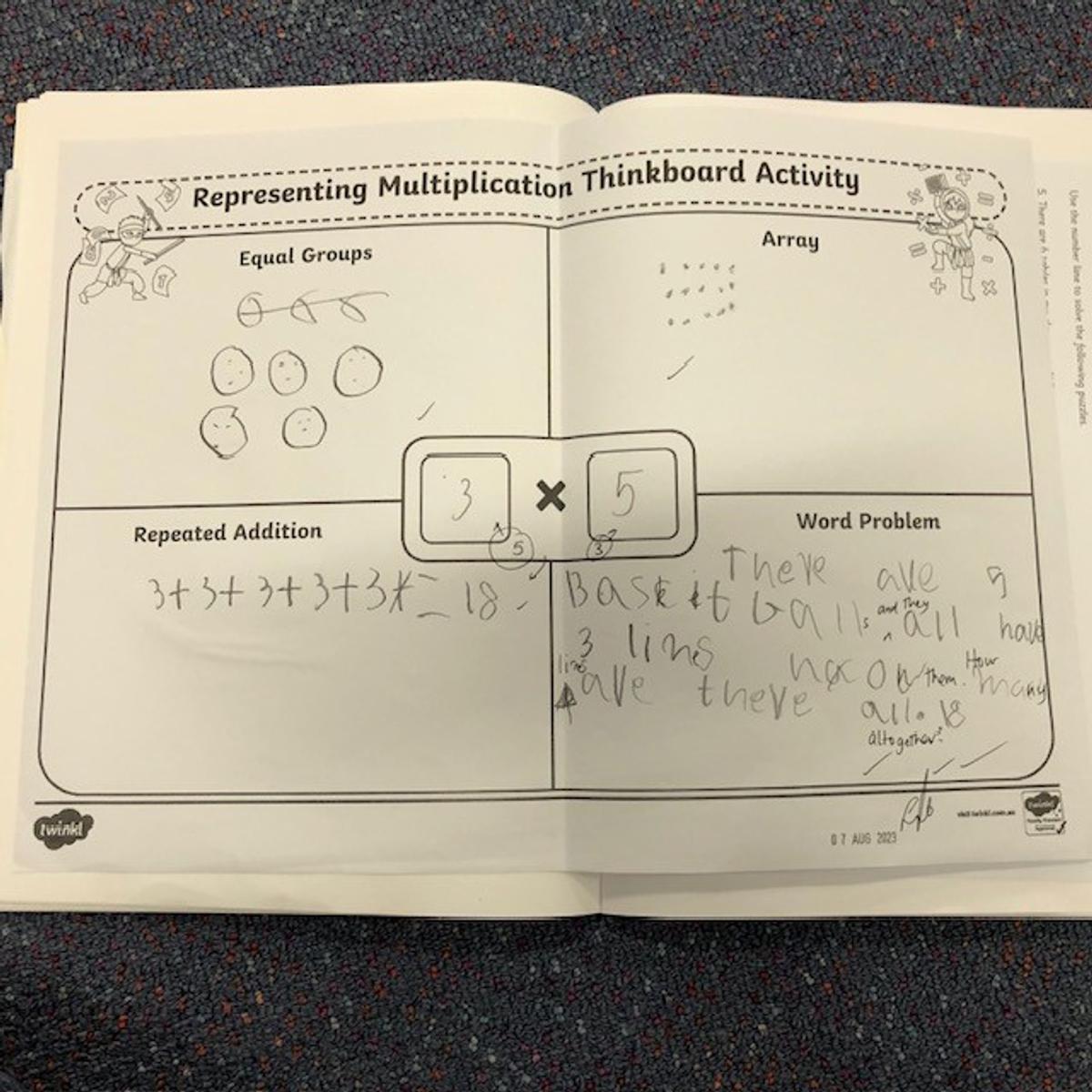







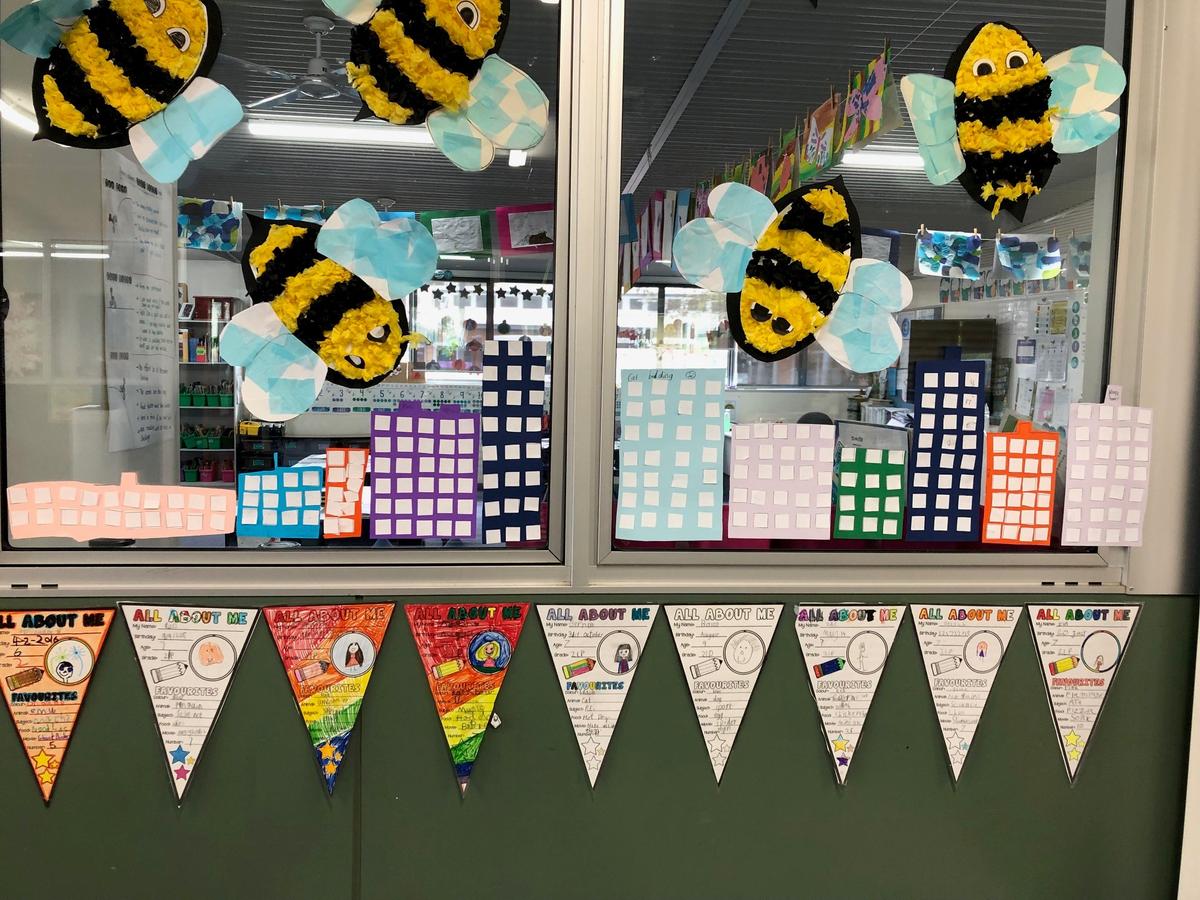
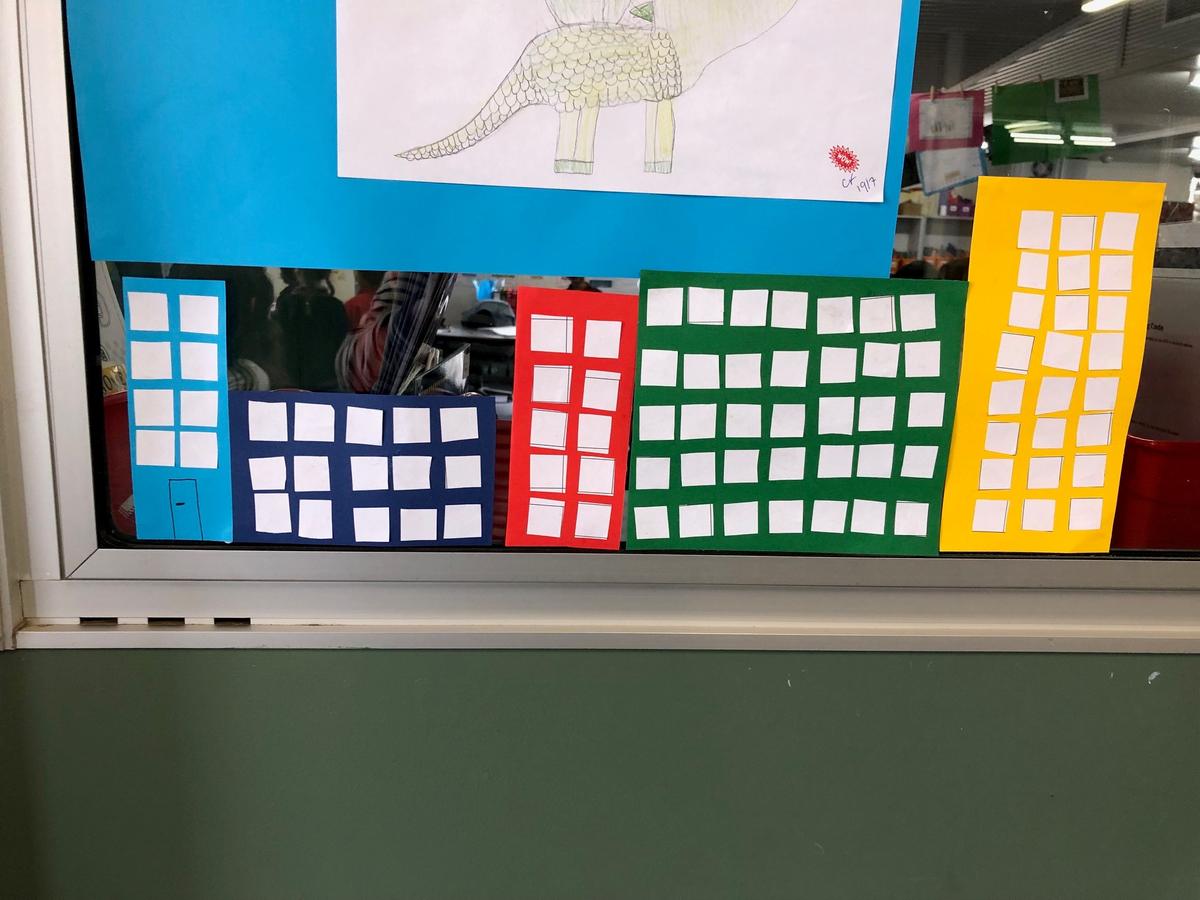
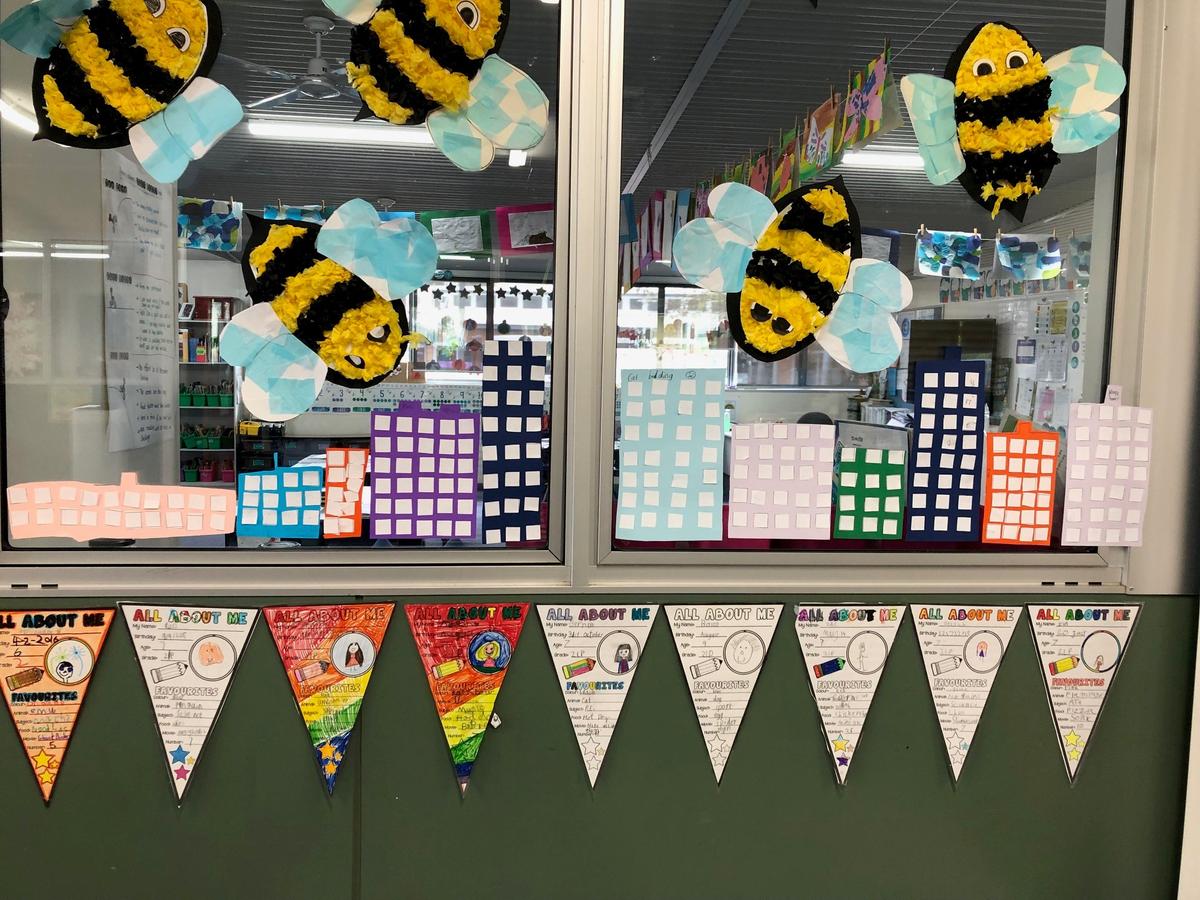
