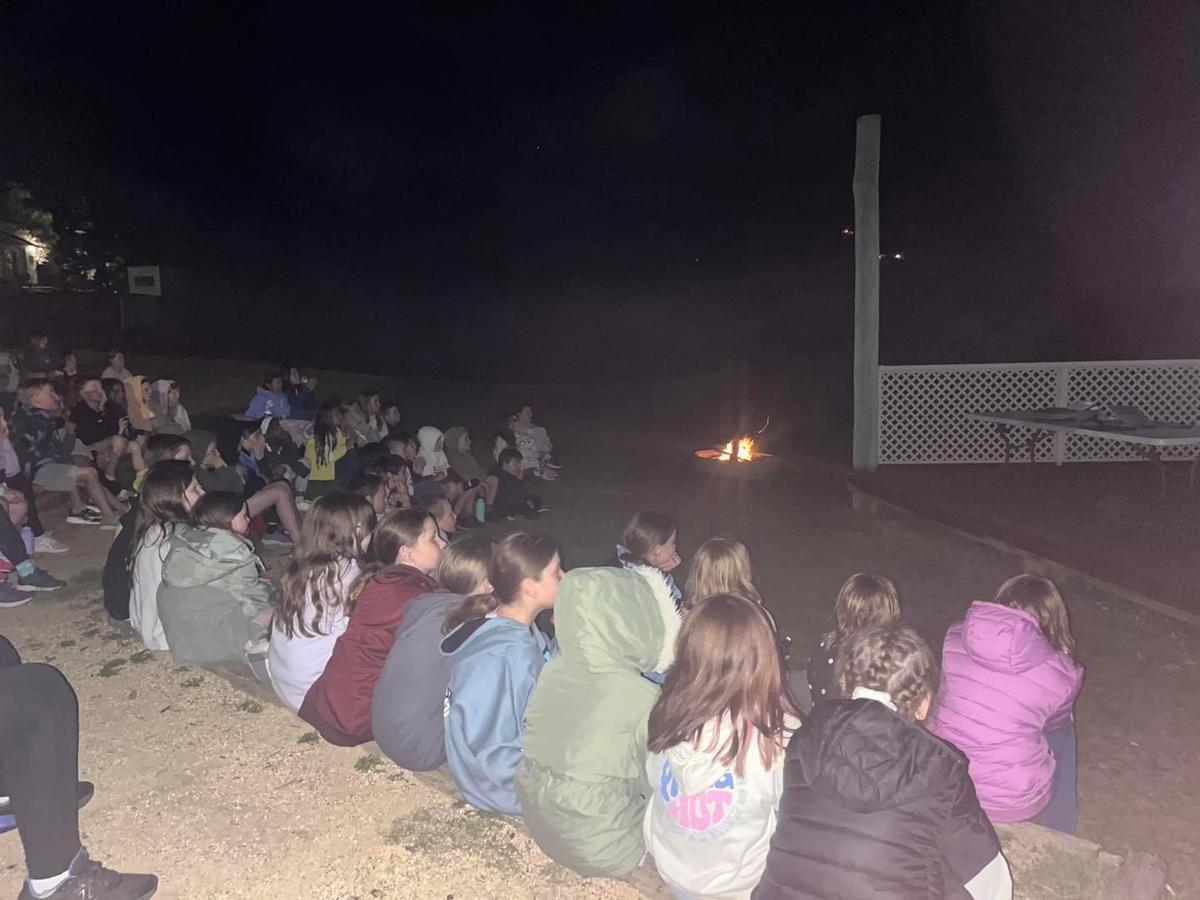
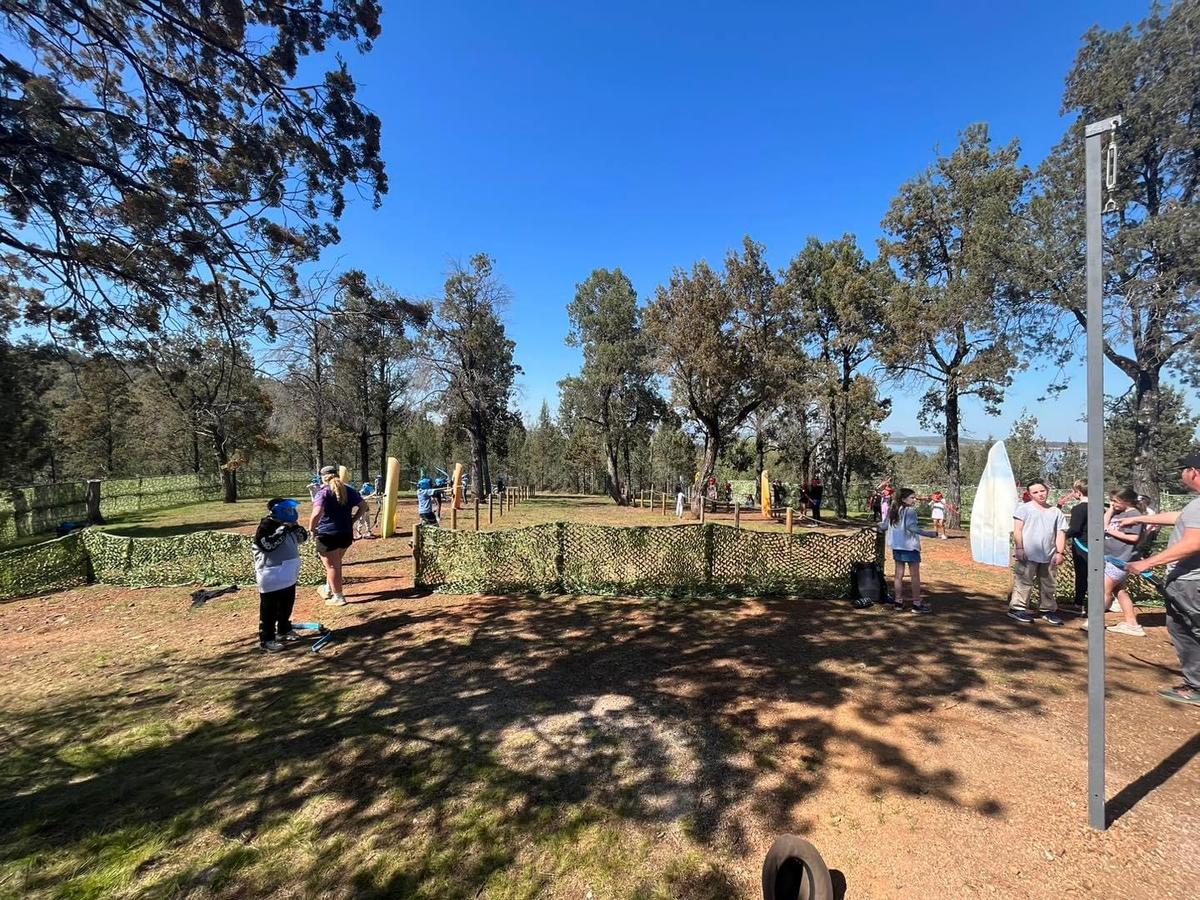
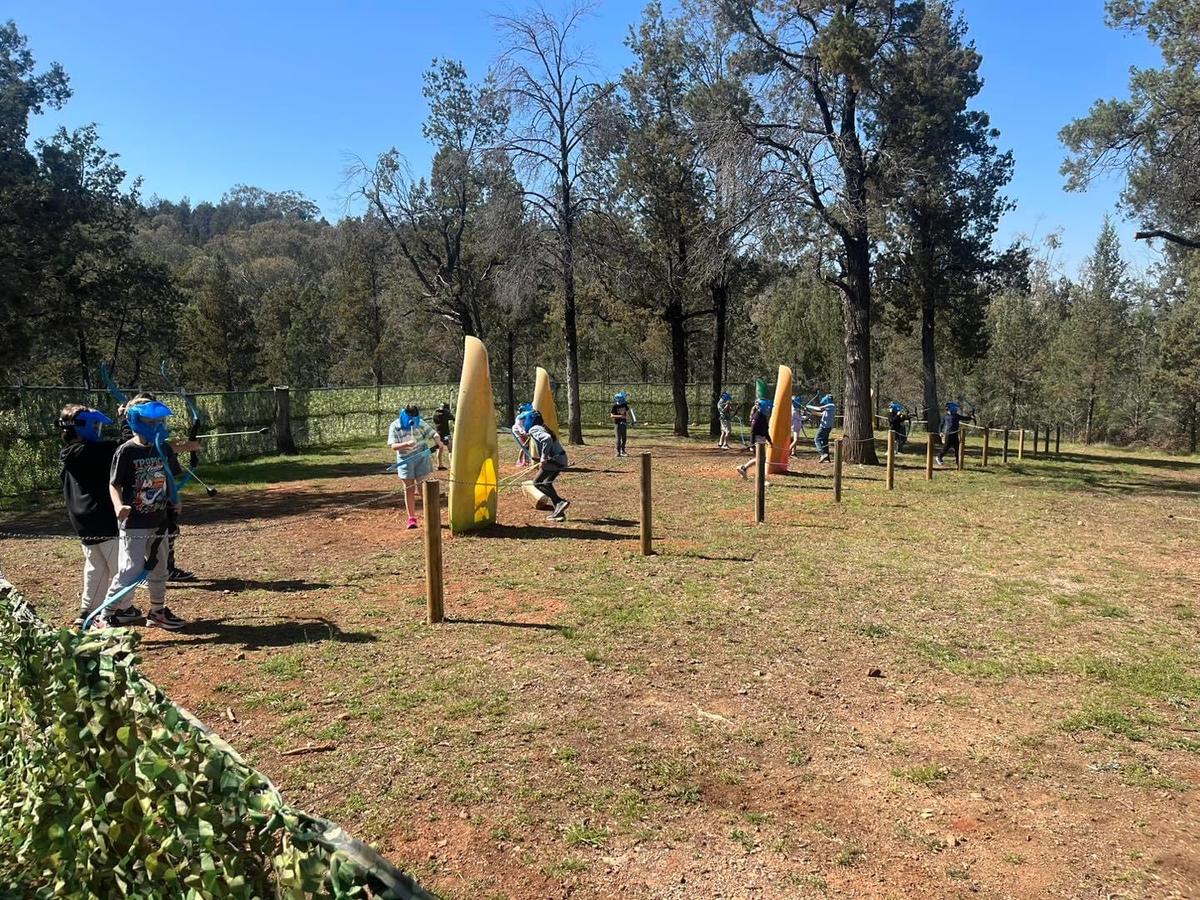
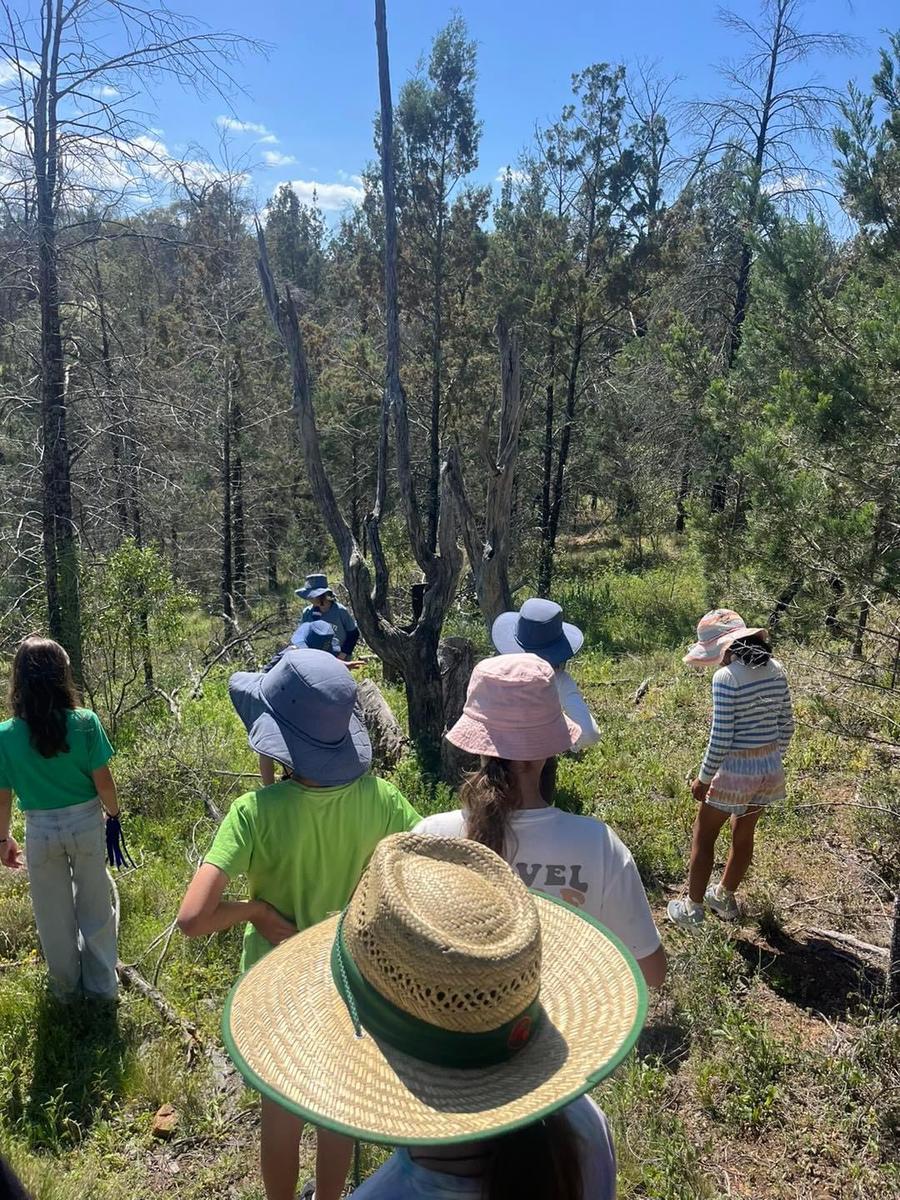
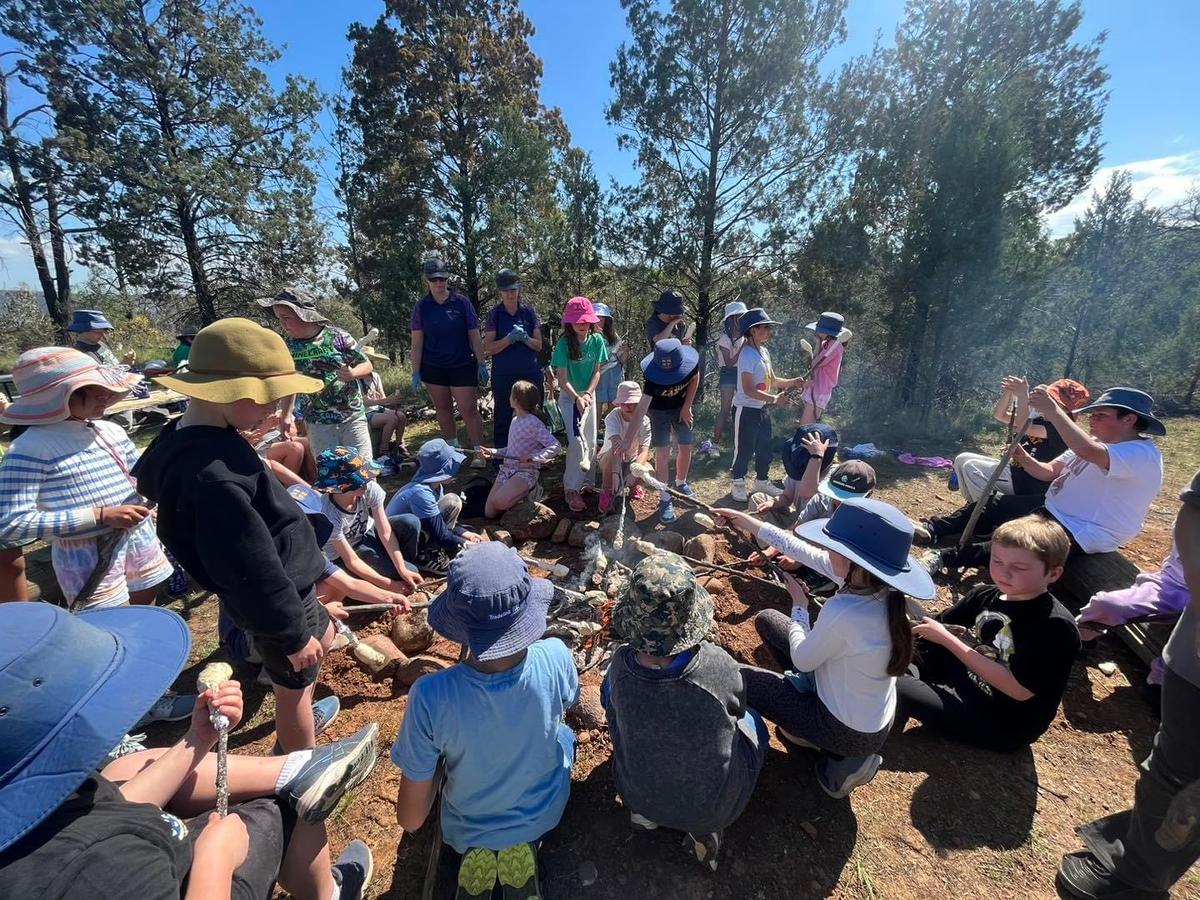
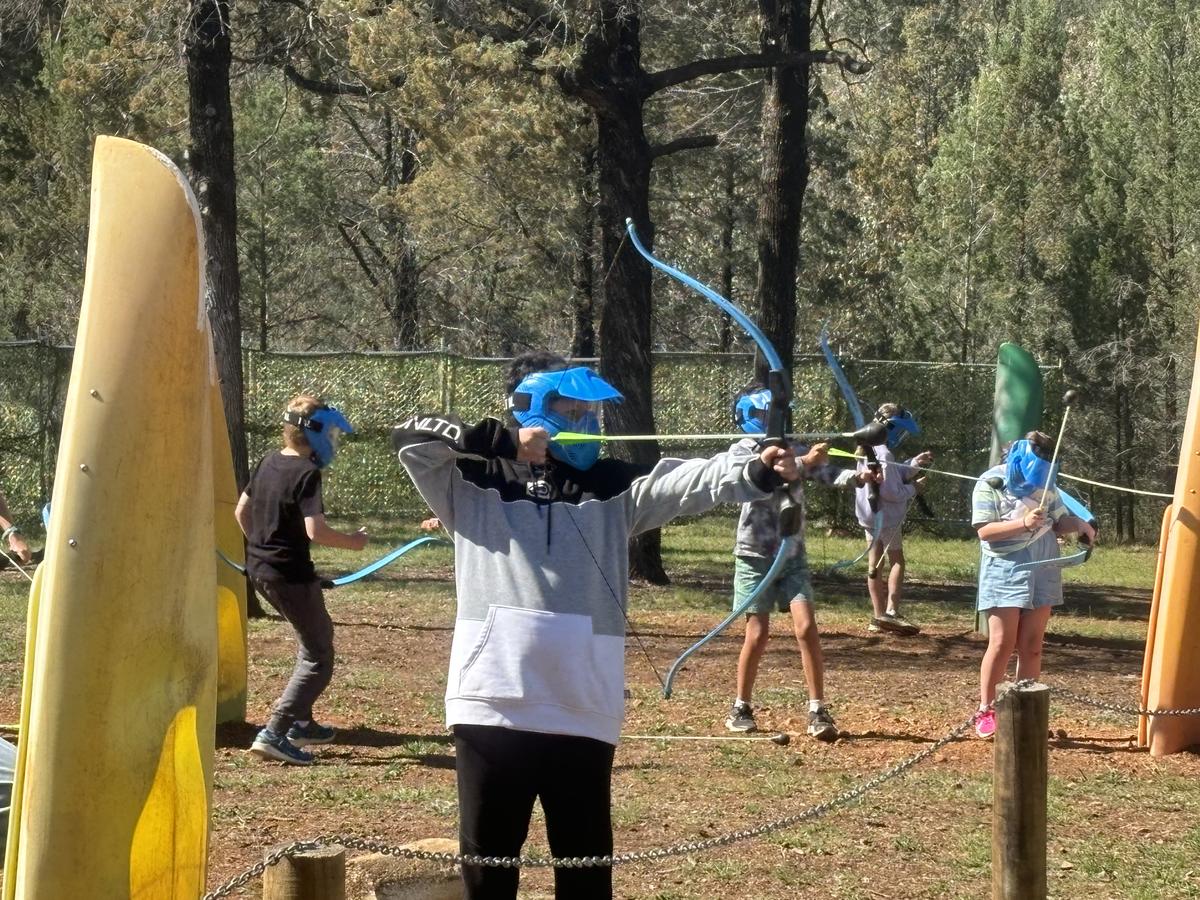
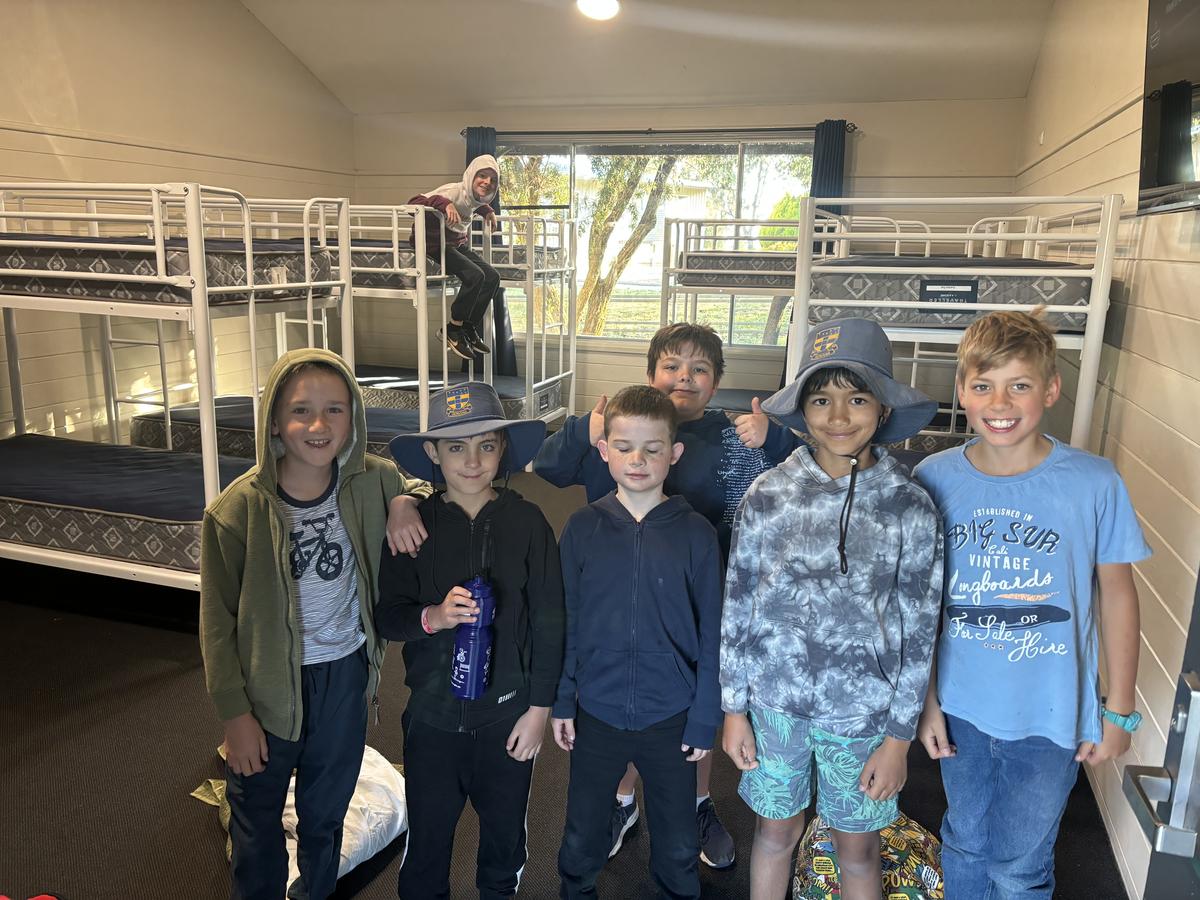
PHOTO GALLERY & Classroom Learning
K - Yr 6 Snapshots

PHOTO GALLERY & Classroom Learning
K - Yr 6 Snapshots
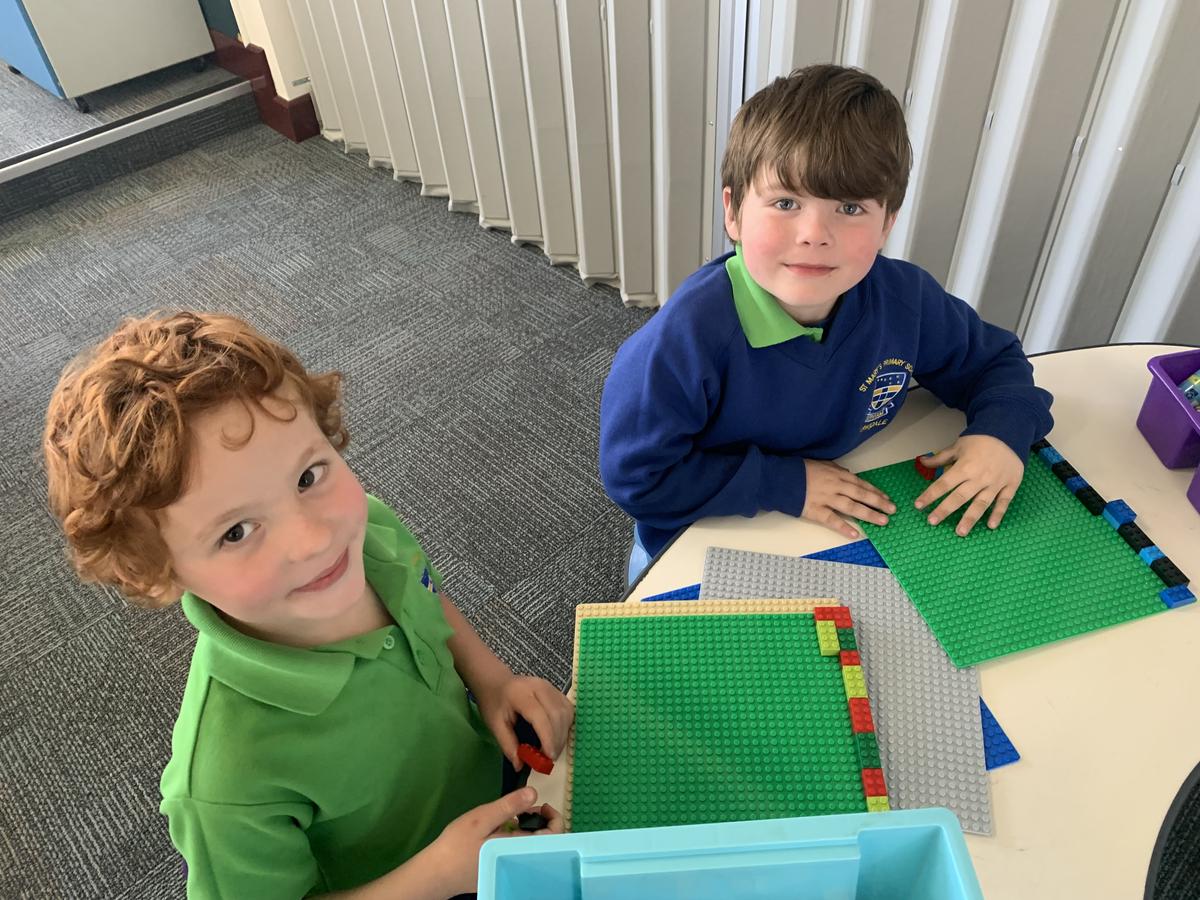
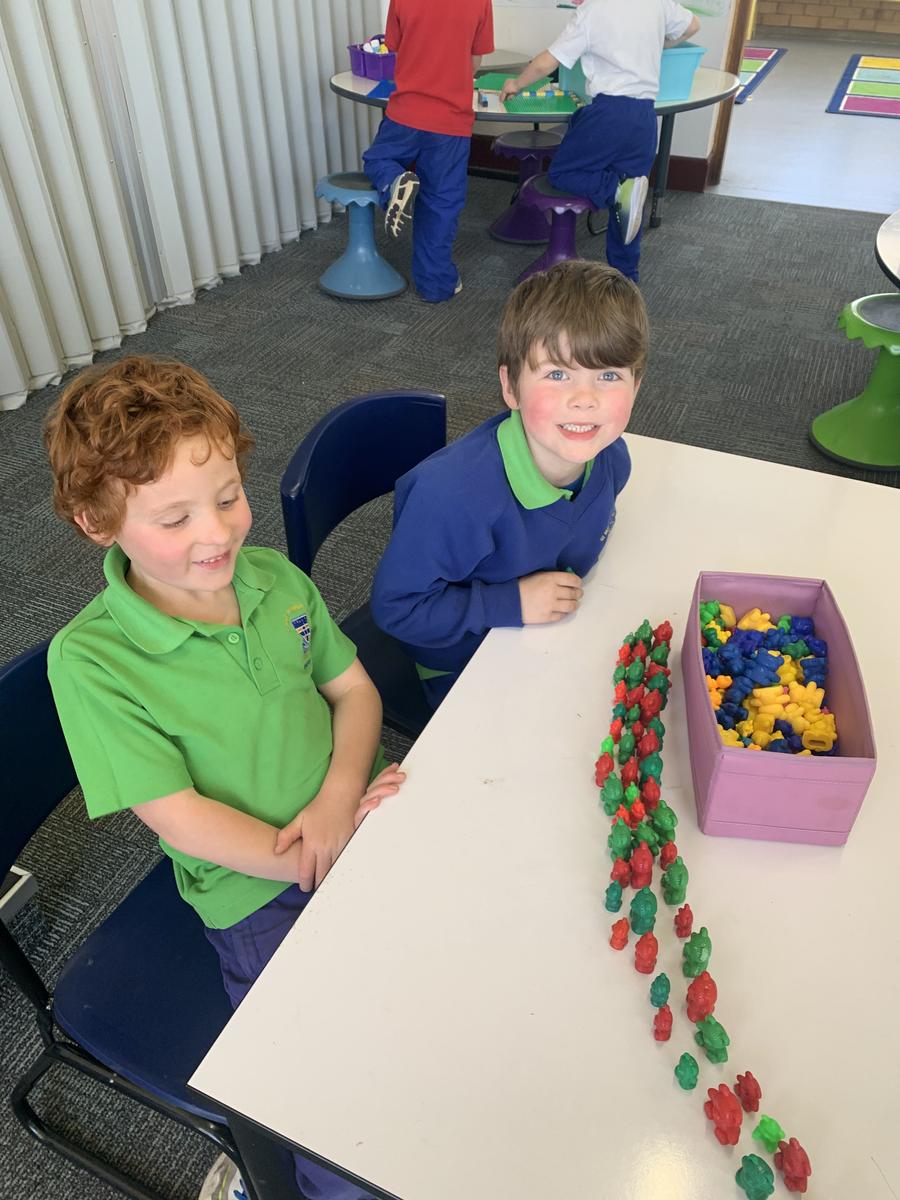








































































English
Getting ready for our 'Publishing Party




