Stay Safe Online - Multi Factor Authenticati
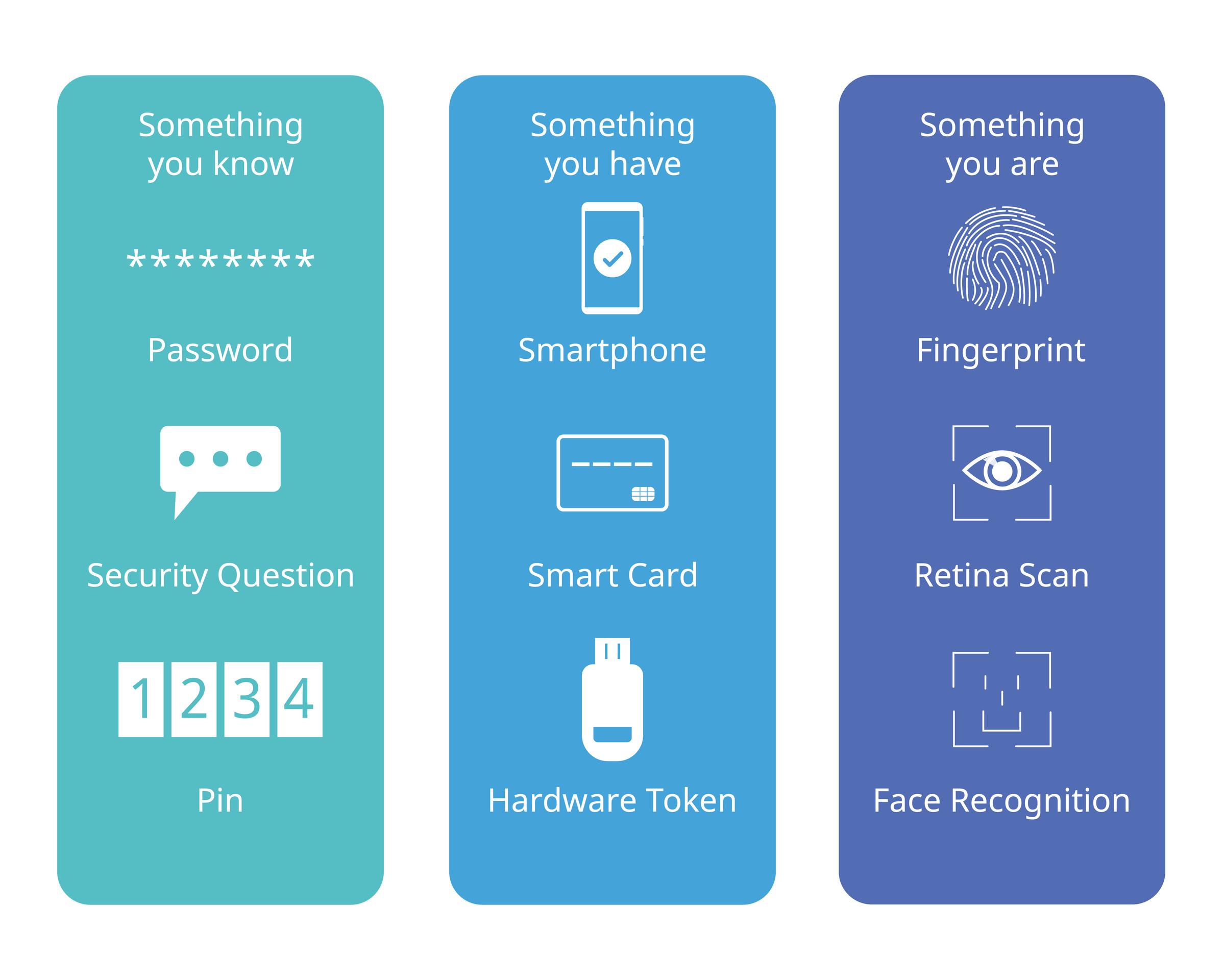
Overview: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification to access their accounts.