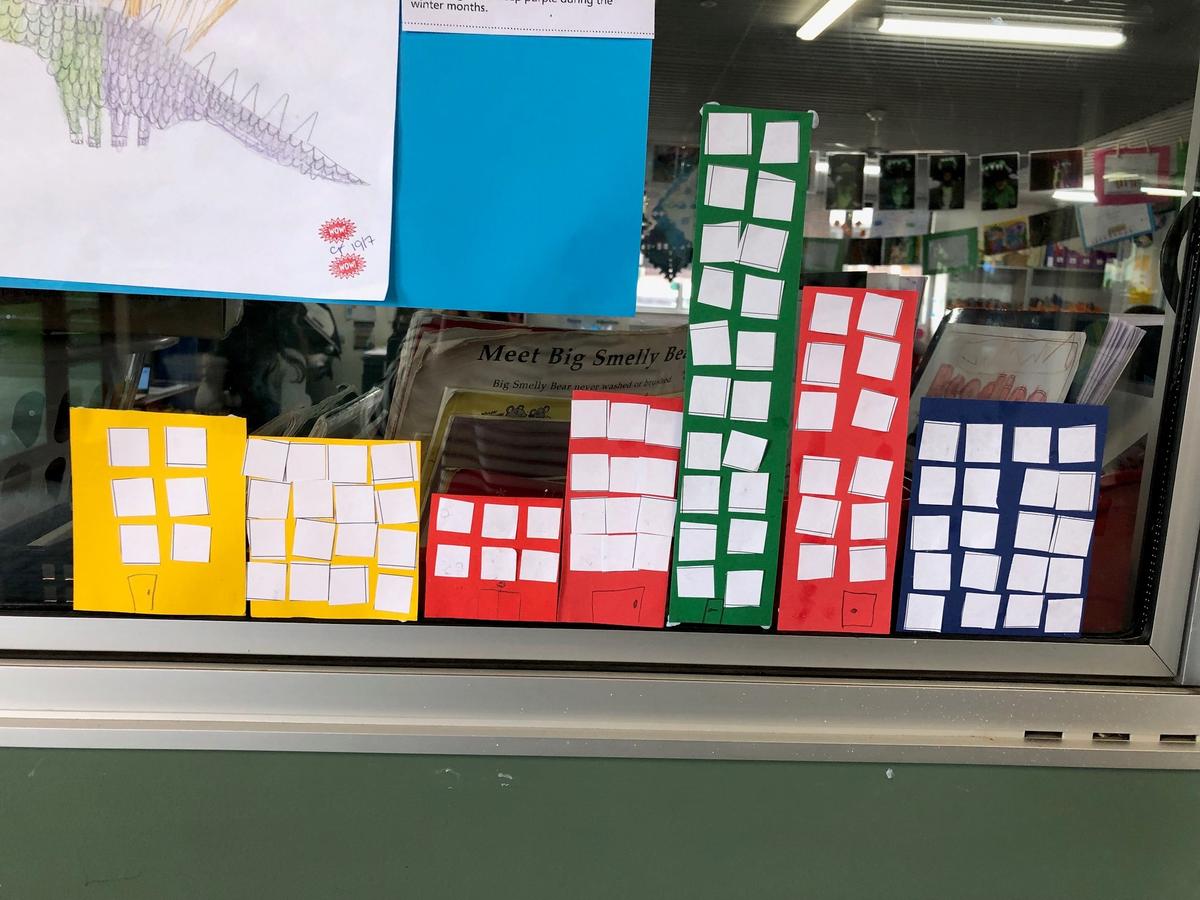
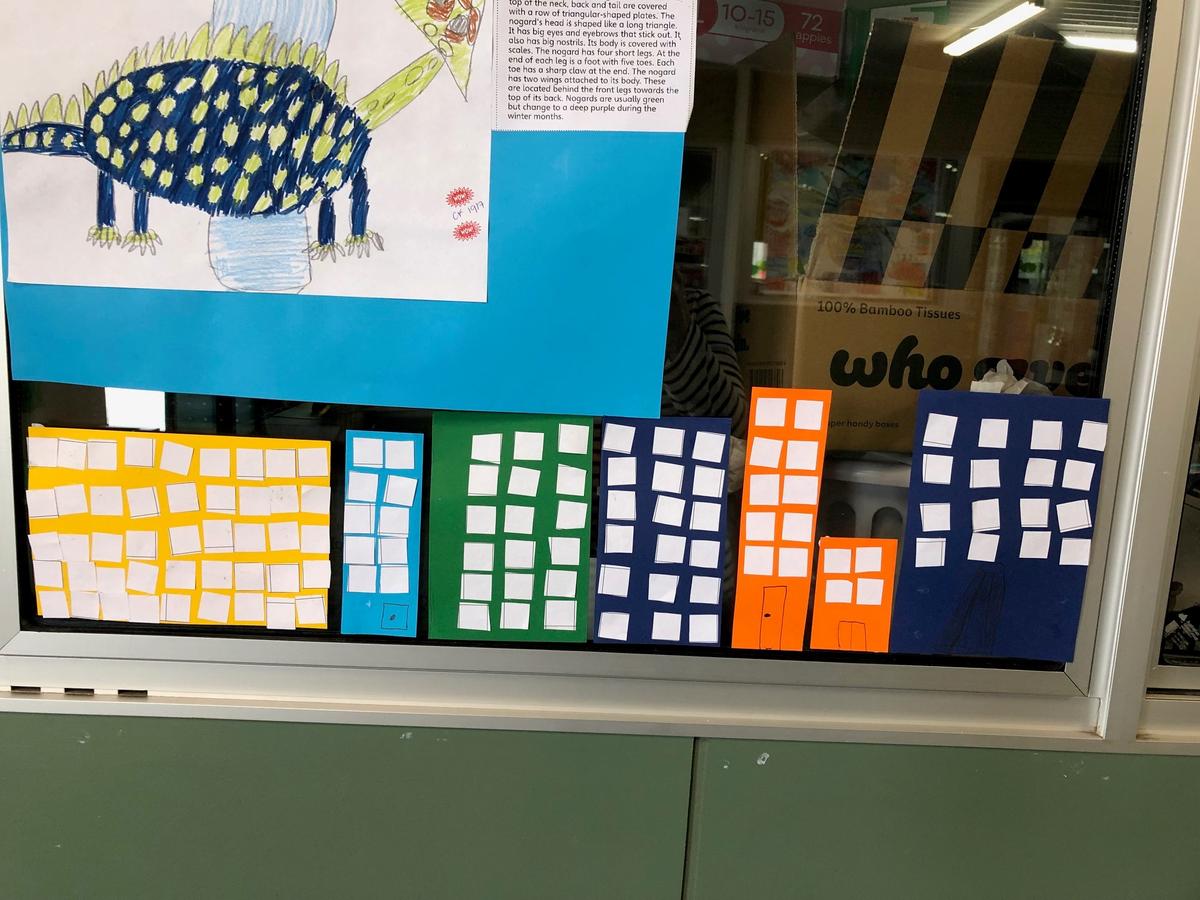
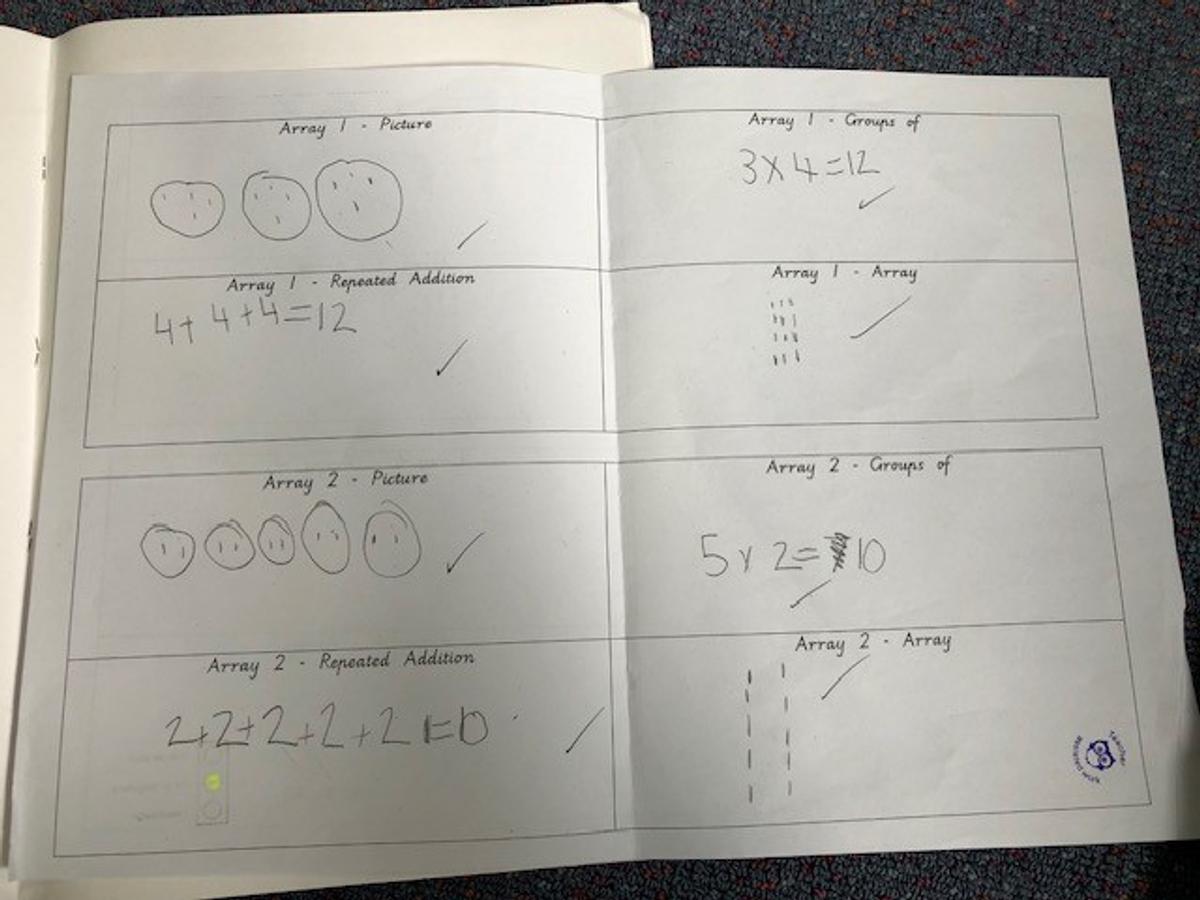
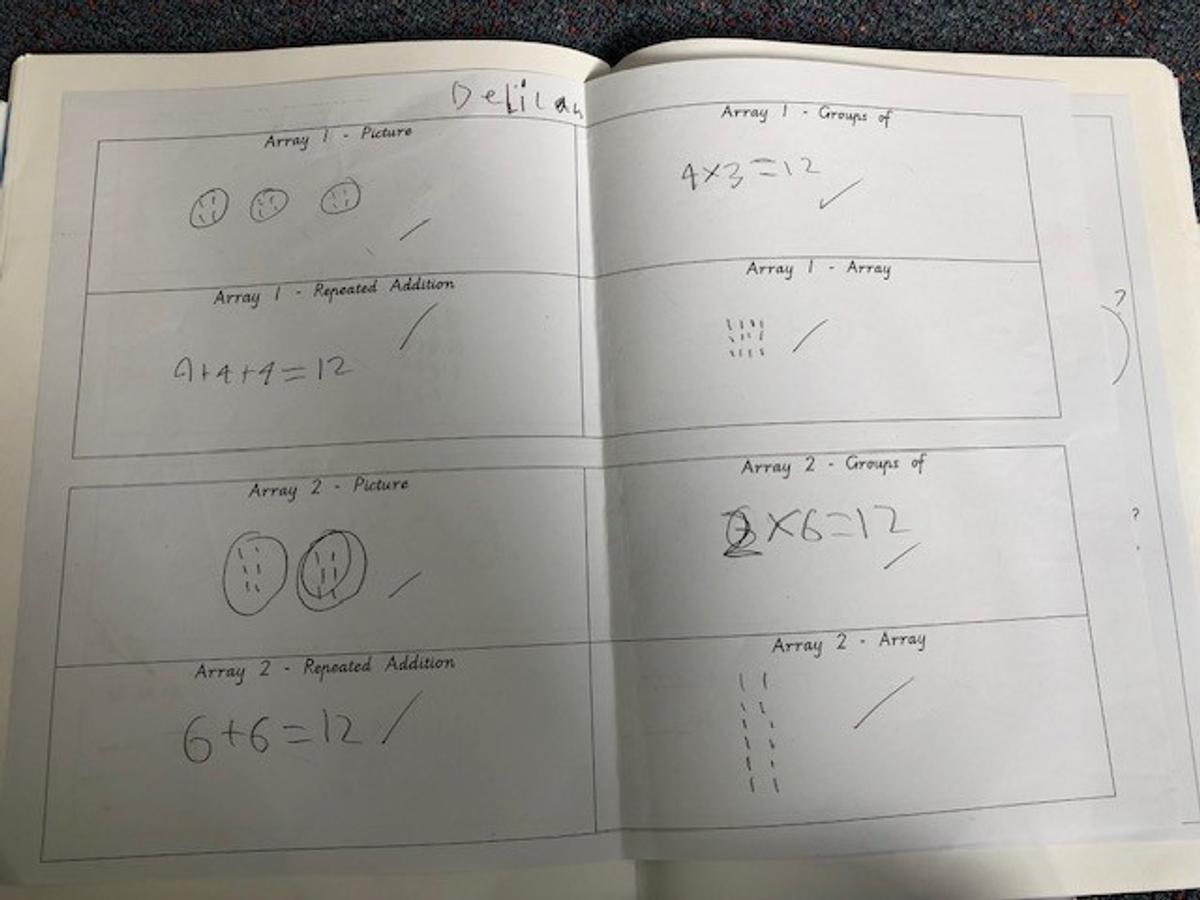
Grade 1/2s learnt that an array is a way of arranging things in rows and columns. When you buy things like a pack of cookies, a pack of toy cars, or even a carton of eggs, the items in the package are lined up to create an array. An array always has rows and columns. The rows are the horizontal lines that go from left to right. Students know they can multiply the number of items in the row by the column and vice versa, and for division students can count the total number items and divide by either the row or the column.