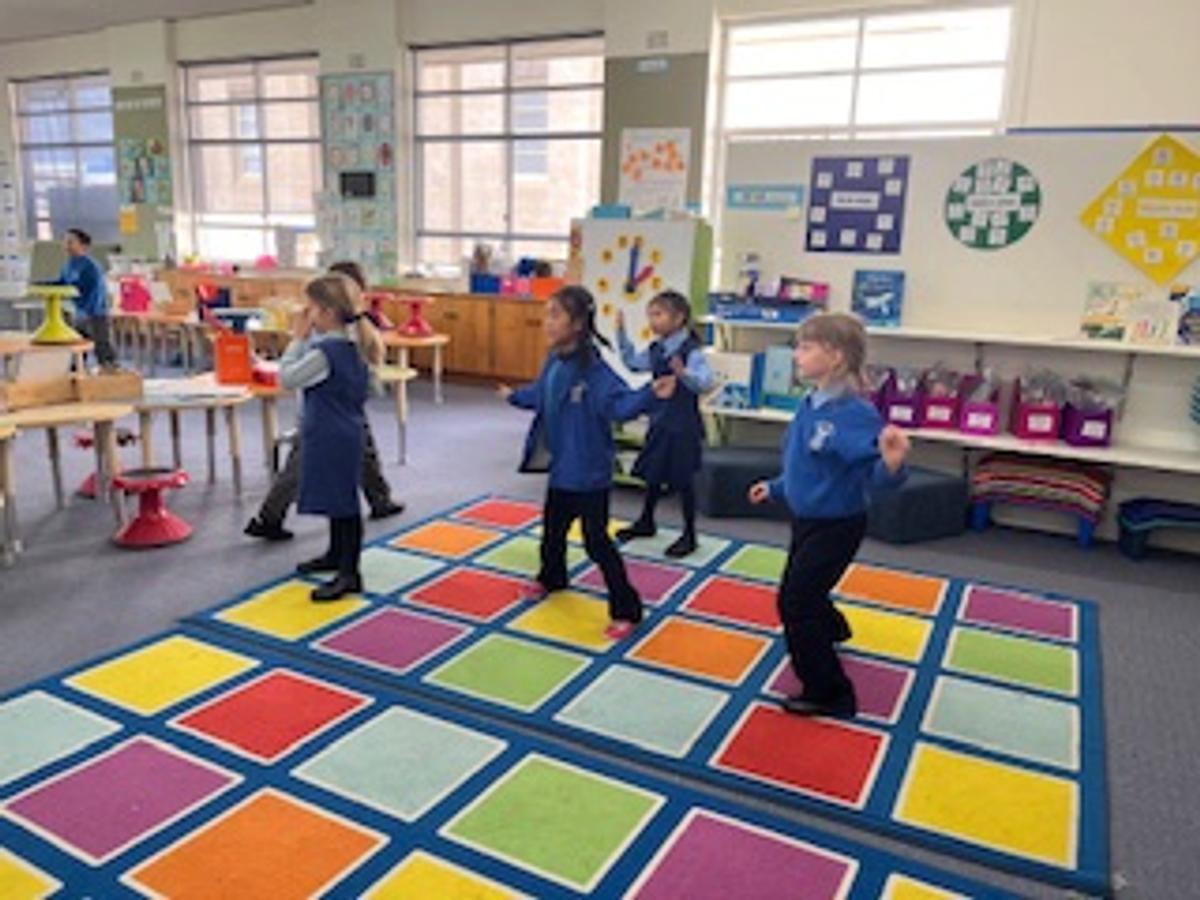
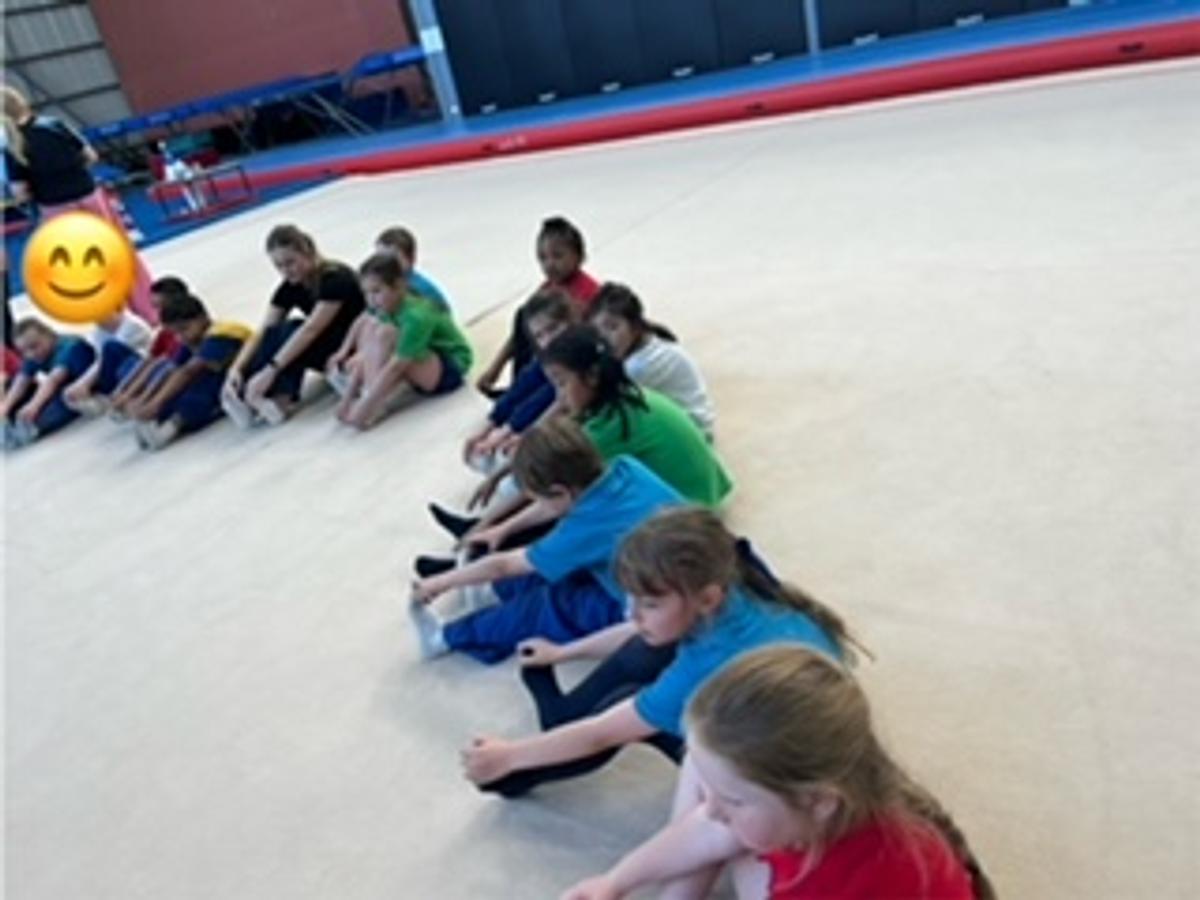
Dance
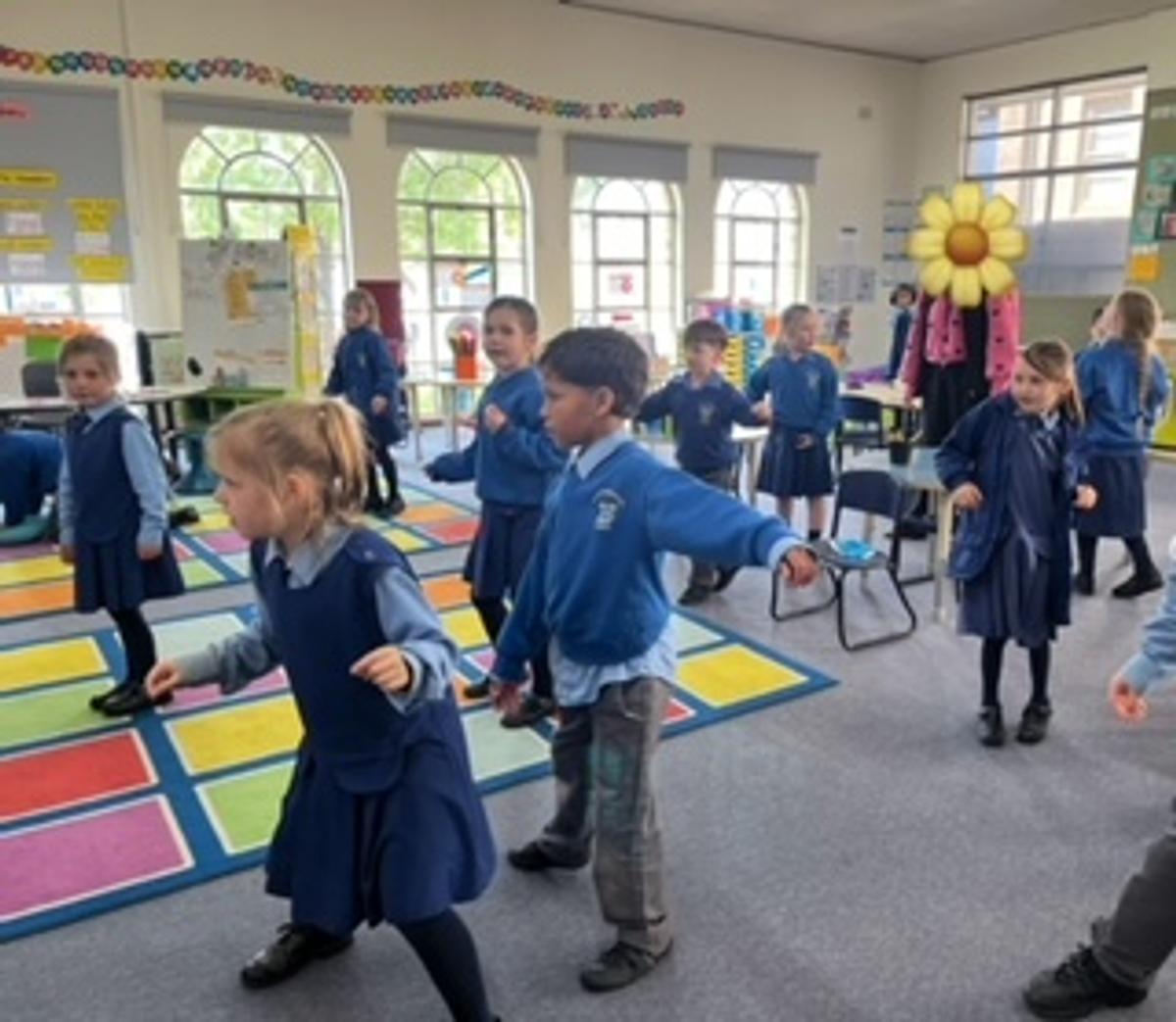






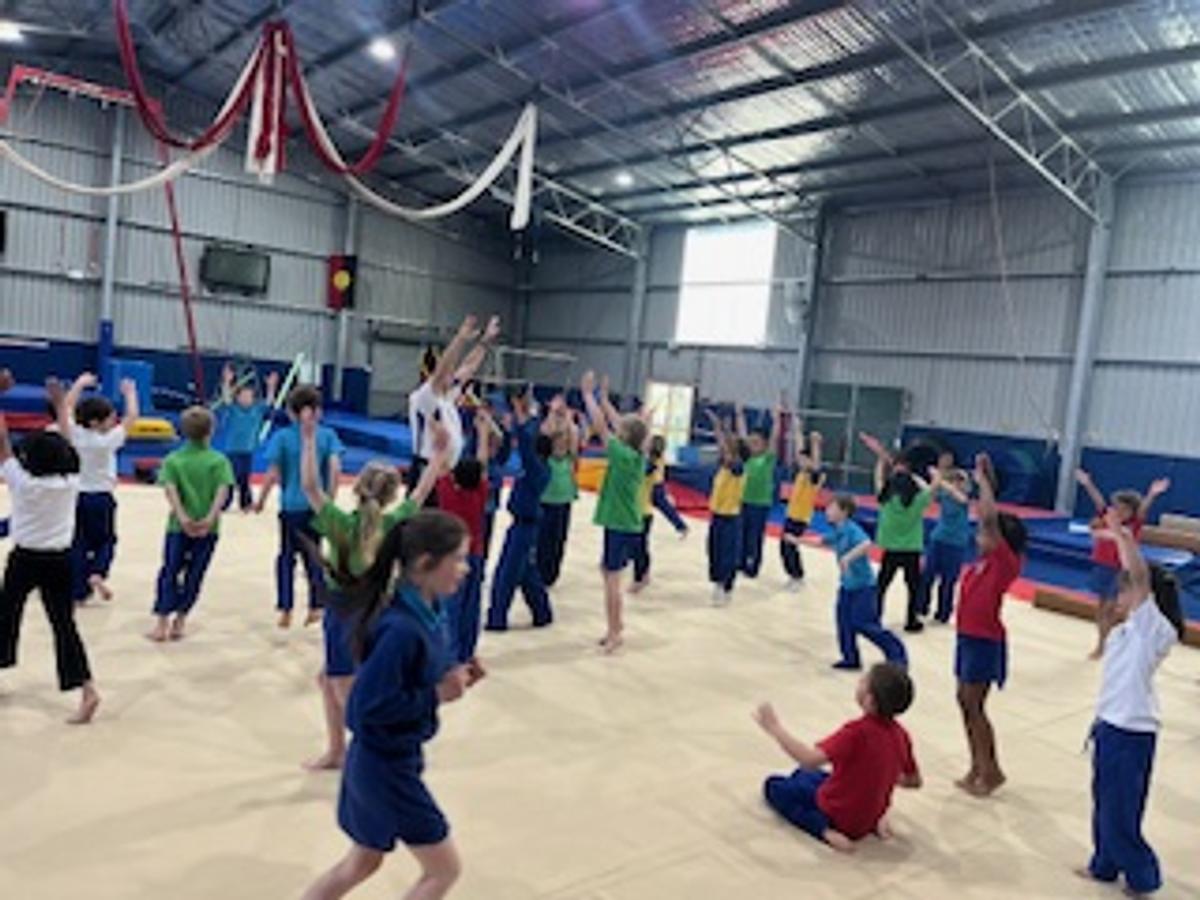
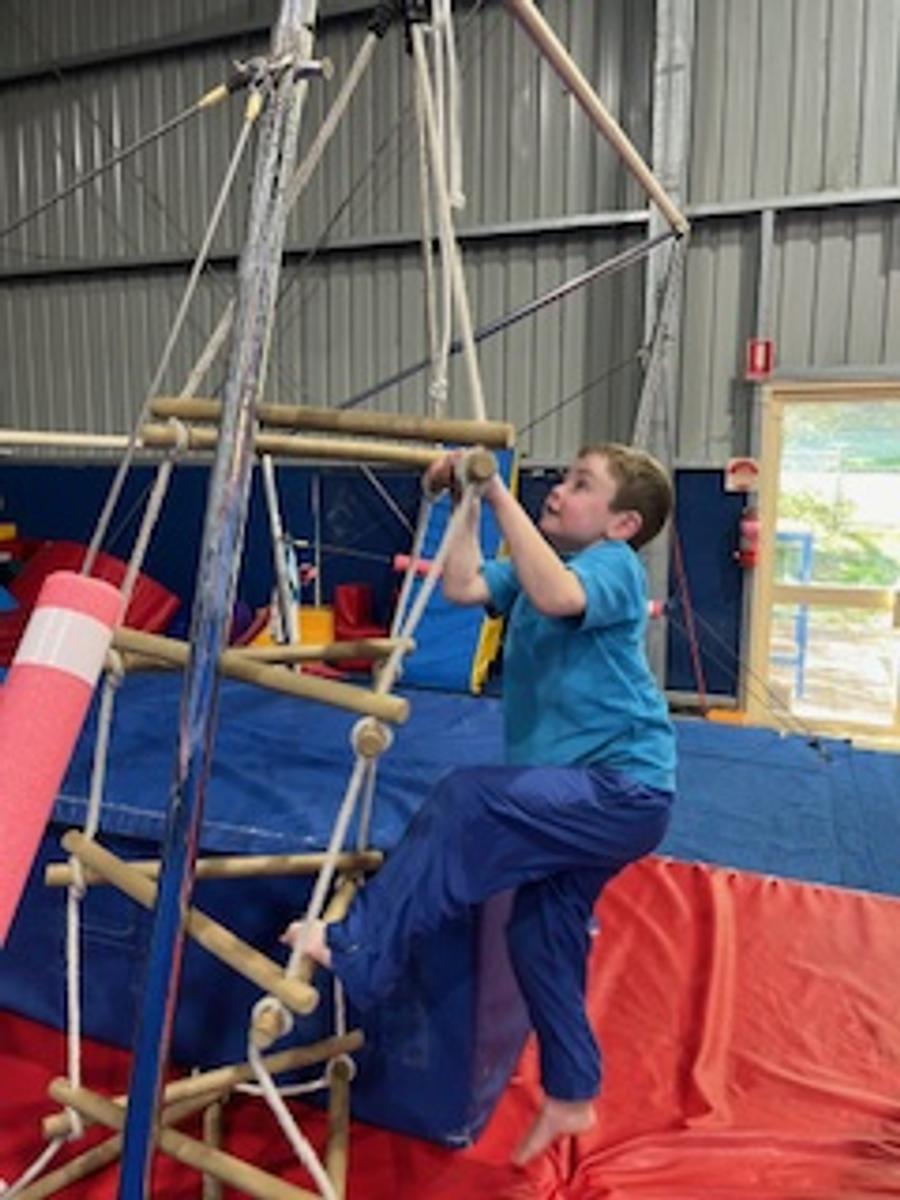
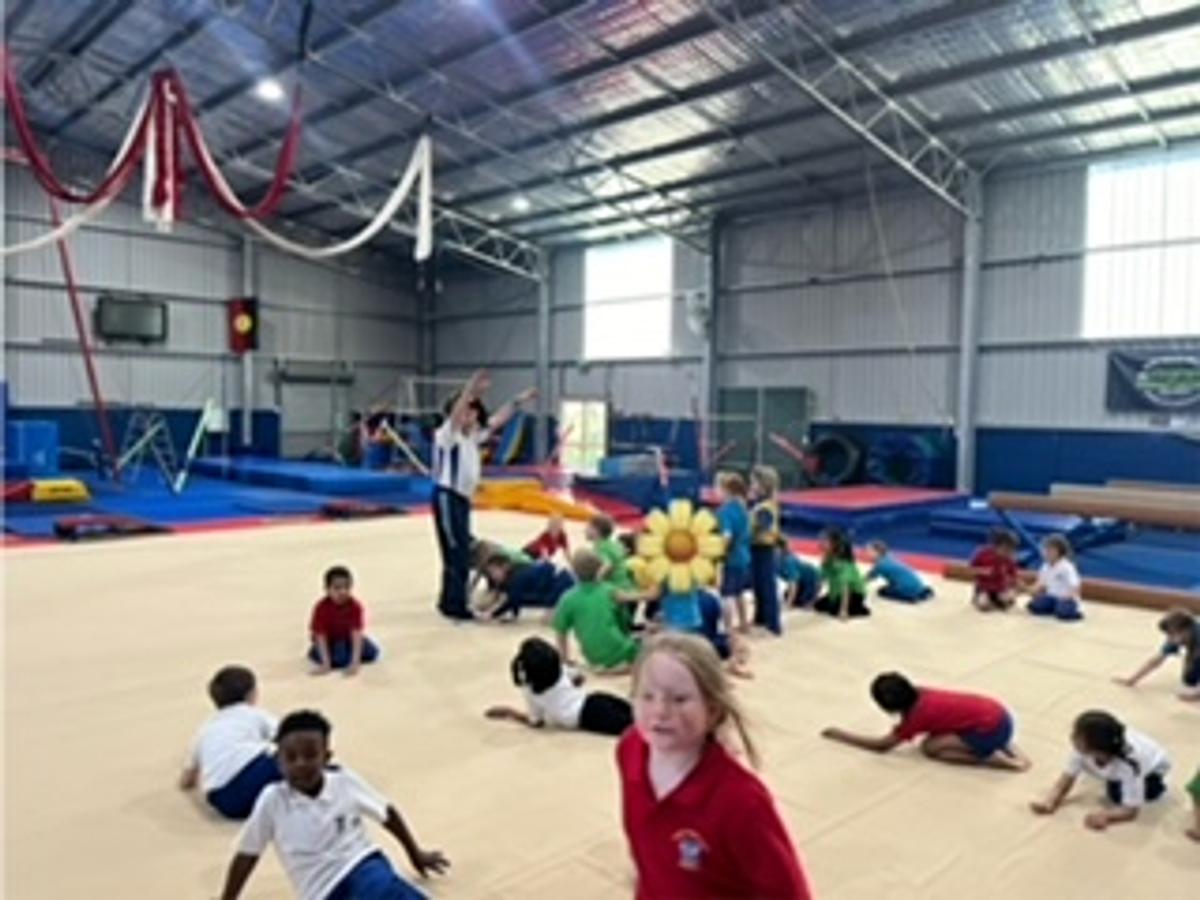
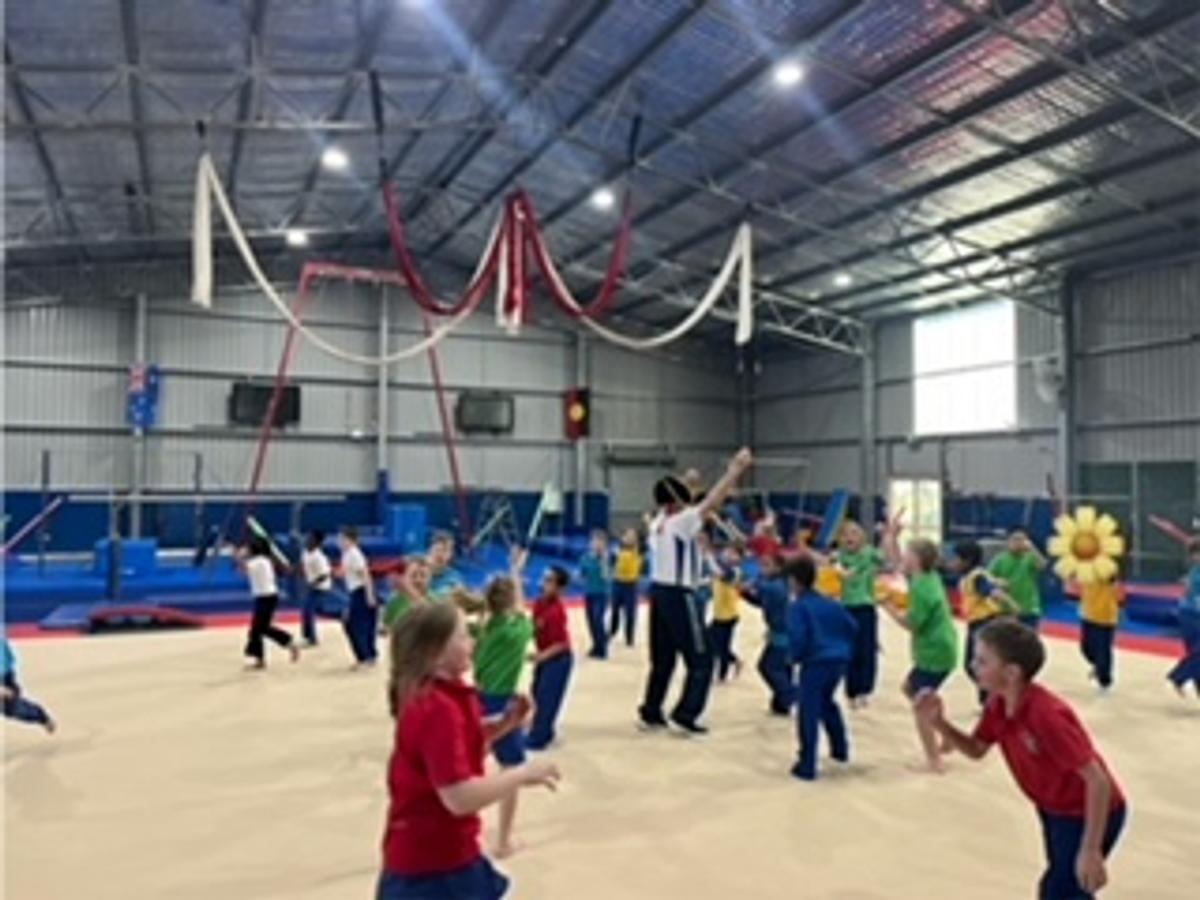
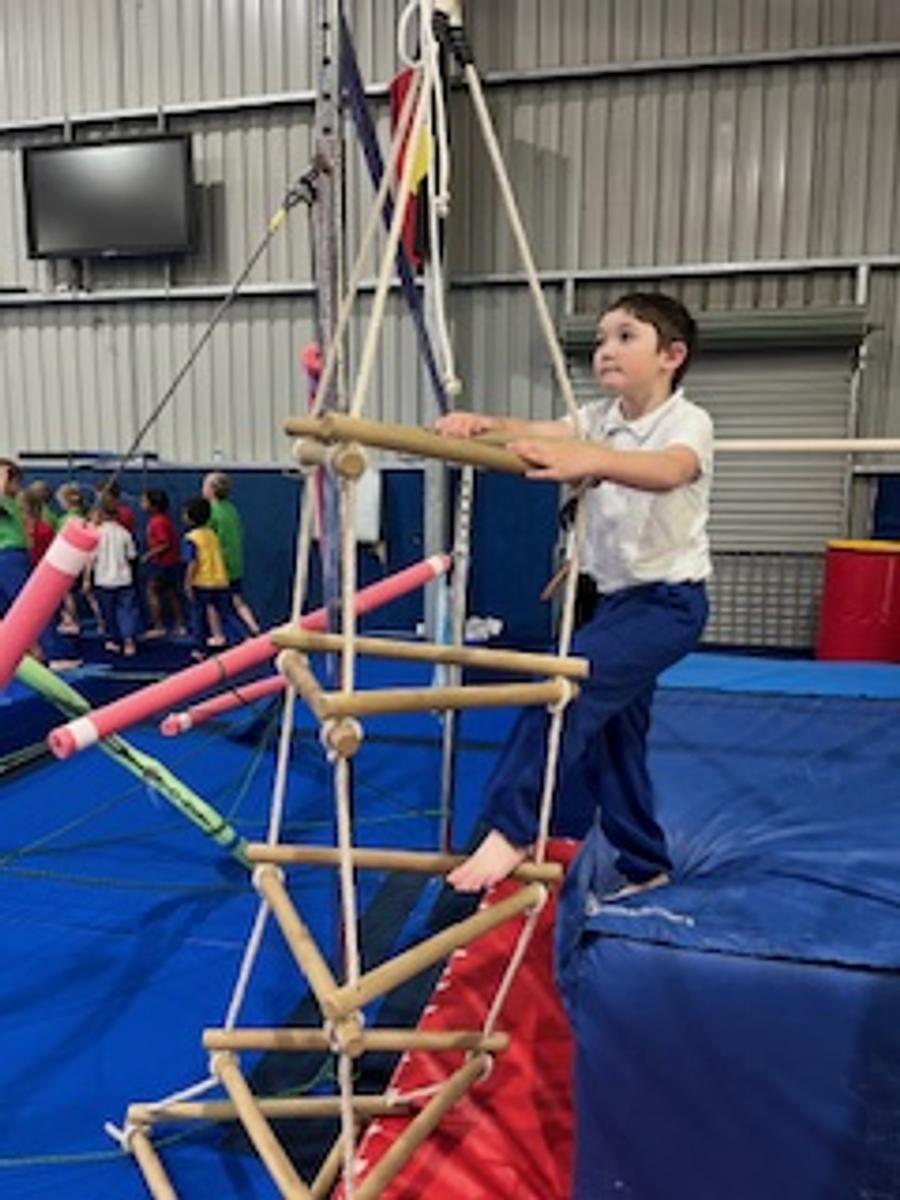
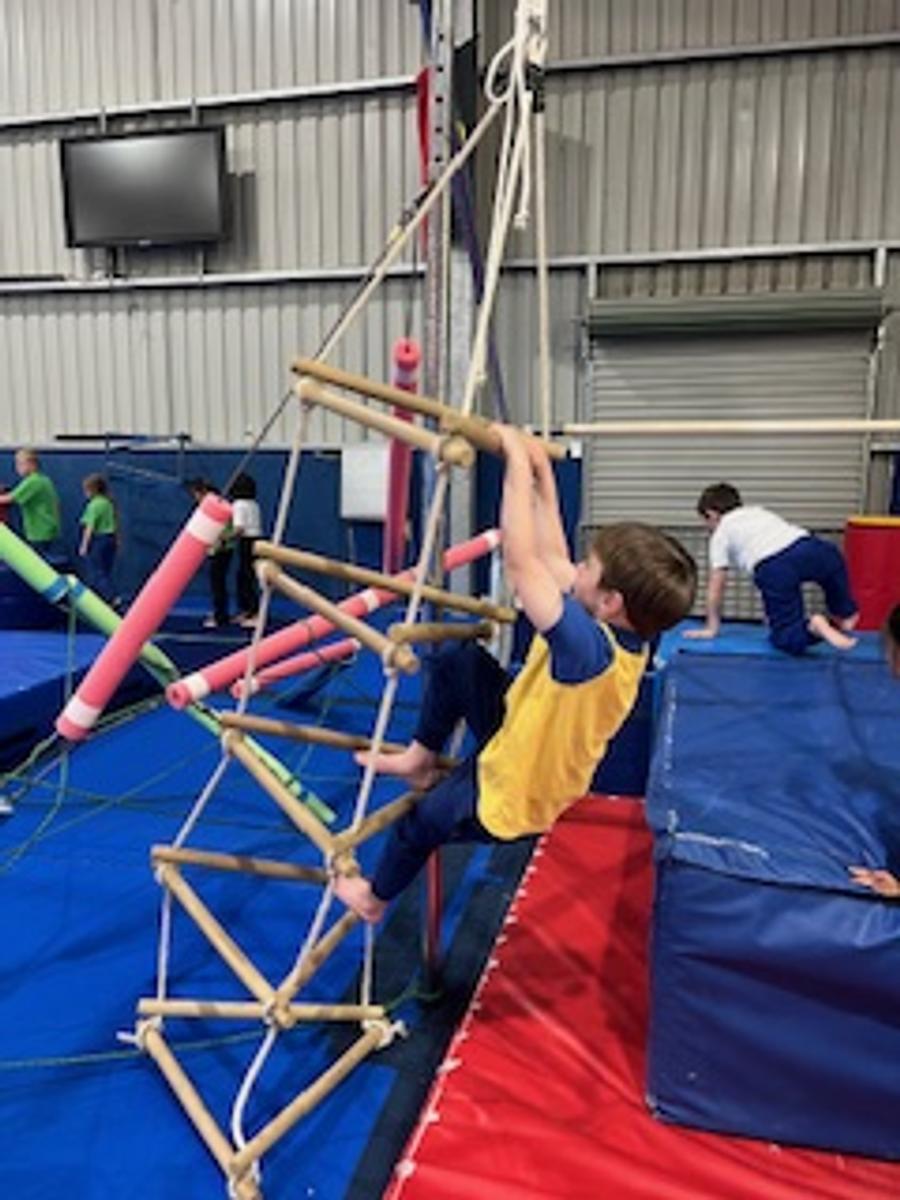
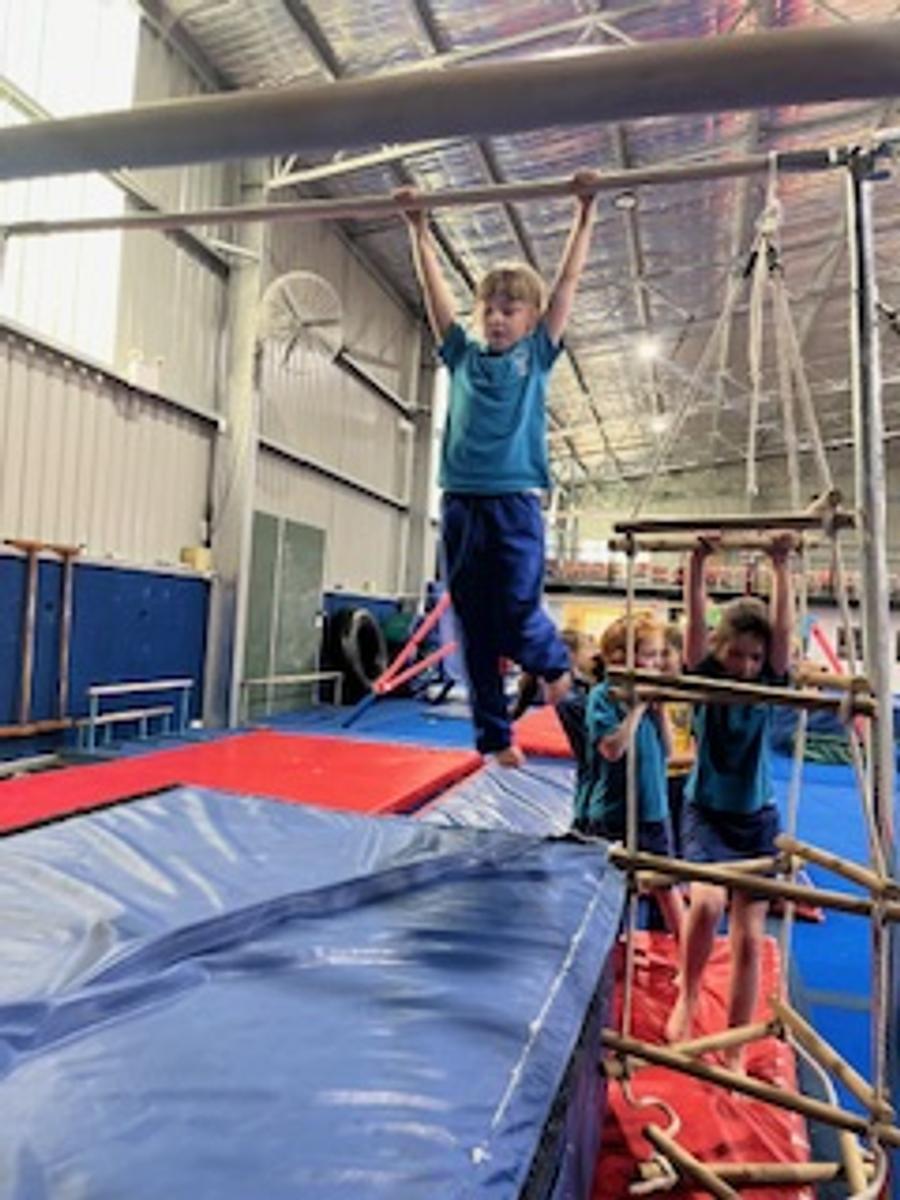
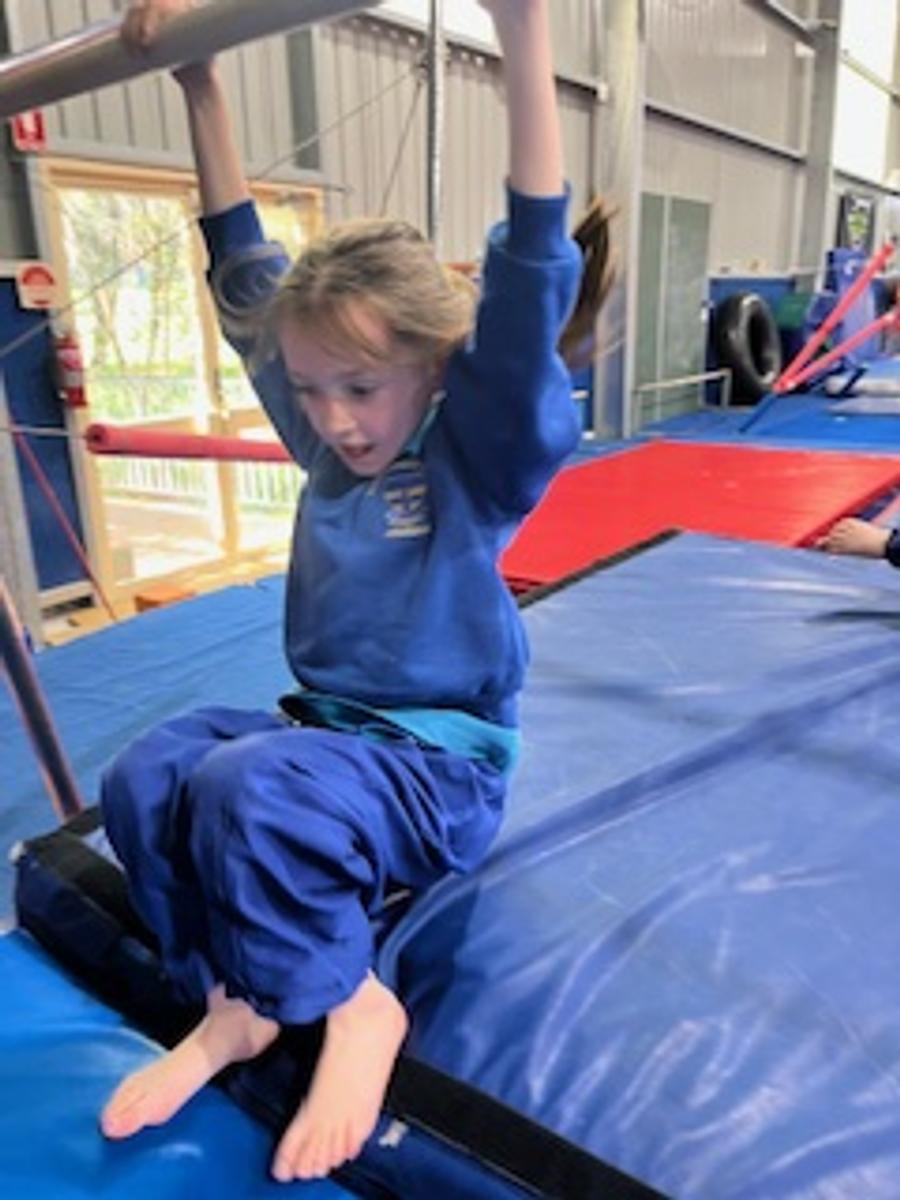
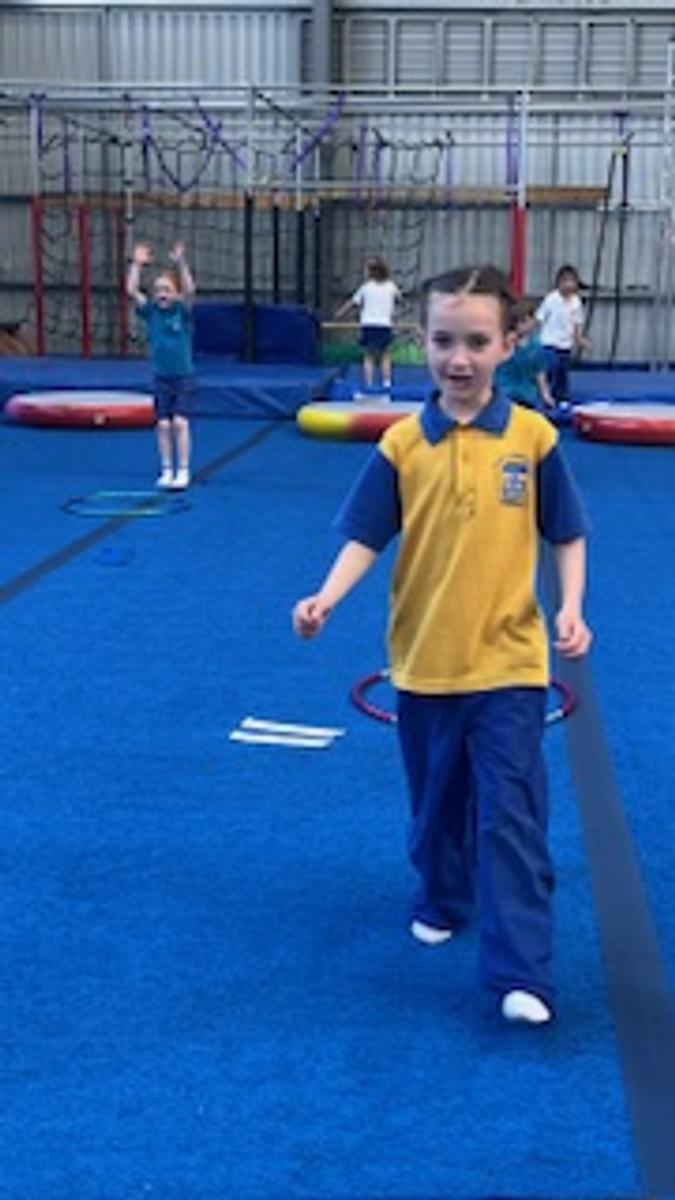
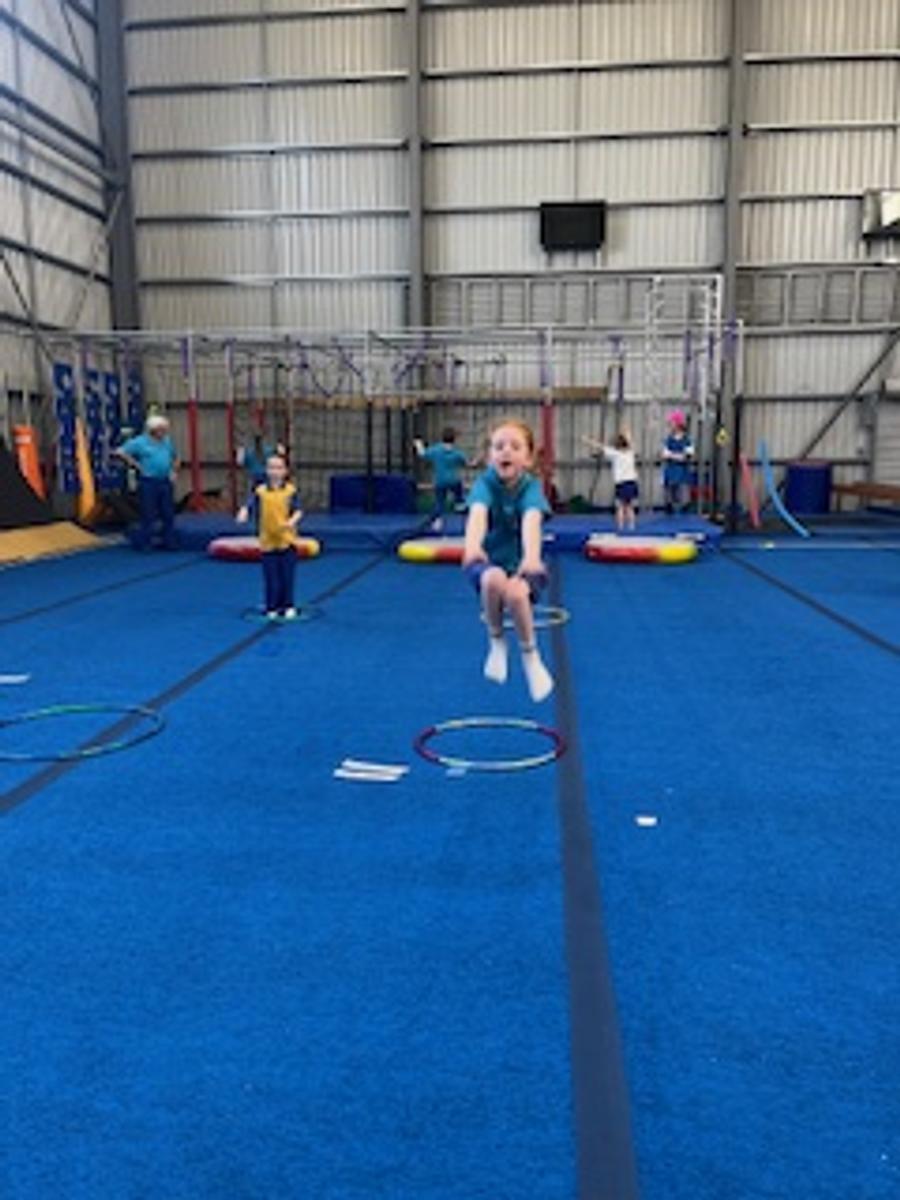
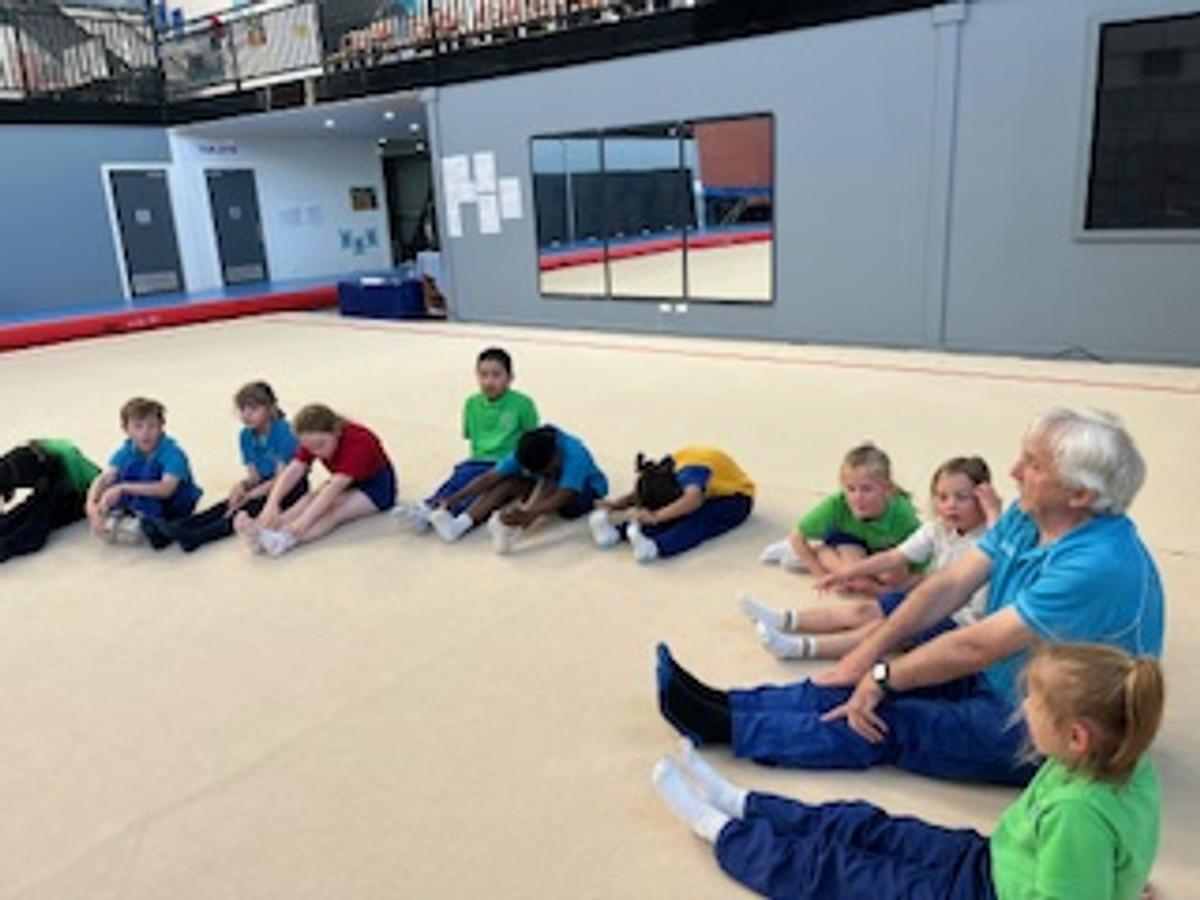
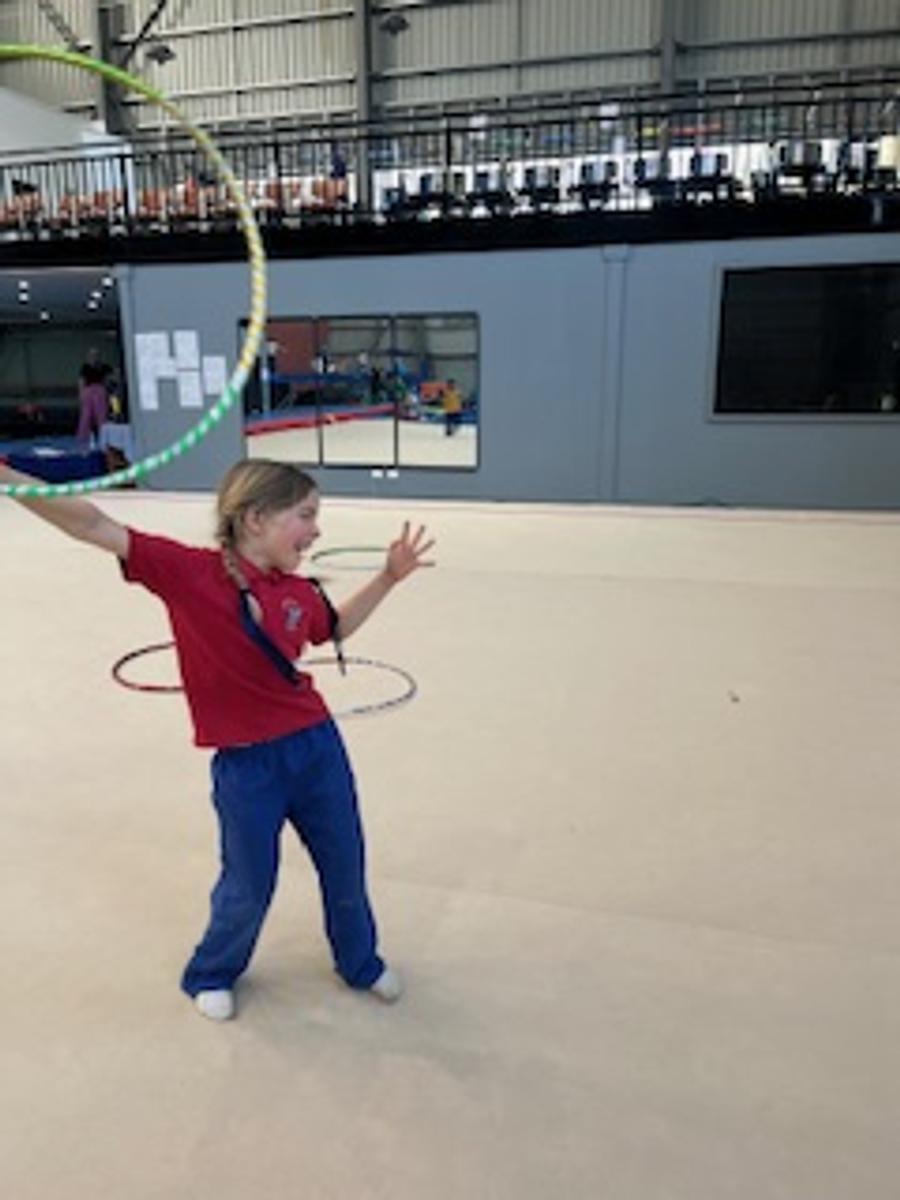