Significance for Home Users: Enabling MFA for online accounts adds an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access and helps prevent account takeover by cybercriminals. By requiring both a password and a secondary form of authentication, such as a one-time passcode or biometric verification, home users can significantly enhance the security of their accounts.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) offers several benefits in enhancing security beyond passwords and protecting against unauthorized access. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Security:
- MFA adds an additional layer of security beyond passwords by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as something they know (password), something they have (token or device), or something they are (biometric data). This multi-layered approach makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they obtain or guess a user's password.
- Reduced Risk of Unauthorized Access:
- By requiring multiple factors for authentication, MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive accounts and systems. Even if a user's password is compromised through phishing, brute force attacks, or other means, an additional authentication factor is still required to complete the login process, thwarting most unauthorized access attempts.
- Protection Against Credential Theft:
- MFA mitigates the risk of credential theft and password-based attacks, such as phishing, credential stuffing, and password spraying. Even if attackers obtain users' passwords, they would still need access to the additional authentication factors, such as a mobile device or biometric data, making it more challenging to compromise accounts.
- Compliance Requirements:
- Many regulatory standards and industry frameworks, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, require the implementation of MFA as part of security best practices. Adhering to MFA requirements helps organizations comply with regulatory mandates and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Improved User Experience:
- While MFA adds an extra step to the authentication process, modern MFA solutions are designed to balance security with usability, providing convenient and user-friendly authentication methods. Options such as push notifications, biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or face recognition), and one-time passcodes (OTP) via SMS or authenticator apps offer a seamless user experience while enhancing security.
- Adaptability and Flexibility:
- MFA solutions offer flexibility in authentication methods and deployment options, allowing organizations to choose the most suitable approach based on their security requirements, user preferences, and infrastructure. Whether it's hardware tokens, software-based OTP generators, biometric authentication, or risk-based authentication, organizations can tailor MFA solutions to meet their specific needs.
- Protection Across Various Platforms:
- MFA can be implemented across a wide range of platforms and services, including email, cloud applications, VPNs, social media accounts, and more. By deploying MFA uniformly across different systems and services, organizations can maintain consistent security standards and protect user accounts across various digital environments.
In summary, multi-factor authentication (MFA) offers significant benefits in adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, protecting against credential theft, complying with regulatory requirements, enhancing the user experience, providing adaptability and flexibility, and ensuring protection across various platforms and services. Implementing MFA is a crucial step in bolstering cybersecurity defenses and safeguarding sensitive data in today's threat landscape.
- Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for various accounts and online services is crucial for enhancing security and protecting against unauthorized access. Here's a guide on how to enable MFA for different types of accounts:
1. Email Accounts:
- Gmail (Google Account):
- Sign in to your Google Account.
- Go to the Security section.
- Under "Signing in to Google," select "2-Step Verification."
- Follow the prompts to set up MFA, choosing from options like receiving codes via SMS, using an authenticator app, or using a security key.
- Outlook (Microsoft Account):
- Sign in to your Microsoft Account.
- Go to Security settings.
- Under "Security info," select "Two-step verification."
- Follow the instructions to set up MFA, which may include verifying your identity and choosing verification methods.
2. Social Media Accounts:
- Facebook:
- Go to Facebook Settings.
- Select "Security and Login."
- Scroll down to "Use two-factor authentication" and click "Edit."
- Follow the prompts to set up MFA using options like text messages, authentication apps, or security keys.
- Twitter:
- Go to Twitter Settings.
- Select "Account."
- Under "Security," click "Security and account access."
- Toggle on "Two-factor authentication" and follow the prompts to set it up using options like text messages or authentication apps.
3. Financial Accounts:
- Bank Accounts:
- Many banks offer MFA options for online banking. Check with your bank's website or mobile app settings for MFA setup instructions.