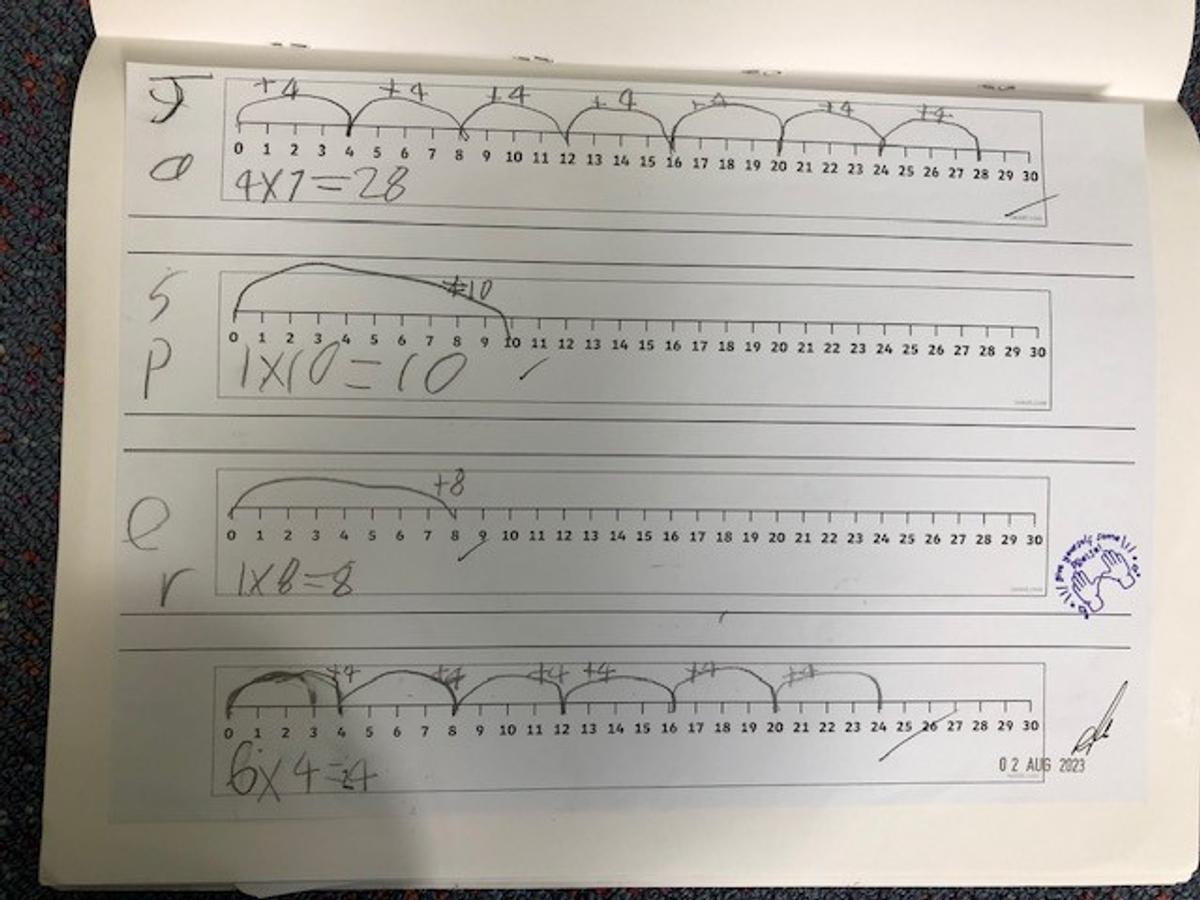
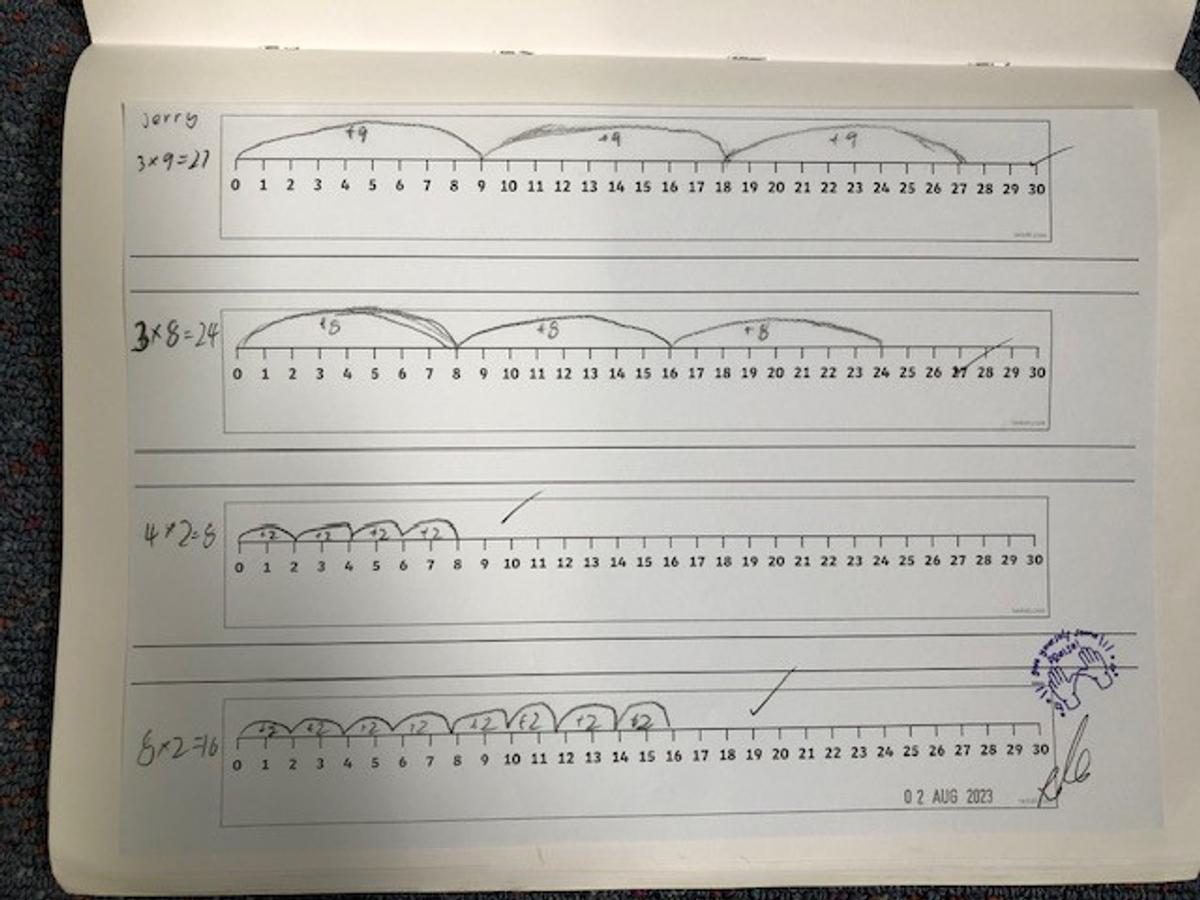
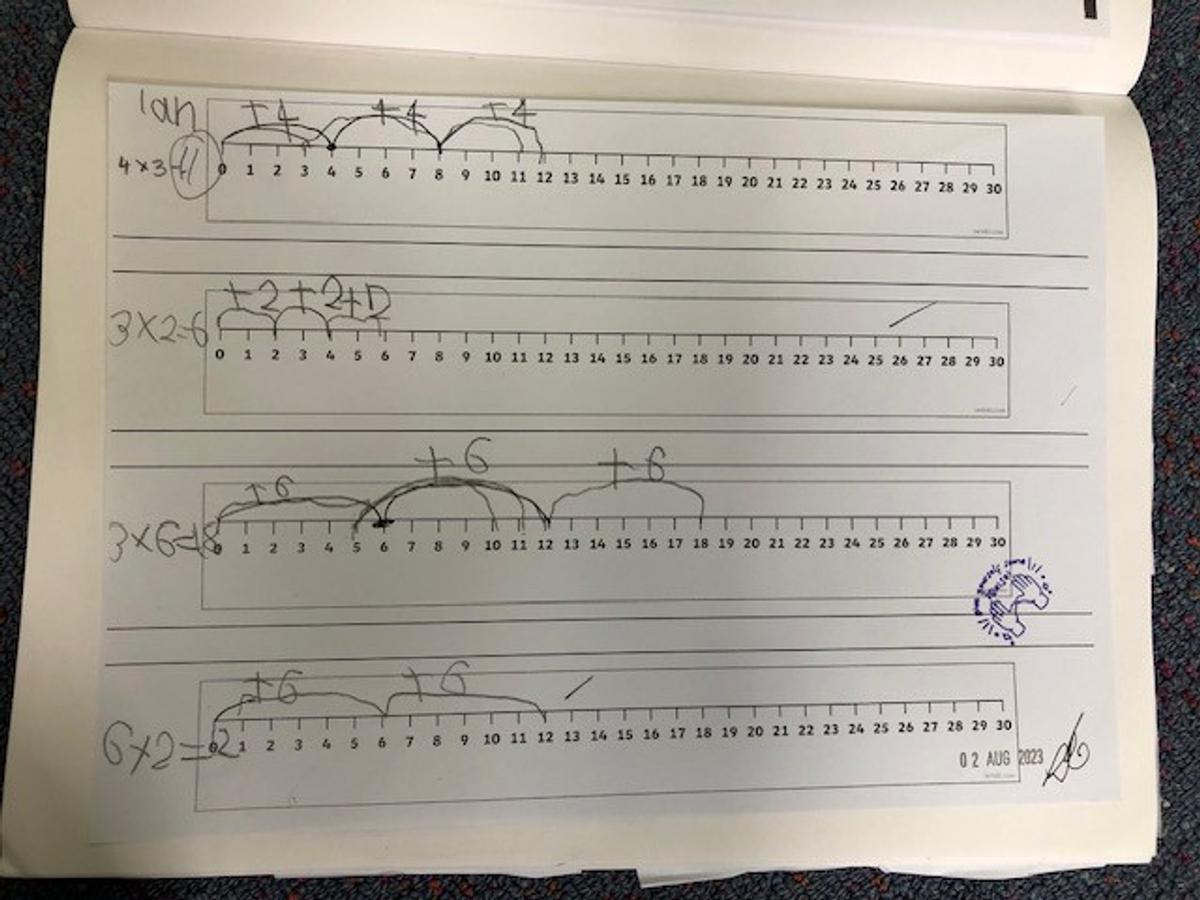
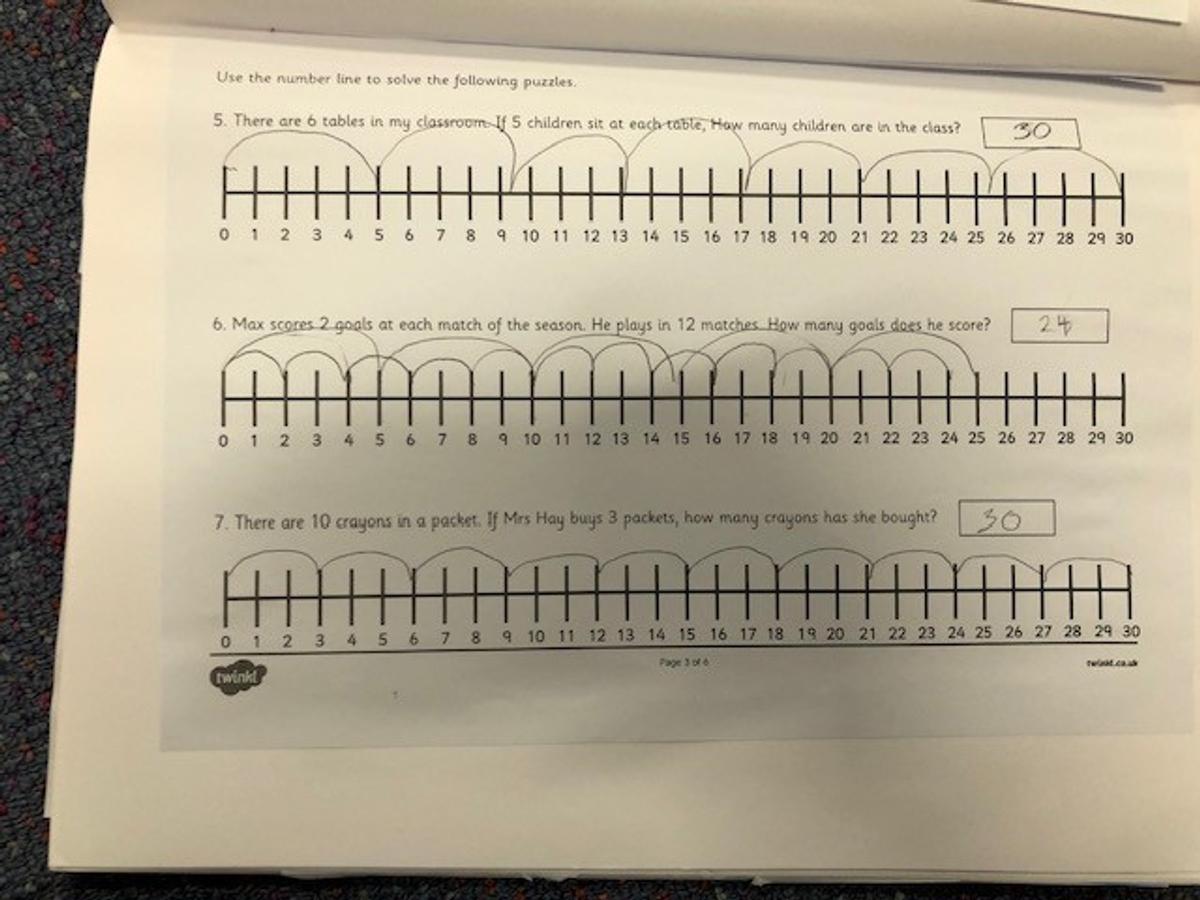
To perform multiplication on a number line, we start from zero and move towards the right side of the number line for a given number of times. For example if we were to multiply 3 × 5 using a number line we would need to start from zero and draw three groups of 5 equal intervals on the number line. To perform division on a number line, we start from the largest number and move towards the left side of the number line for a given number of times. For example if we were to divide 15 by 3 using a number line we would need to start from 15 and draw five groups of 3 equal intervals on the number line.