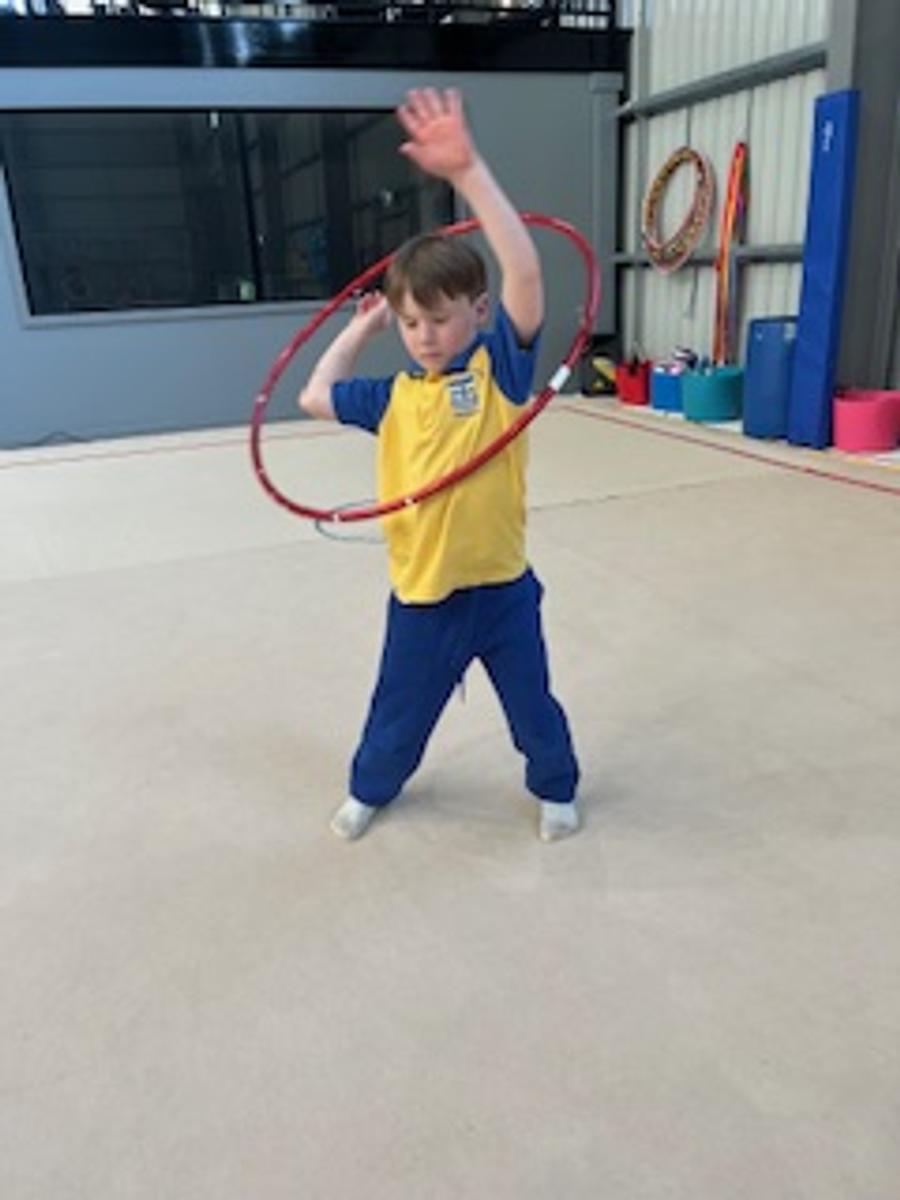
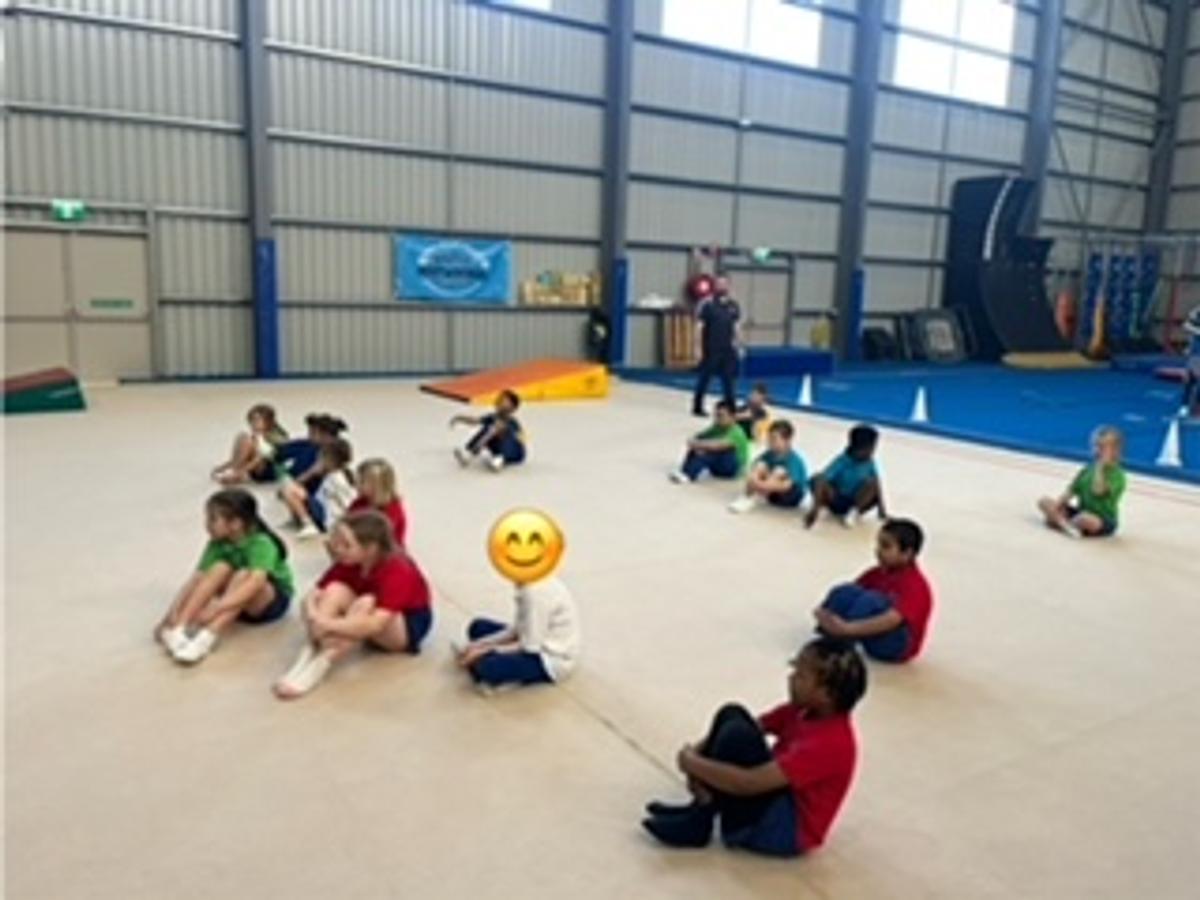
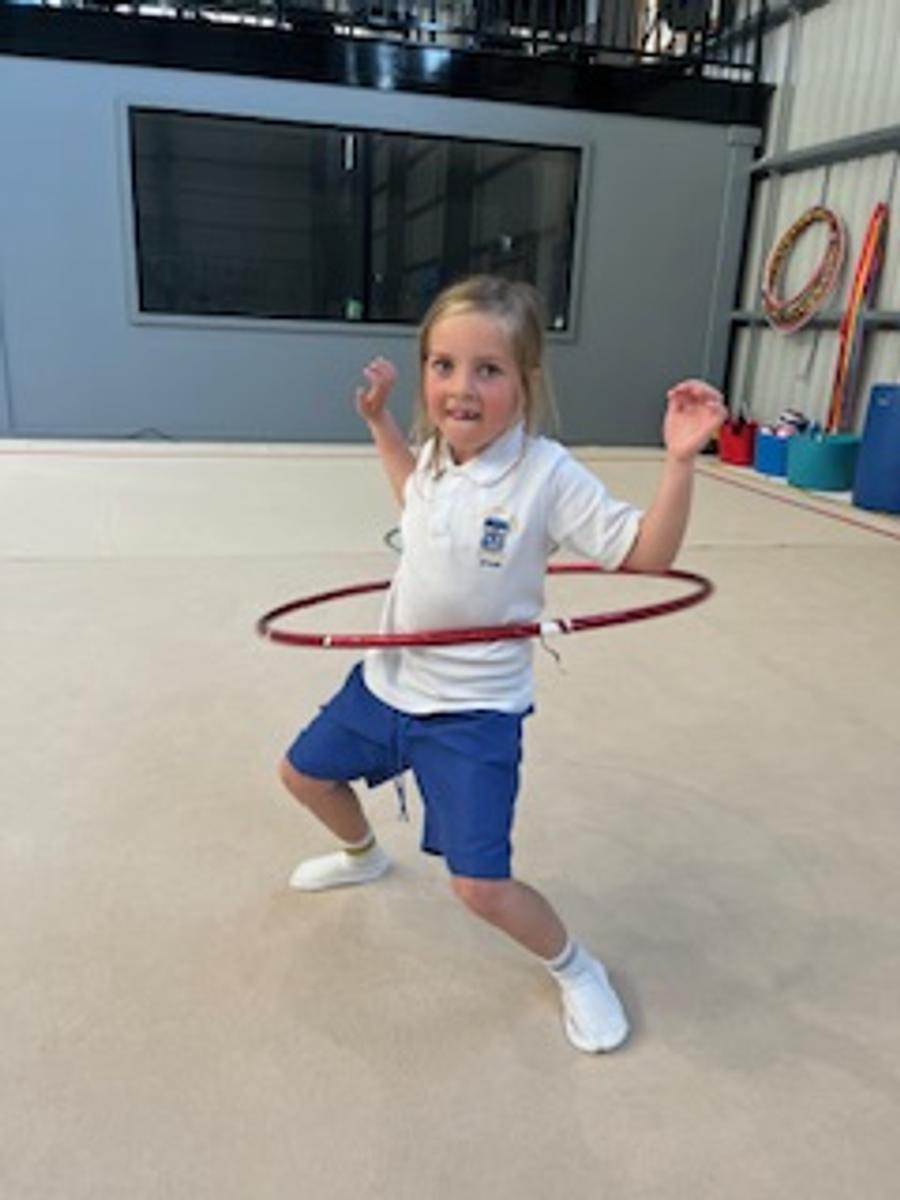
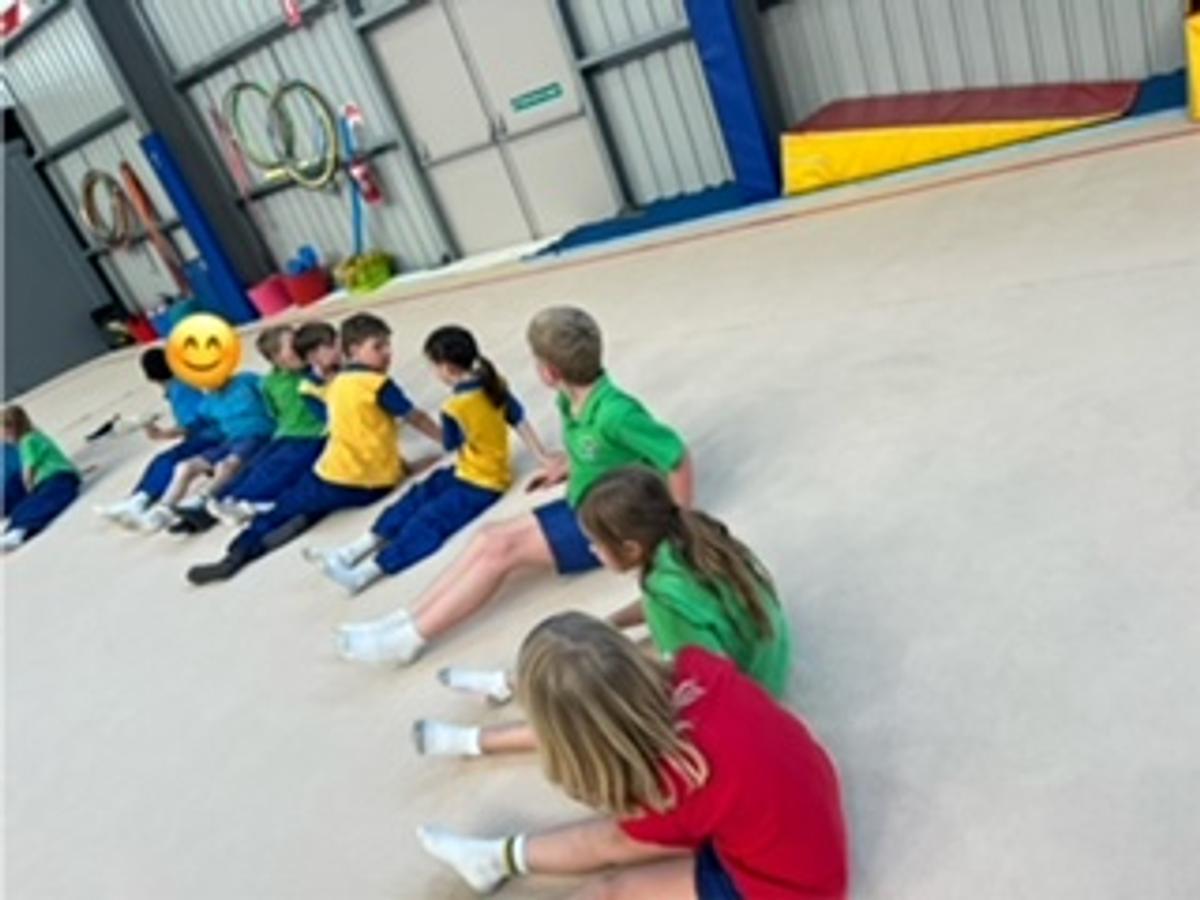
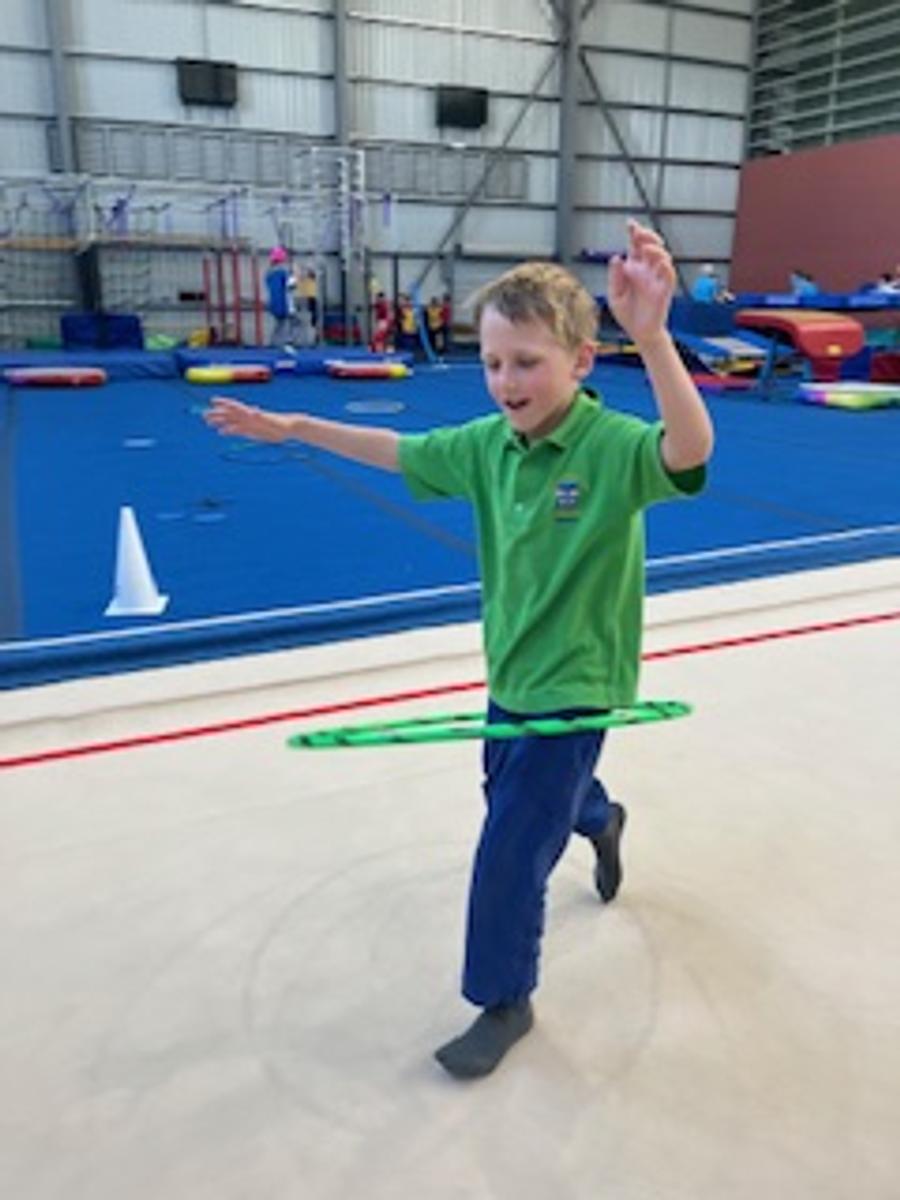
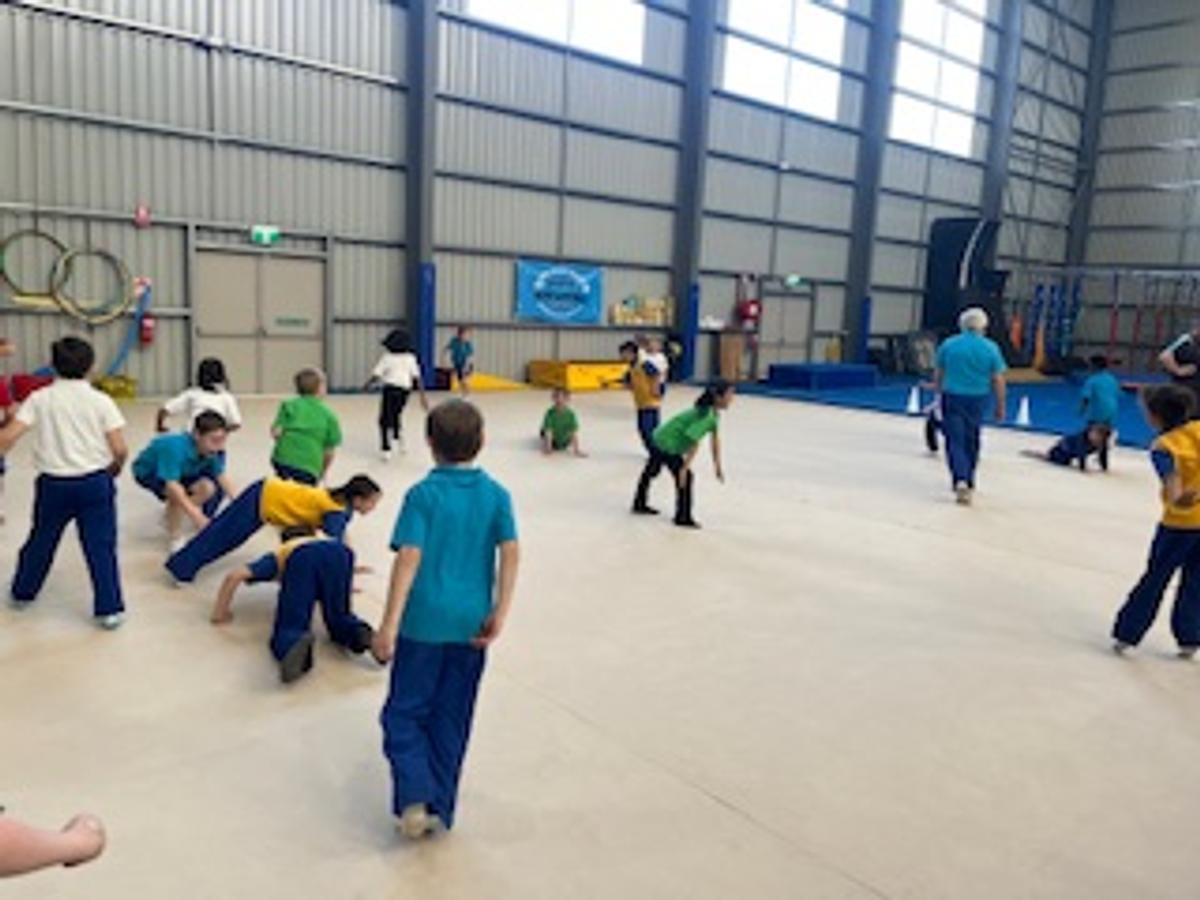
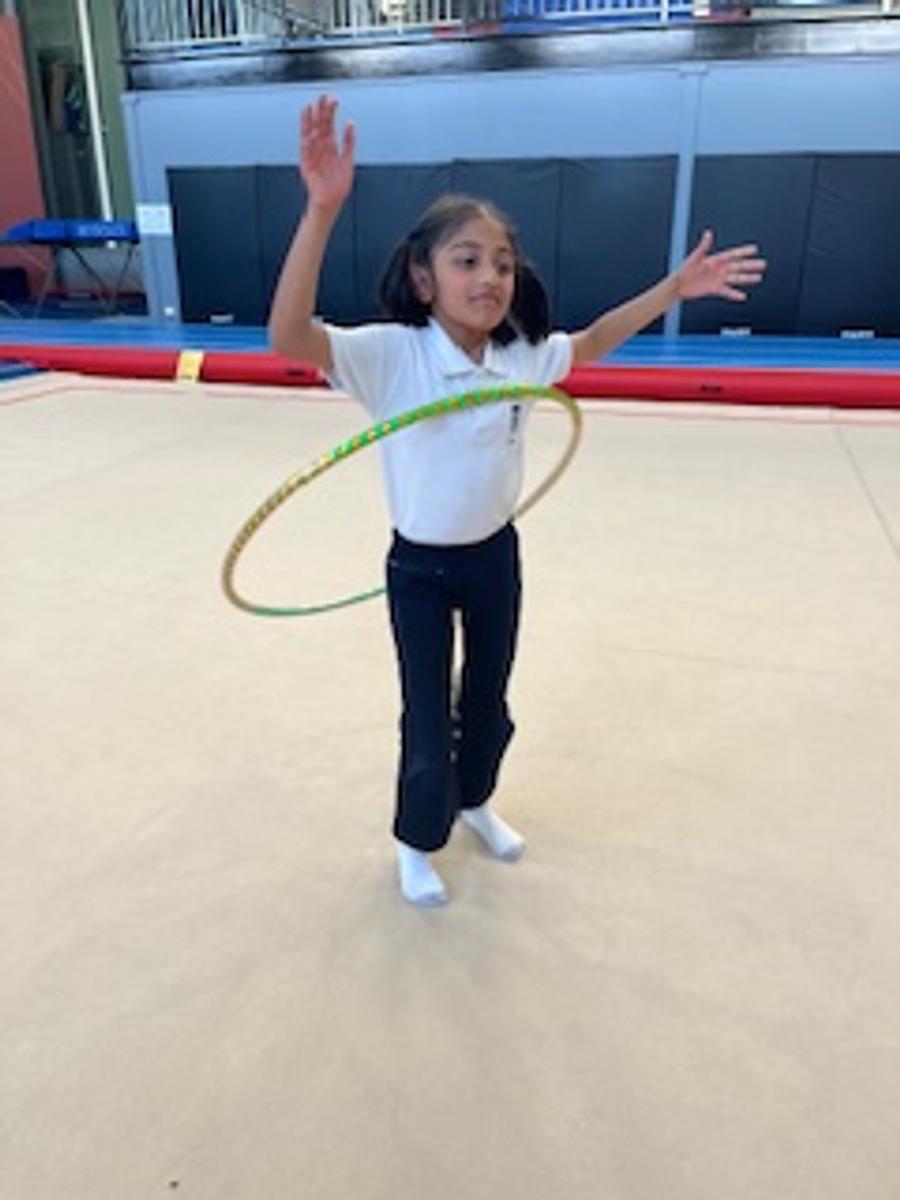
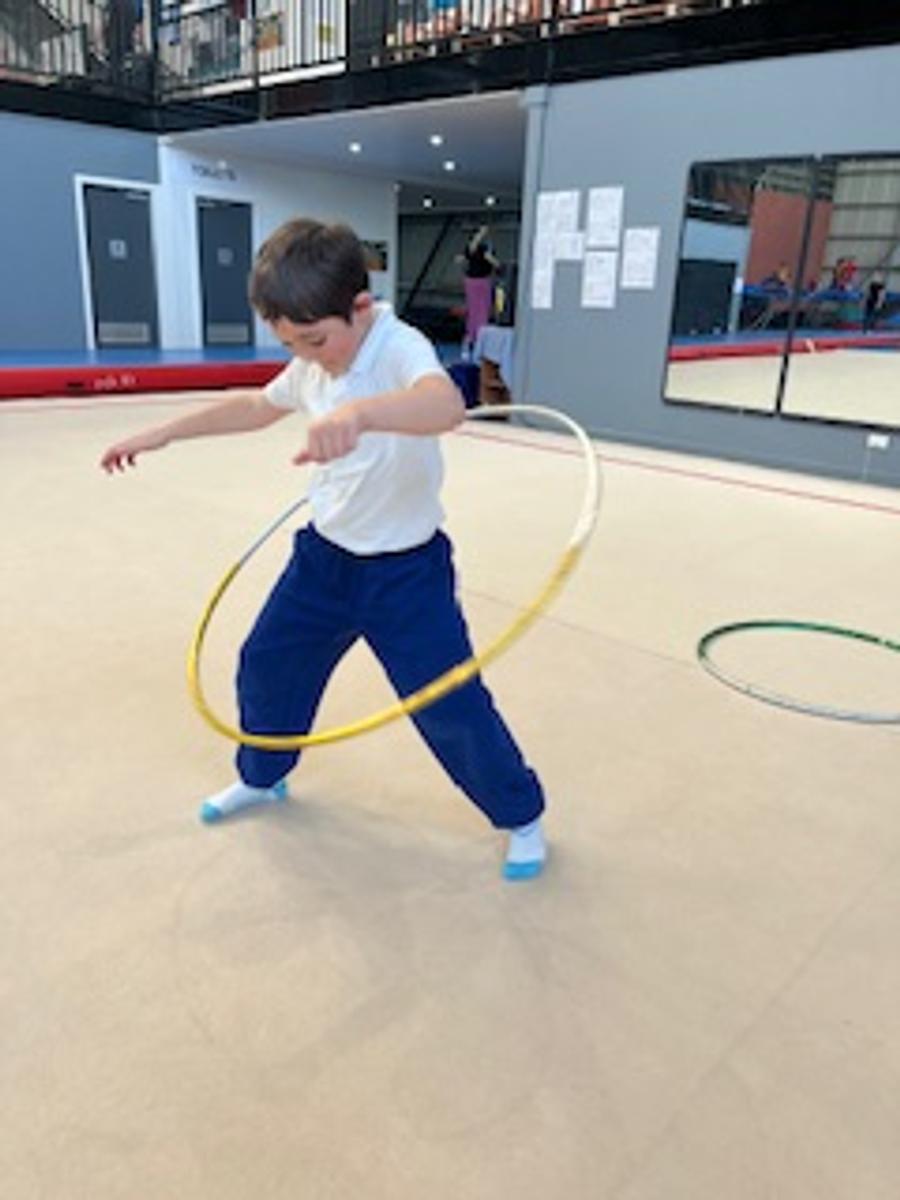
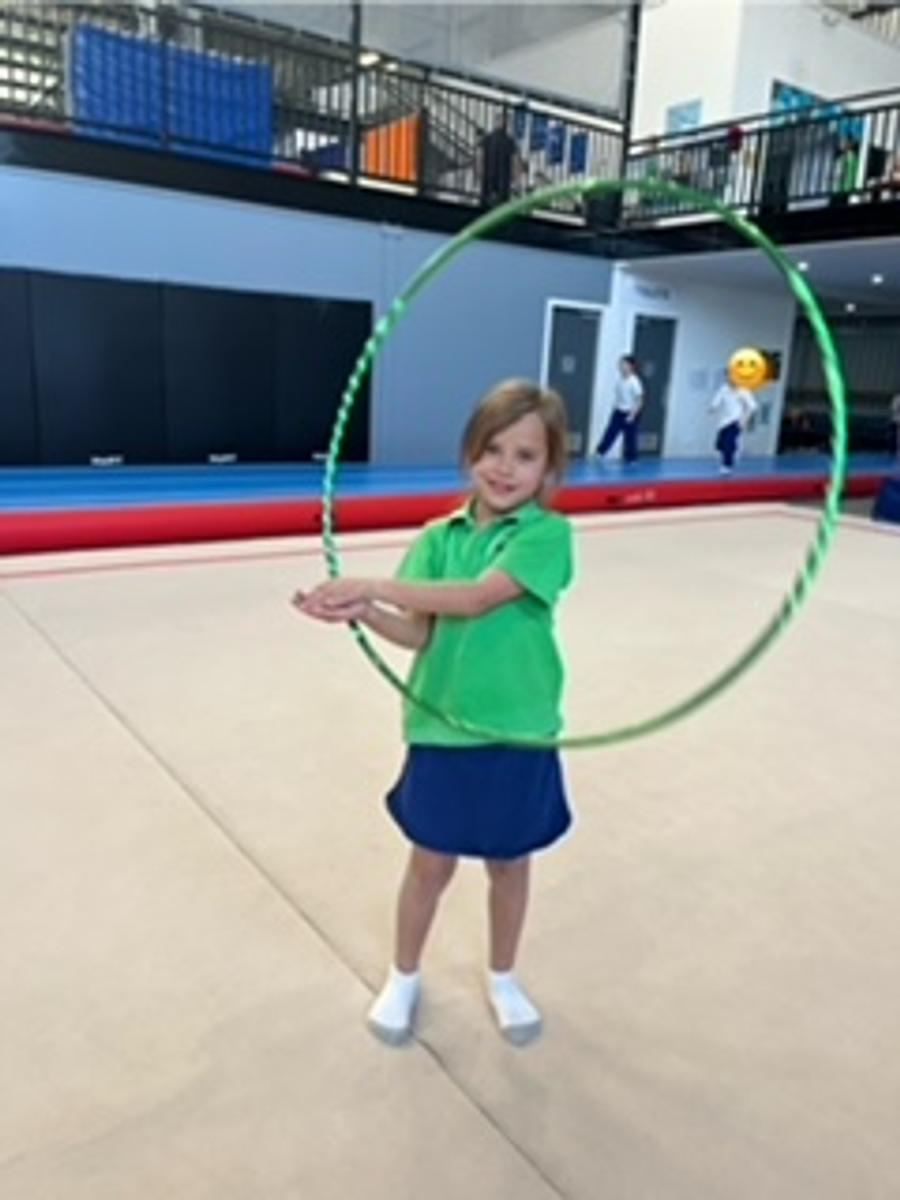
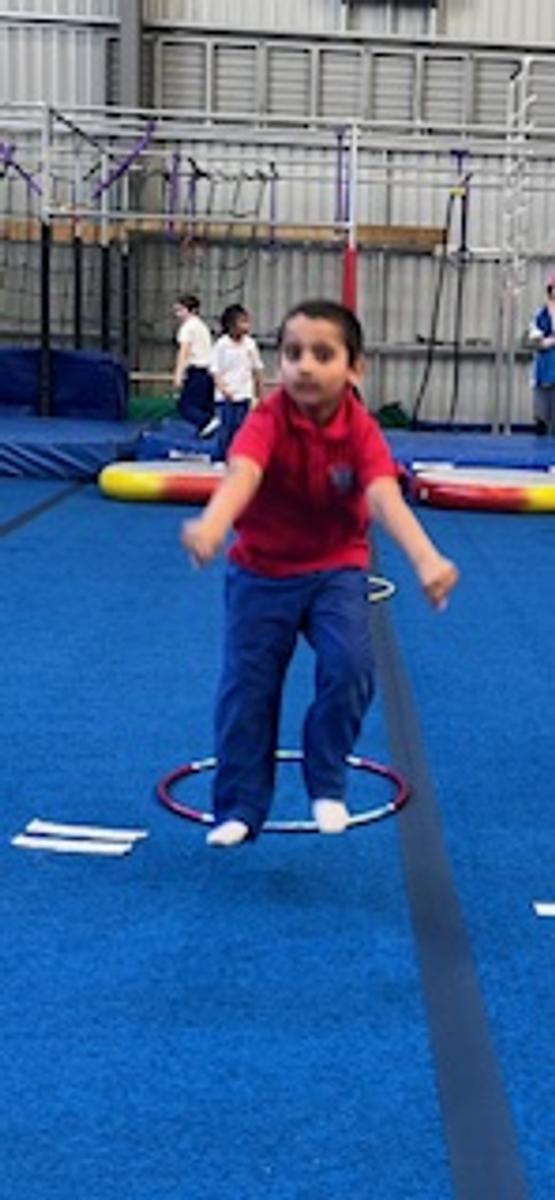
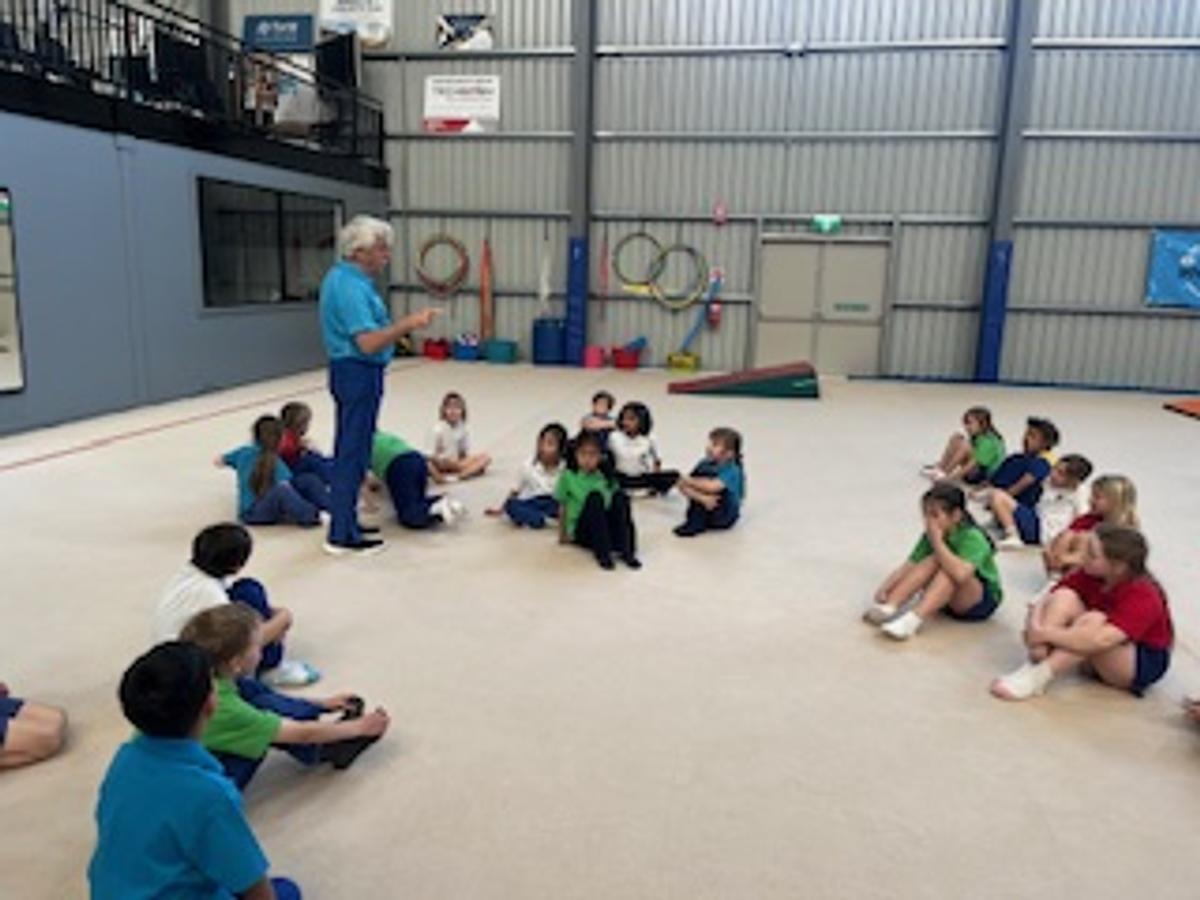
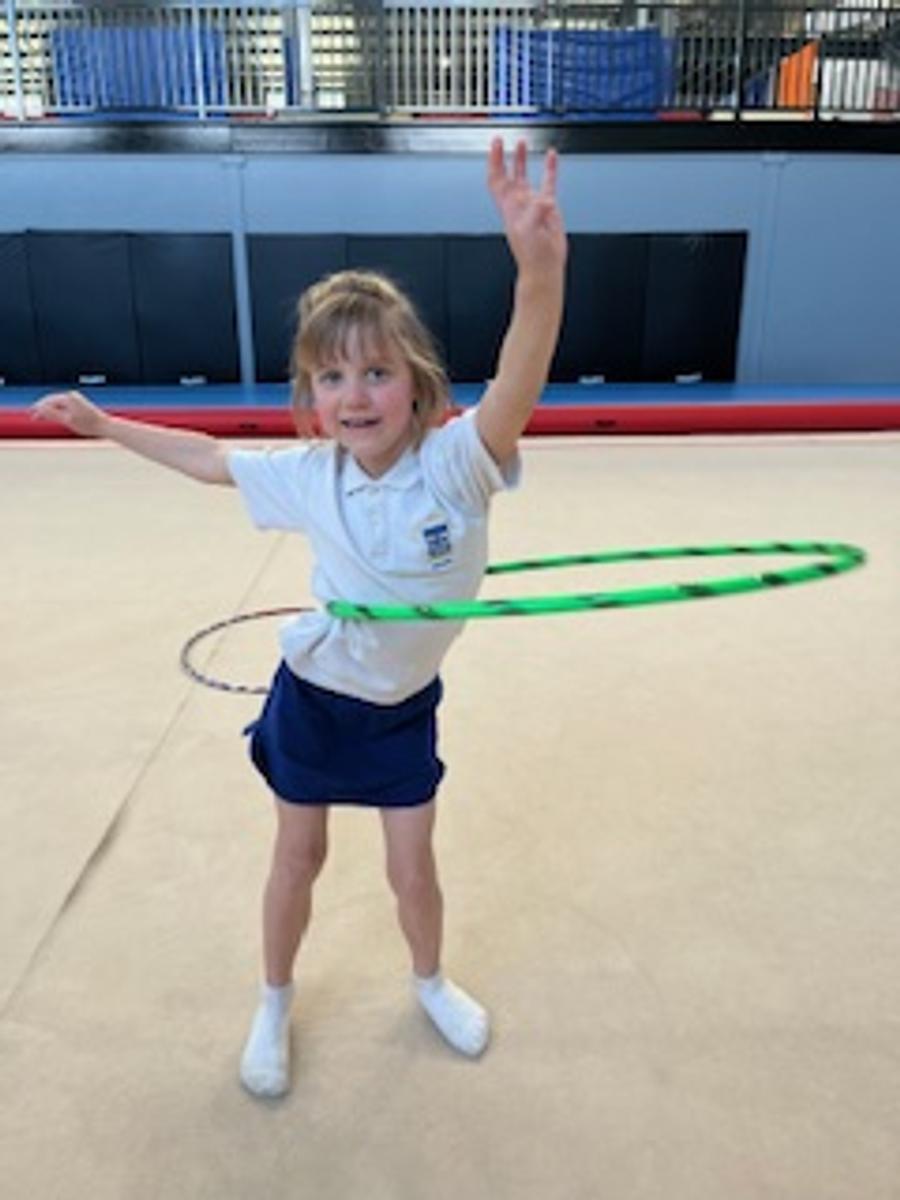
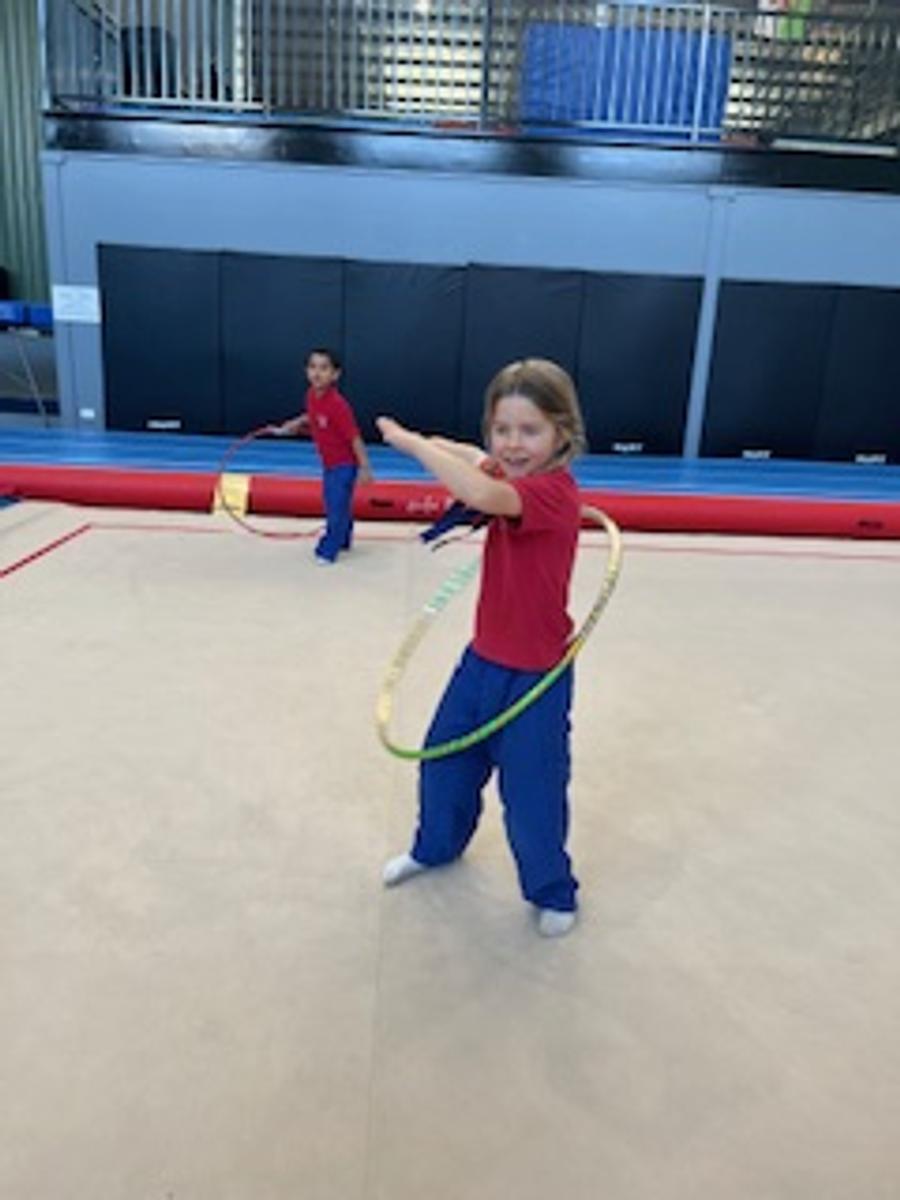
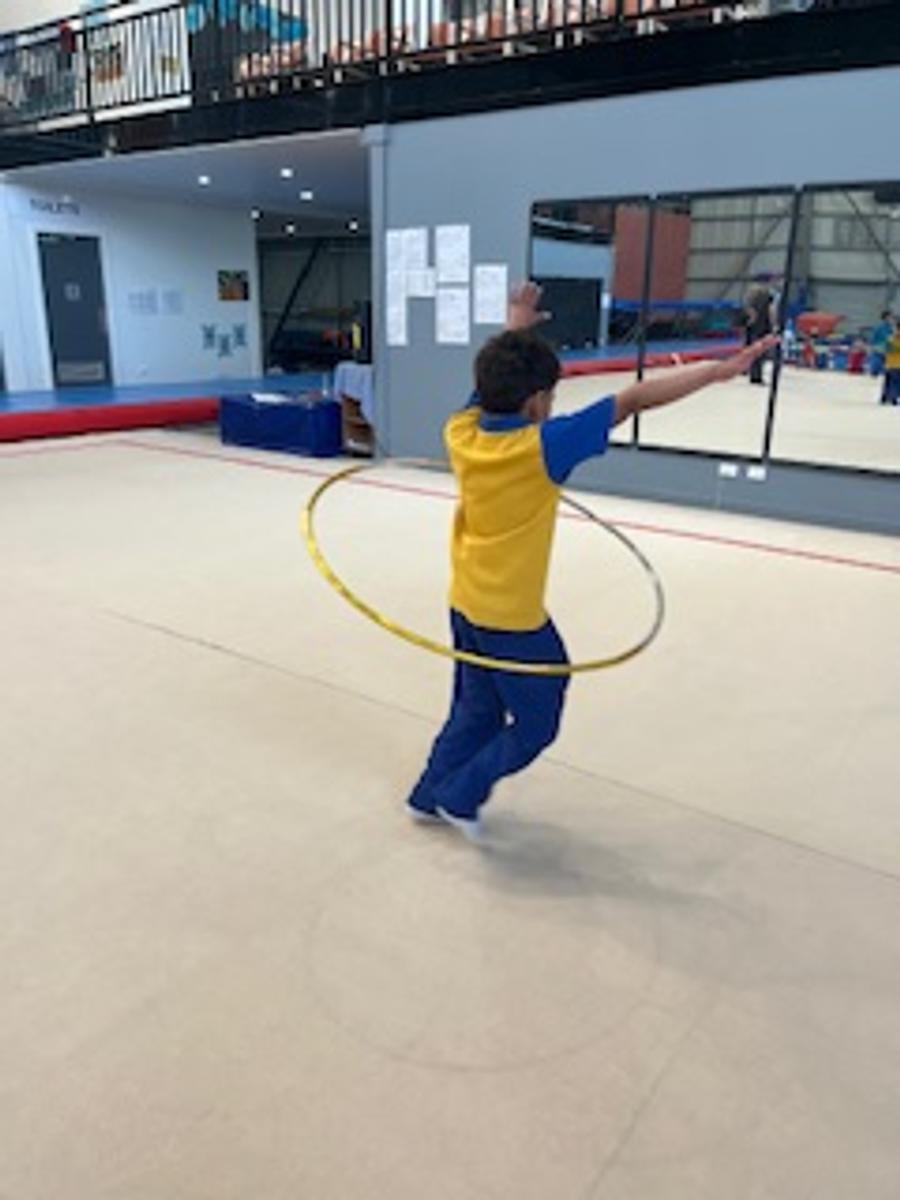
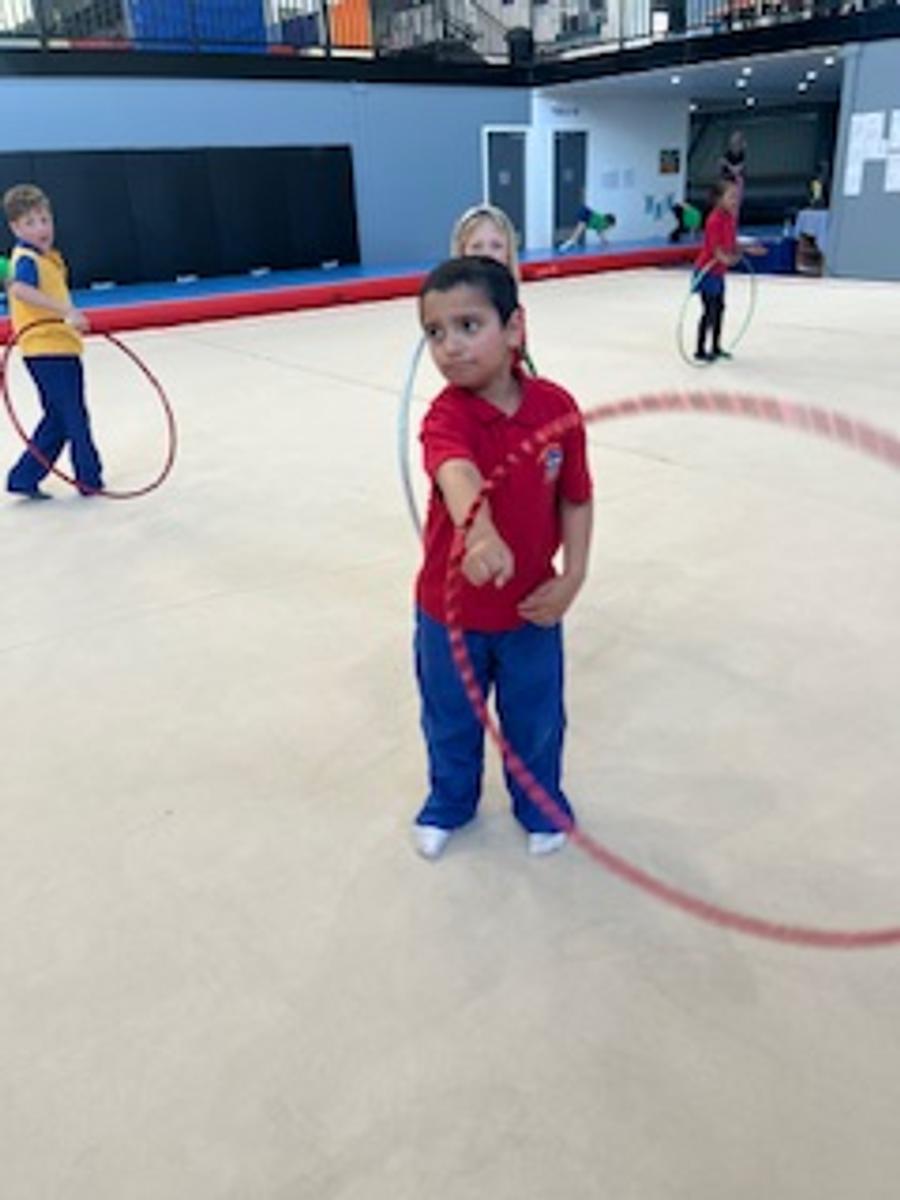