- Investment Accounts:
- Log in to your investment account provider's website or app.
- Look for security or account settings where you can enable MFA. Follow the provided instructions to set it up.
General Tips for Enabling MFA:
- Choose Strong Authentication Methods:
- Whenever possible, use authentication methods like authenticator apps or security keys, as they are more secure than SMS-based verification codes.
- Keep Backup Codes:
- Save backup codes provided during MFA setup in a secure location. These codes can be used to access your accounts if you lose access to your primary MFA method.
- Regularly Review Security Settings:
- Periodically review your account security settings to ensure MFA is enabled and up-to-date. Remove any old or unused authentication methods.
- Educate Yourself:
- Familiarize yourself with different MFA options and understand how they work. Choose the ones that best fit your security needs and preferences.
By following these steps and enabling MFA for your accounts and online services, you can significantly enhance security and protect your sensitive information from unauthorized access. MFA adds an extra layer of protection beyond passwords, making it much harder for attackers to compromise your accounts.
If you use a password manage like 1Password it can identify the accounts and/or applications that you can apply MFA to.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) provides additional layers of security beyond passwords by requiring users to present two or more forms of verification. Here's a discussion of different MFA methods, including SMS codes, authenticator apps, hardware tokens, and biometric authentication, along with recommendations on choosing the most secure option available:
1. SMS Codes:
- Description: SMS-based MFA involves receiving a one-time verification code via text message to a registered mobile phone number.
- Pros: Widely available, easy to implement, and familiar to users.
- Cons: Vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks, interception, and phishing scams. Relies on the security of the mobile network.
- Recommendation: While SMS codes are better than relying solely on passwords, they are considered less secure compared to other MFA methods due to their susceptibility to interception and social engineering attacks. Therefore, it's recommended to use more secure options if available.
2. Authenticator Apps:
- Description: Authenticator apps generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) that users enter along with their passwords during login.
- Pros: More secure than SMS codes, as the codes are generated locally on the device and don't rely on network connectivity. Provides better protection against phishing attacks.
- Cons: Requires users to install and set up an authenticator app on their mobile device or computer.
- Recommendation: Authenticator apps, such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy, are a more secure option compared to SMS codes and are recommended for users who prioritize security.
3. Hardware Tokens:
- Description: Hardware tokens are physical devices that generate one-time passwords or act as a second-factor authentication mechanism.
- Pros: Provides strong security, as tokens generate unique codes without relying on network connectivity or mobile devices. Resistant to phishing attacks.
- Cons: Costly to deploy and manage. Users must carry the token with them.
- Recommendation: Hardware tokens offer high security but may not be practical for all users due to cost and convenience factors. They are typically recommended for organizations with stringent security requirements or for users with high-security needs.
4. Biometric Authentication:
- Description: Biometric authentication verifies users' identities based on physical characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans.
- Pros: Offers strong security and user convenience. Difficult to replicate or spoof biometric data.
- Cons: Requires compatible hardware (e.g., fingerprint scanner, facial recognition camera). Biometric data may be stored centrally, raising privacy concerns.
- Recommendation: Biometric authentication provides excellent security and user experience, but its availability depends on device support. It can be used in conjunction with other MFA methods for added security.
Recommendation:
- Choose the Most Secure Option Available: While SMS codes are better than relying solely on passwords, they are considered less secure due to vulnerabilities. Authenticator apps and hardware tokens offer stronger security and are recommended for users who prioritize security. Biometric authentication provides a balance of security and convenience but depends on device support.
- Consider Risk and Usability: When selecting an MFA method, consider the balance between security, usability, and cost. Choose a method that provides adequate security without overly inconveniencing users or straining resources.
In summary, while all MFA methods offer improved security over passwords alone, it's essential to prioritize the most secure option available, such as authenticator apps or hardware tokens, whenever possible. Biometric authentication can also be a secure and user-friendly option, depending on device support and user preferences.