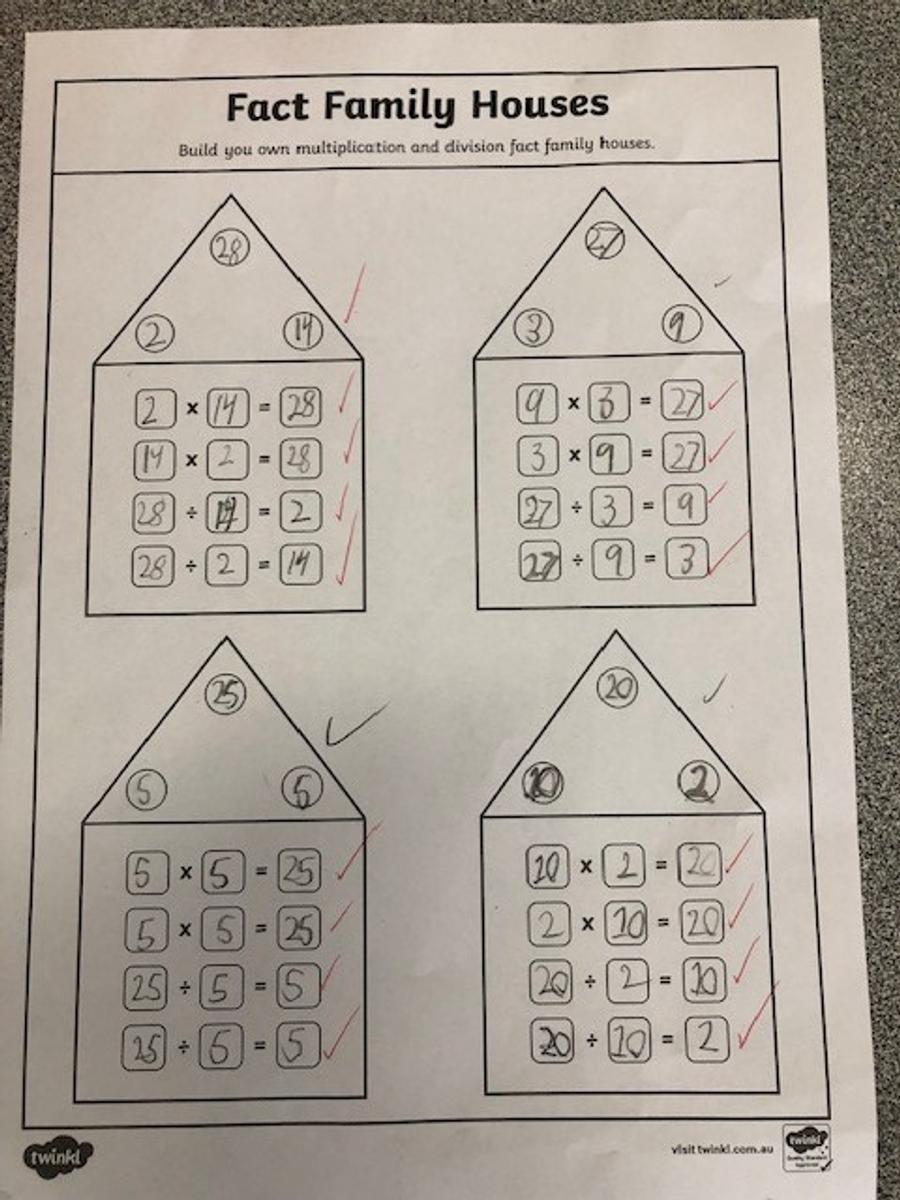
Multiplication and division are inverse operations. This means they are opposites. All multiplication sentences can be rewritten as two different division sentences, and all division sentences can be written as two different multiplication sentences. We also call these fact families. For example, 5 multiplied by 3 equals 15 and can rewritten as 15 divided by 5 equals 3.





Using the strategies above, students had a go at solving a range of worded problems for both multiplication and division. Here is a selection of a just a few examples!




























IDEAS & GAMES TO PLAY AT HOME
You can incorporate multiplication and division into everyday activities such as:
Here are same videos of games you might like to play at home as a family to support the use of the four operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division)
For more ideas about how you can support your child's mathematical understanding, visit Victorian Government website https://www.vic.gov.au/how-build-your-childs-numeracy-skills-birth-grade-2
Prepared by the Team 1/2 Teachers