Gymnastics




































































































What is happening in the world of mathematics at St Mary's?
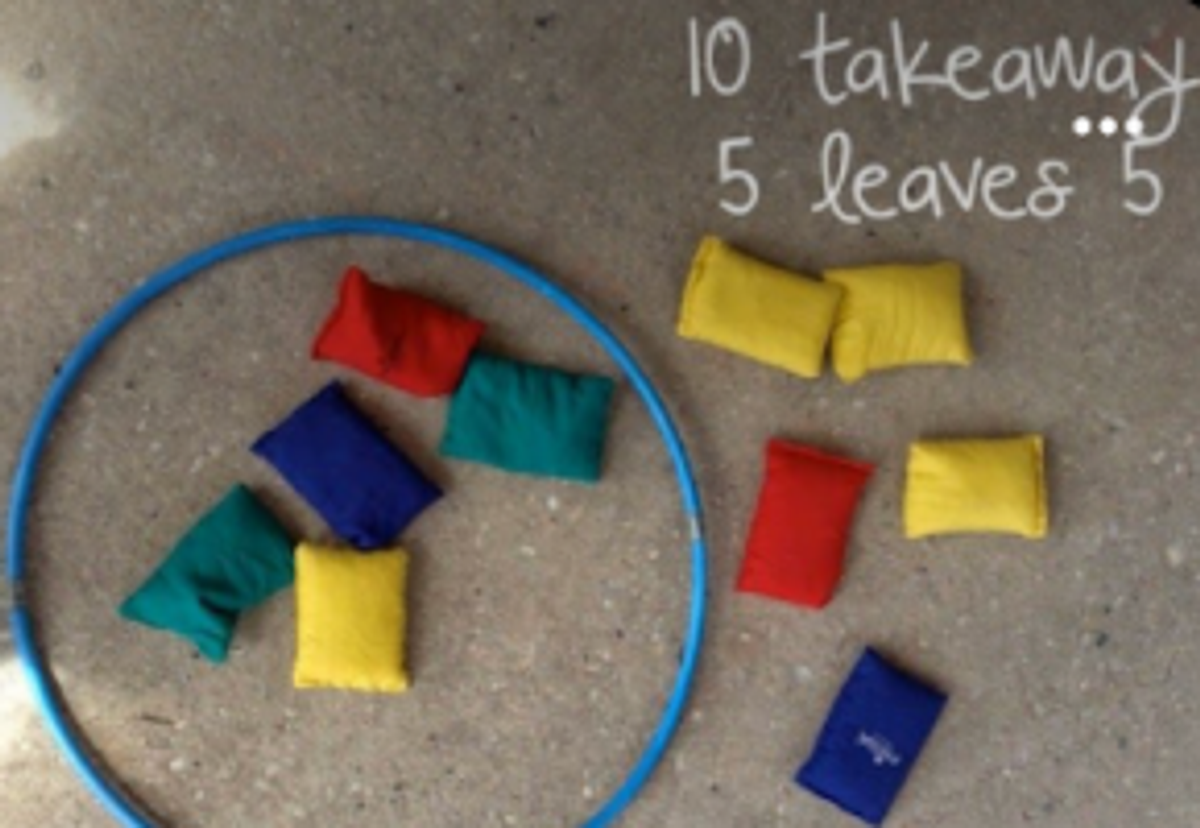
Kindergarten - Subtraction
Kindergarten are using objects to assist when subtracting items.


Problems of the Week:
Hana made twelve muffins for her friends when they came to play. Her friends ate four muffins. How many muffins are there now?
Sebastian has eleven pencils and Sonny has five. How many more pencils does Sebastian have than Sonny?
Stage 1 - Division
In Stage 1, the children have been showing their understanding of division as sharing and grouping. There are many easy ways you can support this at home. Ask your child to practice division by sharing objects equally.
For example, share 8 objects into 2 equal groups. Using objects such as your child’s toys, items of food, or buttons helps them visualise what the calculation means and keeps them interested.
Problems of the Week:
I have 30 lollies to share equally with 5 people.
How many lollies will each person receive?
Is there another way to share the 30 lollies equally
with more or less people?
Stage 2 - Fractions
Stage 2 has been working on Mass.
Compare Objects Using a Kilogram: Engage your child in a fun, hands-on activity by gathering various household items such as a bag of flour, a litre of milk, and a book. Use a kitchen scale to weigh each item and compare its mass to a 1 kg reference weight. Encourage your child to predict whether each item is heavier, lighter, or about the same as a kilogram before measuring.
Recognise the Need for a Formal Unit to Measure Mass: Discuss with your child why it's important to have standard units of measurement, such as kilograms, to avoid confusion. You can demonstrate this by asking them to imagine if everyone used different objects to describe the mass of things, like comparing an apple to a cat's weight, which could lead to misunderstandings.


Which objects being measured are more than, less than or about the same as 1 kilogram.
Stage 3 - Angles
Stage 3 are working on Multiplicative Relations this week prior to moving onto to having fun with Angles.
Use Everyday Examples: Incorporate angles into everyday situations. For example, discuss the angles formed by the hands of a clock, the corners of a book, or the intersection of roads.
Angle: Formed by 2 straight lines meeting at a common endpoint, called the vertex. An angle can describe the amount of turn between its 2 arms (lines).
Arm: One of the rays or lines which form an angle.
Vertex: Where 2 straight sides of a two-dimensional shape meet.
Protractor: An instrument used to measure and construct angles.
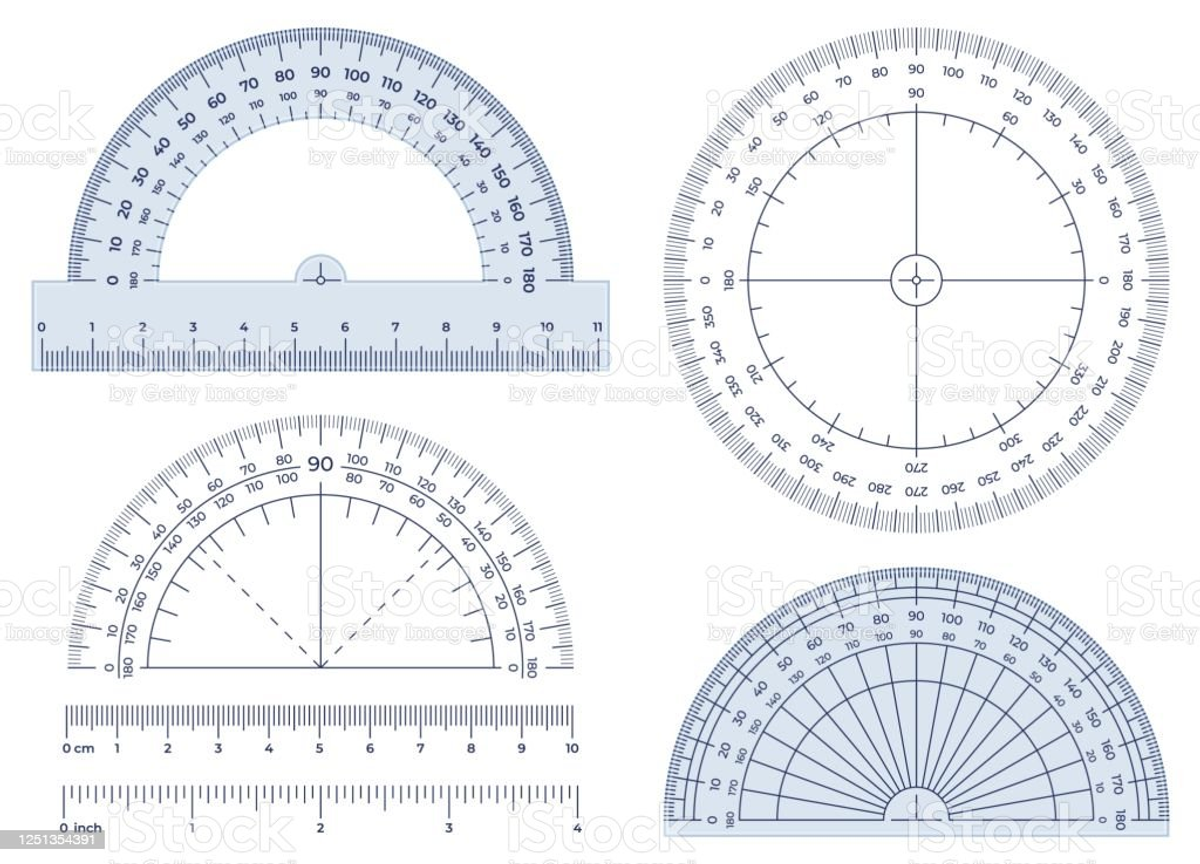

Degrees: A unit for measuring an angle. Angles are measured as a proportion of a full turn which is equivalent to 360 degrees, so that one degree is equal to of a full turn. Written as α°.
Angle size: is the measure of turn from one arm to another. Angles are usually measured in degrees (°), minutes (‘) and seconds (“) and in an anticlockwise format.